Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 636-639. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
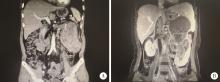
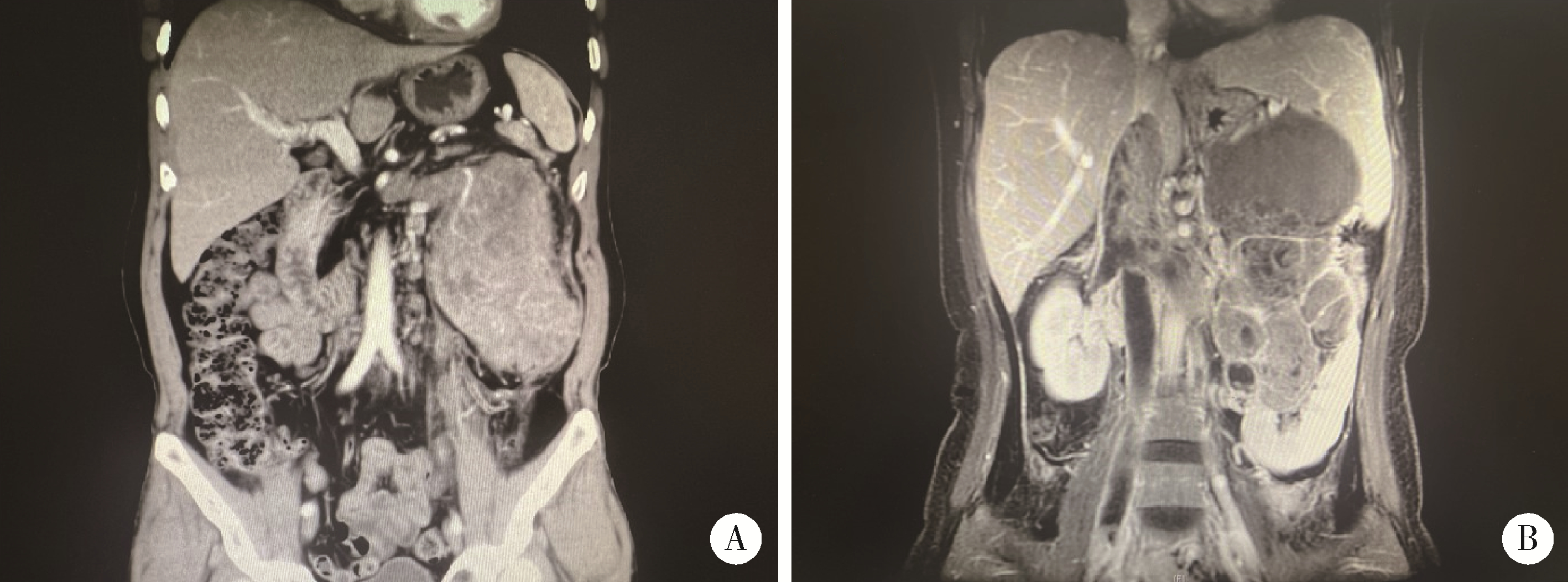
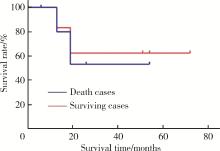
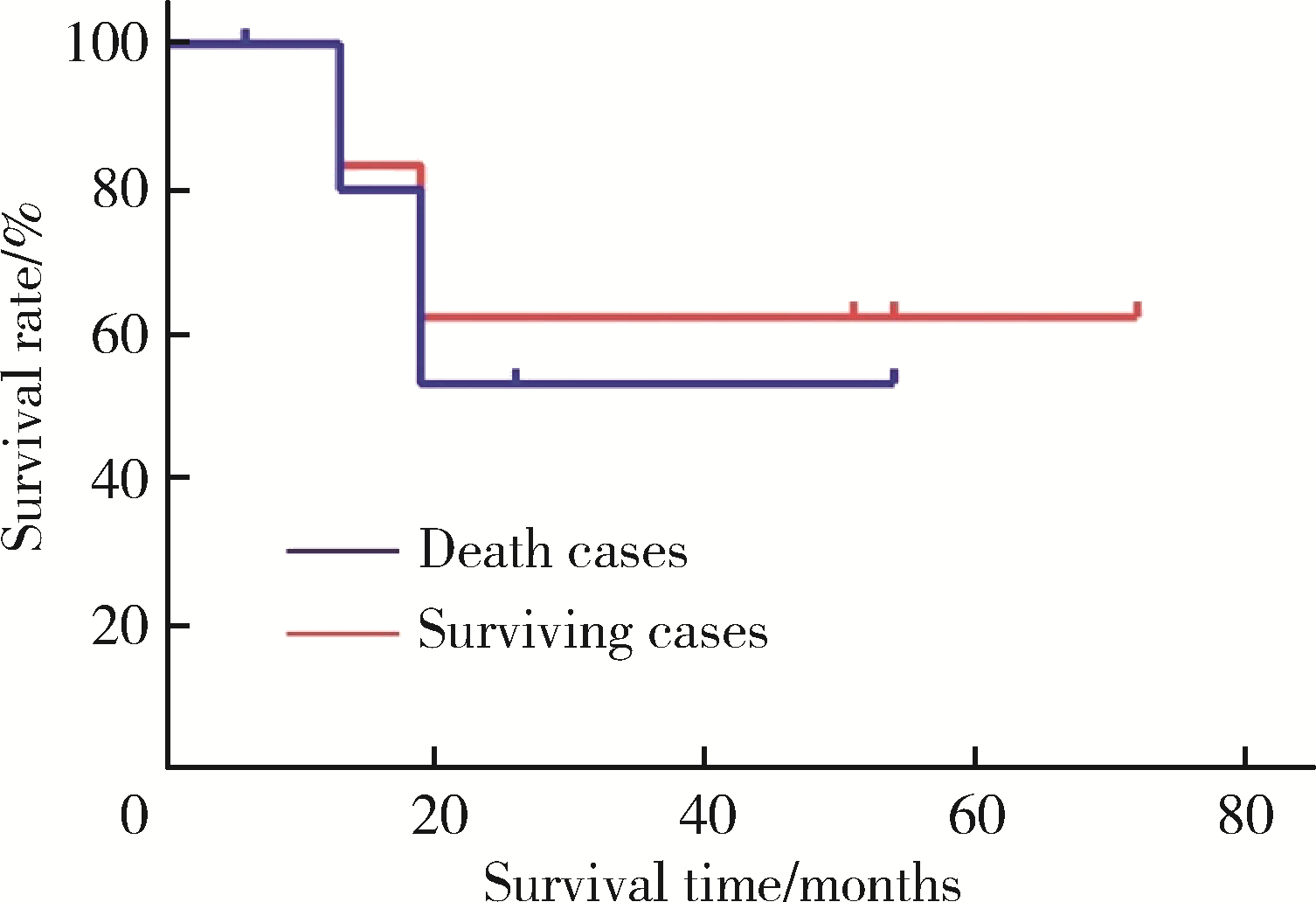
Experience in diagnosis and treatment of 6 cases of renal Ewing's sarcoma with venous thrombus
Binshuai WANG1,Min QIU1,Qianjin ZHANG2,Maofeng TIAN3,Lei LIU1,Guoliang WANG1,Min LU4,Xiaojun TIAN1,Shudong ZHANG1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Urology, The Affiliated Suqian First People's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Suqian 223800, Jiangsu, China
3. Department of Urology, Boxing People's Hospital, Binzhou 256500, Shandong, China
4. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R737.1
| 1 | 邓超, 宁刚. 原发肾脏尤文肉瘤2例并文献复习[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2022, 20 (6): 180- 182. |
| 2 |
Coffin CM , Dehner LP . Peripheral neurogenic tumors of the soft tissues in children and adolescents: A clinicopathologic study of 139 cases[J]. Pediatr Pathol, 1989, 9 (4): 387- 407.
doi: 10.3109/15513818909022361 |
| 3 |
Venkitaraman R , George MK , Ramanan SG , et al. A single institution experience of combined modality management of extra skeletal Ewings sarcoma[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2007, 5, 3.
doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-5-3 |
| 4 | Narayanan G , Rajan V , Preethi TR . Primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the kidney[J]. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent), 2017, 30 (2): 205- 208. |
| 5 | 何建风, 丁国恒, 孙红军, 等. 肾脏尤文肉瘤或原始神经外胚层肿瘤1例报告并文献复习[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2019, 35 (9): 1548- 1549. |
| 6 |
Murphey MD , Senchak LT , Mambalam PK , et al. From the radiologic pathology archives: Ewing sarcoma family of tumors: Radiologic-pathologic correlation[J]. Radiographics, 2013, 33 (3): 803- 831.
doi: 10.1148/rg.333135005 |
| 7 |
Dogra PN , Goel A , Kumar R , et al. Extraosseous Ewing's sarcoma of the kidney[J]. Urol Int, 2002, 69 (2): 150- 152.
doi: 10.1159/000065566 |
| 8 |
Thyavihally YB , Tongaonkar HB , Gupta S , et al. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney: A single institute series of 16 patients[J]. Urology, 2008, 71 (2): 292- 296.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2007.09.051 |
| 9 |
Celli R , Cai G . Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney: A rare and lethal entity[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2016, 140 (3): 281- 285.
doi: 10.5858/arpa.2014-0367-RS |
| 10 | 黄健, 张旭, 魏强, 等. 2022版中国泌尿外科和男科疾病诊断治疗指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2022: 4- 5. |
| 11 | 毕文浩, 俞能旺, 蒋立城. 肾脏原发性尤文肉瘤1例[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2022, 60 (10): 117- 119. |
| 12 |
Risi E , Iacovelli R , Altavilla A , et al. Clinical and pathological features of primary neuroectodermal tumor/Ewing sarcoma of the kidney[J]. Urology, 2013, 82 (2): 382- 386.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2013.04.015 |
| 13 | 魏晋艳, 刘静妮, 张学凌, 等. 肾脏尤文肉瘤/原始神经外胚层肿瘤与乳头状肾细胞癌的CT征象比较[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2021, 29 (9): 935- 939. |
| 14 | 郑琪, 侯宇川. 肾门尤文肉瘤1例报道并文献复习[J]. 重庆医学, 2020, 49 (3): 515- 516. |
| 15 | 冯瑶杰, 瞿姣, 危春容, 等. 骨外尤文肉瘤/外周原始神经外胚层肿瘤的CT及MRI表现[J]. 放射学实践, 2020, 35 (7): 900- 904. |
| 16 |
Babapour S , Mohseni I , Piri R , et al. Left renal Ewing's sarcoma: A case study and a review of imaging literature[J]. Radiol Case Rep, 2020, 15 (4): 391- 395.
doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2020.01.010 |
| 17 |
Llombart-Bosch A , Machado I , Navarro S , et al. Histological heterogeneity of Ewing's sarcoma/PNET: An immunohistochemical analysis of 415 genetically confirmed cases with clinical support[J]. Virchows Arch, 2009, 455 (5): 397- 411.
doi: 10.1007/s00428-009-0842-7 |
| 18 |
Tarek N , Said R , Andersen CR , et al. Primary Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney: The MD Anderson Cancer Center experience[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2020, 12 (10): 2927.
doi: 10.3390/cancers12102927 |
| 19 | 阳晶, 施鸿金, 李宁, 等. 肾尤文肉瘤/原始神经外胚层肿瘤的诊断及治疗(附1例分析)[J]. 山东医药, 2022, 62 (6): 49- 51. |
| 20 | 毕海, 黄毅, 马潞林, 等. 3例肾尤文肉瘤合并下腔静脉癌栓的诊治[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52 (5): 985- 989. |
| 21 |
Ellinger J , Bastian PJ , Hauser S , et al. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor: Rare, highly aggressive differential diagnosis in urologic malignancies[J]. Urology, 2006, 68 (2): 257- 262.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2006.02.037 |
| [1] | Dong LAN,Zhuo LIU,Yu-xuan LI,Guo-liang WANG,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG,Hong-xian ZHANG. Risk factors for massive hemorrhage after radical nephrectomy and removal of venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 825-832. |
| [2] | LIANG Yin-hua, ZU Xiong-bing, CHENG Xu, LIU Long-fei. Retroperitoneal laparoscopic with renal pedicle rotation for partial nephrectomy of ventro-renal tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 608-612. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 87
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 164
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||