Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 851-855. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
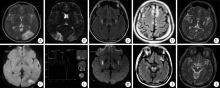
Mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes / myoclonus epilepsy with ragged-red fibers /Leigh overlap syndrome caused by mitochondrial DNA 8344A>G mutation
Yue HOU,Xu-tong ZHAO,Zhi-ying XIE,Yun YUAN,Zhao-xia WANG( )
)
- Department of Neurology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R741
| [1] |
Alston CL, Rocha MC, Lax NZ, et al. The genetics and pathology of mitochondrial disease[J]. J Pathol, 2017,241(2):236-250.
pmid: 27659608 |
| [2] |
El-Hattab AW, Adesina AM, Jones J, et al. MELAS syndrome: Clinical manifestations, pathogenesis, and treatment options[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2015,116(1/2):4-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2015.06.004 |
| [3] |
Lake NJ, Compton AG, Rahman S, et al. Leigh syndrome: one disorder, more than 75 monogenic causes[J]. Ann Neurol, 2016,79(2):190-203.
pmid: 26506407 |
| [4] |
Bonfante E, Koenig MK, Adejumo RB, et al. The neuroimaging of Leigh syndrome: case series and review of the literature[J]. Pediatr Radiol, 2016,46(4):443-451.
doi: 10.1007/s00247-015-3523-5 |
| [5] |
Liu K, Zhao H, Ji K, et al. MERRF/MELAS overlap syndrome due to the m.3291T>C mutation[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2014,29(1):139-144.
doi: 10.1007/s11011-013-9464-5 |
| [6] |
Lorenzoni PJ, Scala RH, Kay CSK, et al. When should MERRF (myoclonus epilepsy associated with ragged-red fibers) be the diagnosis[J]. Arq Neuropsiquiatr, 2014,72(10):803-811.
pmid: 25337734 |
| [7] | 陈涓涓, 陈旭辉, 陈淮菁, 等. m.10158T>C致线粒体脑肌病伴高乳酸血症和卒中样发作叠加Leigh综合征1例临床、病理及基因特点[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2017,50(6):435-439. |
| [8] | 韩漫夫, 白润涛, 冯宏业, 等. 线粒体DNA G13513A突变所致线粒体脑肌病伴高乳酸血症和脑卒中样发作/Leigh重叠综合征[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2009,42(4):248-252. |
| [9] |
Yang H, Lu Q, Cui L. Symmetric thalamic lesions in a patient with a myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers-Leigh spectrum phenotype due to the m.A8344G mutation[J]. Pediatr Neurol, 2014,51(6):e19-20.
doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.08.020 |
| [10] |
Monden Y, Mori M, Kuwajima M, et al. Late-onset Leigh syndrome with myoclonic epilepsy with ragged-red fibers[J]. Brain Dev, 2013,35(6):582-585.
pmid: 22981260 |
| [11] |
Yu N, Zhang YF, Zhang K, et al. MELAS and Kearns-Sayre overlap syndrome due to the mtDNA m. A3243G mutation and large-scale mtDNA deletions[J]. eNeurologicalSci, 2016,4:15-18.
pmid: 29430542 |
| [12] |
Emmanuele V, Silvers DS, Sotiriou E, et al. MERRF and Kearns-Sayre overlap syndrome due to the mitochondrial DNA m.3291T>C mutation[J]. Muscle Nerve, 2011,44(3):448-451.
doi: 10.1002/mus.22149 |
| [13] |
Zuccoli G, Yannes MP, Nardone R, et al. Bilateral symmetrical basal ganglia and thalamic lesions in children: an update (2015)[J]. Neuroradiology, 2015,57(10):973-989.
pmid: 26227169 |
| [14] | 魏妍平, 崔丽英, 彭斌. ND3基因突变导致的线粒体脑肌病重叠综合征二例[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志, 2016,24(10):626-630. |
| [15] |
Sofou K, Steneryd K, Wiklund LM, et al. MRI of the brain in childhood-onset mitochondrial disorders with central nervous system involvement[J]. Mitochondrion, 2013,13(4):364-371.
doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2013.04.008 |
| [16] |
Lee HF, Tsai CR, Chi CS, et al. Leigh syndrome: clinical and neuroimaging follow-up[J]. Pediatr Neurol, 2009,40(2):88-93.
doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2008.09.020 |
| [17] |
Nakamura M, Yabe I, Sudo A, et al. MERRF/MELAS overlap syndrome: a double pathogenic mutation in mitochondrial tRNA genes[J]. J Med Genet, 2010,47(10):659-664.
pmid: 20610441 |
| [18] |
Craven L, Alston CL, Taylor RW, et al. Recent advances in mitochondrial disease[J]. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet, 2017,18:257-275.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-091416-035426 pmid: 28415858 |
| [19] |
Altmann J, Buchner B, Nadaj-Pakleza A, et al. Expanded phenotypic spectrum of the m.8344A>G “MERRF” mutation: data from the German mitoNET registry[J]. J Neurol, 2016,263(5):961-972.
pmid: 26995359 |
| [20] |
Munoz-Malaga A, Bautista J, Salazar JA, et al. Lipomatosis, proximal myopathy, and the mitochondrial 8344 mutation. A lipid storage myopathy[J]. Muscle Nerve, 2000,23(4):538-542.
pmid: 10716764 |
| [21] |
Blakely EL, Alston CL, Lecky B, et al. Distal weakness with respiratory insufficiency caused by the m.8344A > G “MERRF” mutation[J]. Neuromuscul Disord, 2014,24(6):533-536.
pmid: 24792523 |
| [22] |
Howell N, Kubacka I, Smith R, et al. Association of the mitochondrial 8344 MERRF mutation with maternally inherited spinocerebellar degeneration and Leigh disease[J]. Neurology, 1996,46(1):219-222.
pmid: 8559379 |
| [23] |
Han JY, Sung JJ, Park HK, et al. Adult onset Leigh syndrome with mitochondrial DNA 8344 A > G mutation[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2014,21(11):2009-2011.
doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2014.03.020 |
| [24] |
Tsao CY, Herman G, Boue DR, et al. Leigh disease with mitochondrial DNA A8344G mutation: case report and brief review[J]. J Child Neurol, 2003,18(1):62-64.
doi: 10.1177/08830738030180011401 pmid: 12661941 |
| [25] |
Erol I, Alehan F, Horvath R, et al. Demyelinating disease of central and peripheral nervous systems associated with a A8344G mutation in tRNALys[J]. Neuromuscul Disord, 2009,19(4):275-278.
pmid: 19269823 |
| [26] |
Ahmed ST, Craven L, Russell OM, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of mitochondrial myopathies[J]. Neurotherapeutics, 2018,15(4):943-953.
doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-00674-4 |
| [27] |
Molnar MJ, Kovacs GG. Mitochondrial diseases[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2017,145:147-155.
pmid: 28987165 |
| [1] | Xiao-xuan LIU,Xiao-hui DUAN,Shuo ZHANG,A-ping SUN,Ying-shuang ZHANG,Dong-sheng FAN. Genetic distribution in Chinese patients with hereditary peripheral neuropathy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 874-883. |
| [2] | REN Guo-yong,WU Xue-mei, ,LI Jie-yu,SUN Wei-ping,HUANG Yi-ning. Susceptibility vessel sign in subacute stroke patients with large vessel occlusion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1133-1138. |
| [3] | MA Yun-dong1, HUANG Dong, CHEN Yu-feng, JIANG Hao-yun, LIU Jun-hua, SUN Hong-qiang, LI Zhi-hong. Verification of skin paste electrodes used in wireless polysomnography [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 358-363. |
|
||