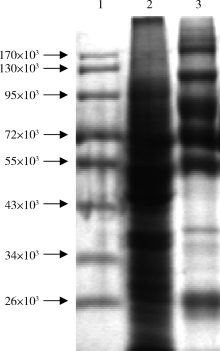
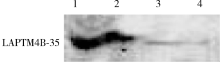
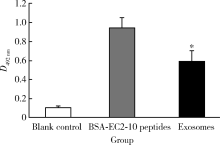
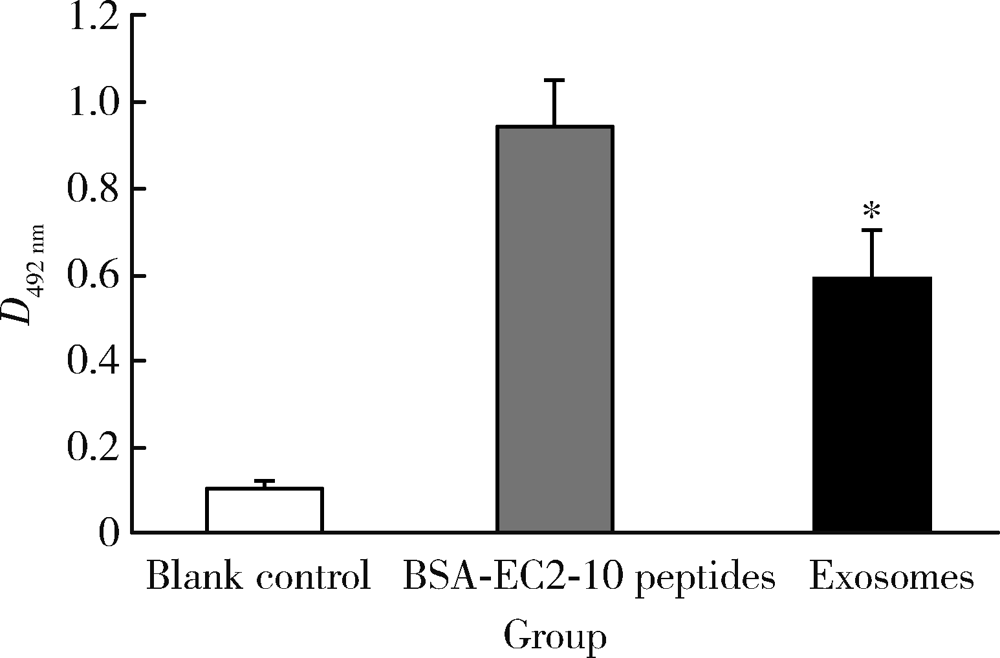
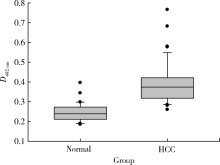
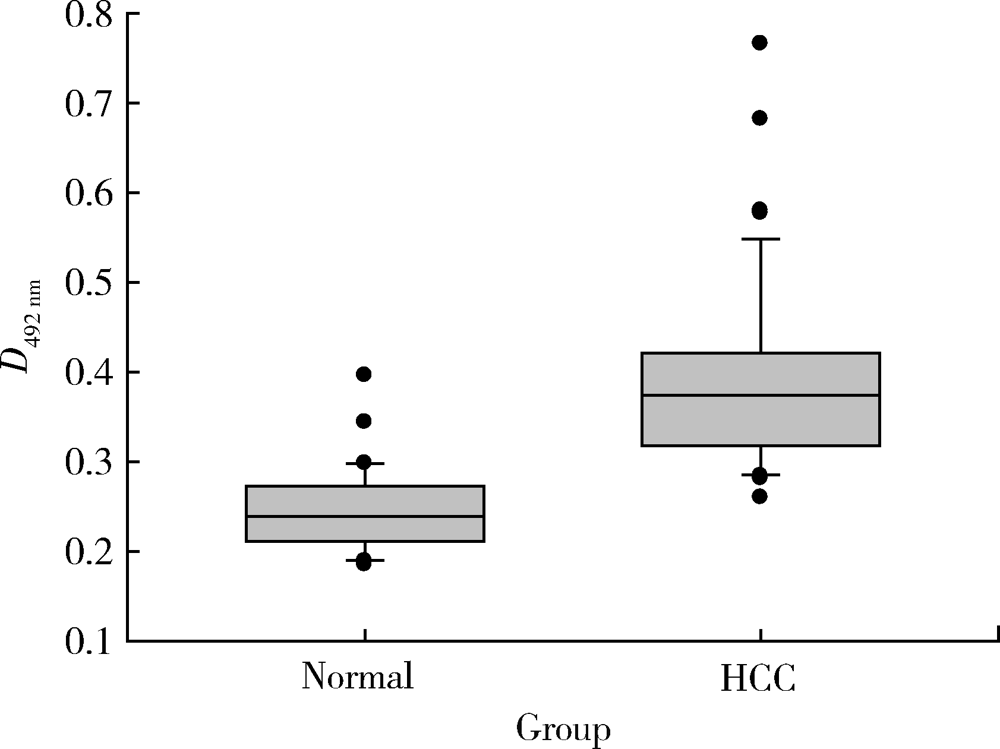
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 710-715. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.04.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
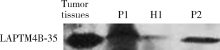
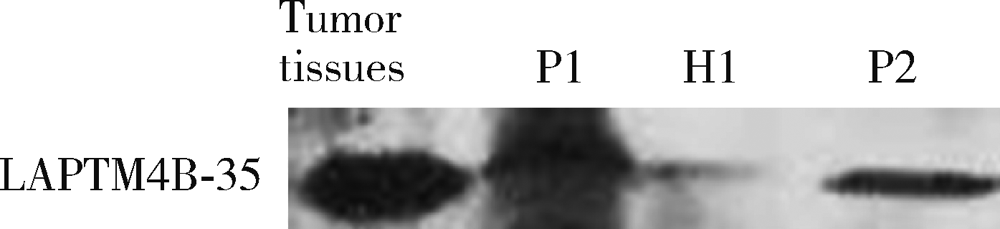
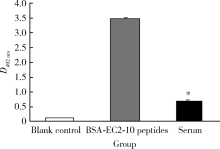
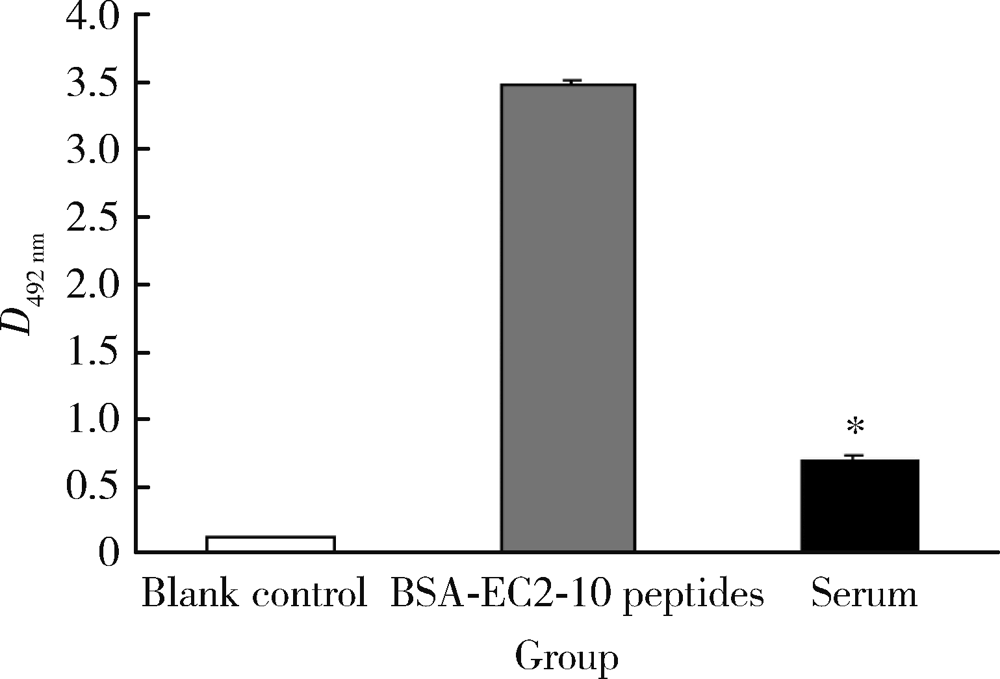
Serum LAPTM4B-35 protein as a novel diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma
PANG Yong,ZHANG Sha,YANG Hua,ZHOU Rou-li( )
)
- Department of Cell Biology, Peking University School of Basic Medical Sciences, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R735.7
| [1] |
Shao GZ, Zhou RL, Zhang QY, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of LAPTM4B, a novel gene upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Oncogene, 2003, 22(32):5060-5069.
doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206832 |
| [2] |
Yang H, Xiong FX, Lin M, et al. LAPTM4B-35 is a novel diagnostic marker and a prognostic factor of hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. J Surgical Oncology, 2010, 101(5):363-369.
doi: 10.1002/jso.v101:5 |
| [3] |
Yang H, Xiong FX, Lin M, et al. LAPTM4B-35 overexpression is a risk factor for tumor recurrence and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2010, 136(2):275-281.
doi: 10.1007/s00432-009-0659-4 pmid: 19690886 |
| [4] | 何静, 邵根泽, 周柔丽, 等. 肝癌中高表达的新基因LAPTM4B对细胞增殖及成瘤性的影响 [J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2003, 35(4):348-352. |
| [5] |
Li L, Shan Y, Yang H, et al. Upregulation of LAPTM4B-35 promotes malignant transformation and tumorigenesis in L02 human liver cell line [J]. Anat Rec (Hoboken), 2011, 294(7):1135-1142.
doi: 10.1002/ar.v294.7 |
| [6] |
Liu XR, Xiong FX, Wei XH, et al. LAPTM4B-35, a novel tetratransmembrane protein and its PPRP motif play critical roles in proliferation and metastatic potential of HCC cells [J]. Cancer Sci, 2009, 100(12):2335-2340.
doi: 10.1111/cas.2009.100.issue-12 |
| [7] |
Li L, Wei XH, Pan YP, et al. LAPTM4B: A novel cancer-asso-ciated gene motivates multi-drug resistance through efflux and activating PI3K/Akt signaling [J]. Oncogene, 2010, 29(43):5785-5795.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.303 pmid: 20711237 |
| [8] |
Yang H, Xiong FX, Wei XH, et al. LAPTM4B-35 promotes growth and metastasis of hepatocelluar carcinoma [J]. Cancer Lett, 2010, 264(2):209-217.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.01.025 |
| [9] | 刘歆荣, 周柔丽, 张青云, 等. 人肝癌相关新基因编码产物LAPTM4B的鉴定及其生物学特性 [J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2003, 35(4):340-347. |
| [10] |
Keller S, Sanderson MP, Stoeck A, et al. Exosomes: from biogenesis and secretion to biological function [J]. Immunol Lett, 2006, 107(2):102-108.
doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2006.09.005 |
| [11] |
Simons M, Raposo G. Exosomes: vesicular carriers for intercellular communication [J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2009, 21(4):575-581.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007 |
| [12] |
Simpson RJ. Exosomes: proteomic insights and diagnostic potential [J]. Expert Rev Proteomics, 2009, 6(3):267-283.
doi: 10.1586/epr.09.17 |
| [13] |
Mitchell PJ, Welton J, Staffurth J. Can urinary exosomes act as treatment response markers in prostate cancer? [J]. J Transl Med, 2009, 7:4.
doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-7-4 pmid: 19138409 |
| [14] |
Nilsson J, Skog J, Nordstrand A, et al. Prostate cancer-derived urine exosomes: a novel approach to biomarkers for prostate cancer [J]. Br J Cancer, 2009, 100(10):1603-1607.
doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605058 |
| [15] | Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, et al. Isolation and characte-rization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids [J]. Curr Protoc Cell Biol, 2006, Chapter 3: Unit 3.22. |
| [16] |
Navabi H, Croston D, Hobot J, et al. Preperation of human ova-rian cancer ascites-derived exosomes for a clinical trial [J]. Blood Cells Mol Dis, 2005, 35(2):149-152.
doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.06.008 |
| [17] |
Houali K, Wang X, Shimizu Y, et al. A new diagnostic marker for secreted Epstein-Barr virus encoded LMP1 and BARF1, oncoproteins in the serum and saliva of patients with nasopharyn-geal carcinoma [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2007, 13(17):4993-5000.
pmid: 17785549 |
| [18] |
Viaud S, Théry C, Ploix S, et al. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes for cancer immunotherapy: what’s next? [J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70(4):1281-1285.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3276 |
| [19] | Koga K, Matsumoto K, Akiyoshi T, et al. Purification, characte-rization and biological significance of tumor-derived exosomes [J]. Anticancer Res, 2005, 25(6A):3703-3707. |
| [20] | Zhou RL. LAPTM4B: a novel diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma [M]// Wan-Yee Lau. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Basic research. Philippines: InTech Press, 2012: 1-34. |
| [21] |
Yang Z, Senninger N, Flammang I, et al. Clinical impact of circulating LAPTM4B-35 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2019, 145(5):1165-1178.
doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02863-w |
| [1] | Jiajun LIU, Guokang LIU, Yuhu ZHU. Immune-related severe pneumonia: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [2] | Kewei CHEN,Zhuo LIU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Jianfei YE,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of renal angiomyolipoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 617-623. |
| [3] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [4] | Jie YANG,Jieli FENG,Shudong ZHANG,Lulin MA,Qing ZHENG. Clinical effects of transesophageal echocardiography in different surgical methods for nephrectomy combined with Mayo Ⅲ-Ⅳ vena tumor thrombectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [5] | Binshuai WANG,Min QIU,Qianjin ZHANG,Maofeng TIAN,Lei LIU,Guoliang WANG,Min LU,Xiaojun TIAN,Shudong ZHANG. Experience in diagnosis and treatment of 6 cases of renal Ewing's sarcoma with venous thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [6] | Xiaodong CHAI,Ziwen SUN,Haishuang LI,Liangyi ZHU,Xiaodan LIU,Yantao LIU,Fei PEI,Qing CHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics of the CD8+ T lymphocytes infiltration and its mechanism in distinct molecular subtype of medulloblastoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 512-518. |
| [7] | Guozhong LIN,Changcheng MA,Chao WU,Yu SI,Jun YANG. Application of microchannel technique in minimally invasive resection of cervical intraspinal tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 318-321. |
| [8] | Xiaotong LING,Liuyang QU,Danni ZHENG,Jing YANG,Xuebing YAN,Denggao LIU,Yan GAO. Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [9] | Wen-gen LI,Xiao-dong GU,Rui-qiang WENG,Su-dong LIU,Chao CHEN. Expression and clinical significance of plasma exosomal miR-34-5p and miR-142-3p in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1022-1027. |
| [10] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [11] | Dong LAN,Zhuo LIU,Yu-xuan LI,Guo-liang WANG,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG,Hong-xian ZHANG. Risk factors for massive hemorrhage after radical nephrectomy and removal of venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 825-832. |
| [12] | Zhong CAO,Hong-bing CEN,Jian-hong ZHAO,Jun MEI,Ling-zhi QIN,Wei LIAO,Qi-lin AO. Expression and significance of INSM1 and SOX11 in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and solid pseudopapillary neoplasm [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 575-581. |
| [13] | Yu-yang YE,Lin YUE,Xiao-ying ZOU,Xiao-yan WANG. Characteristics and microRNA expression profile of exosomes derived from odontogenic dental pulp stem cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 689-696. |
| [14] | Li LIANG,Xin LI,Lin NONG,Ying DONG,Ji-xin ZHANG,Dong LI,Ting LI. Analysis of microsatellite instability in endometrial cancer: The significance of minimal microsatellite shift [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 254-261. |
| [15] | Yu-mei LAI,Zhong-wu LI,Huan LI,Yan WU,Yun-fei SHI,Li-xin ZHOU,Yu-tong LOU,Chuan-liang CUI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of anorectal melanoma: A report of 68 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 262-269. |
|
||