Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 617-623. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.04.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
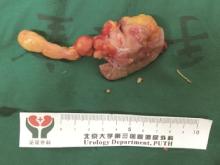
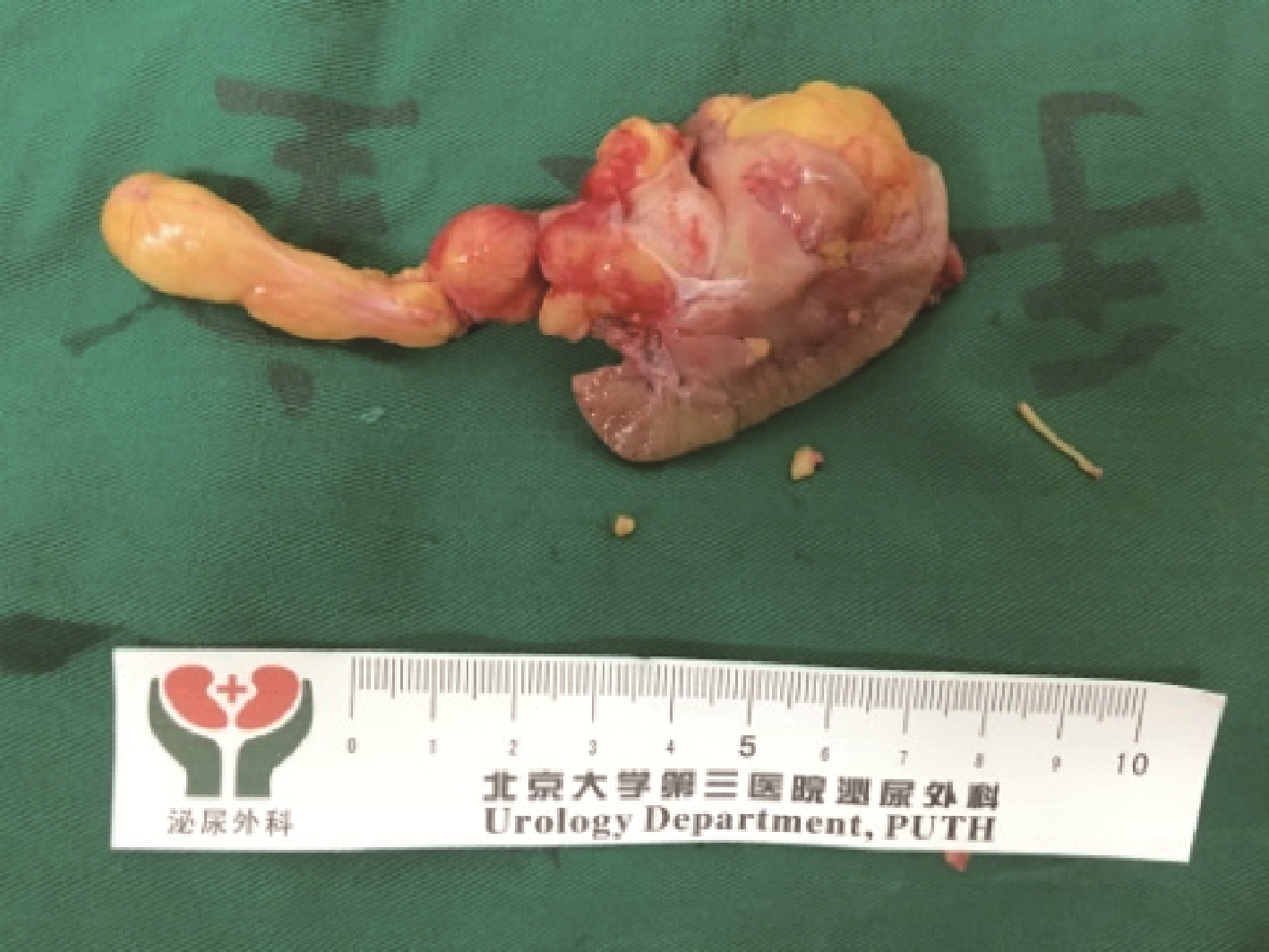
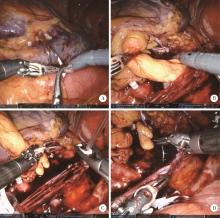
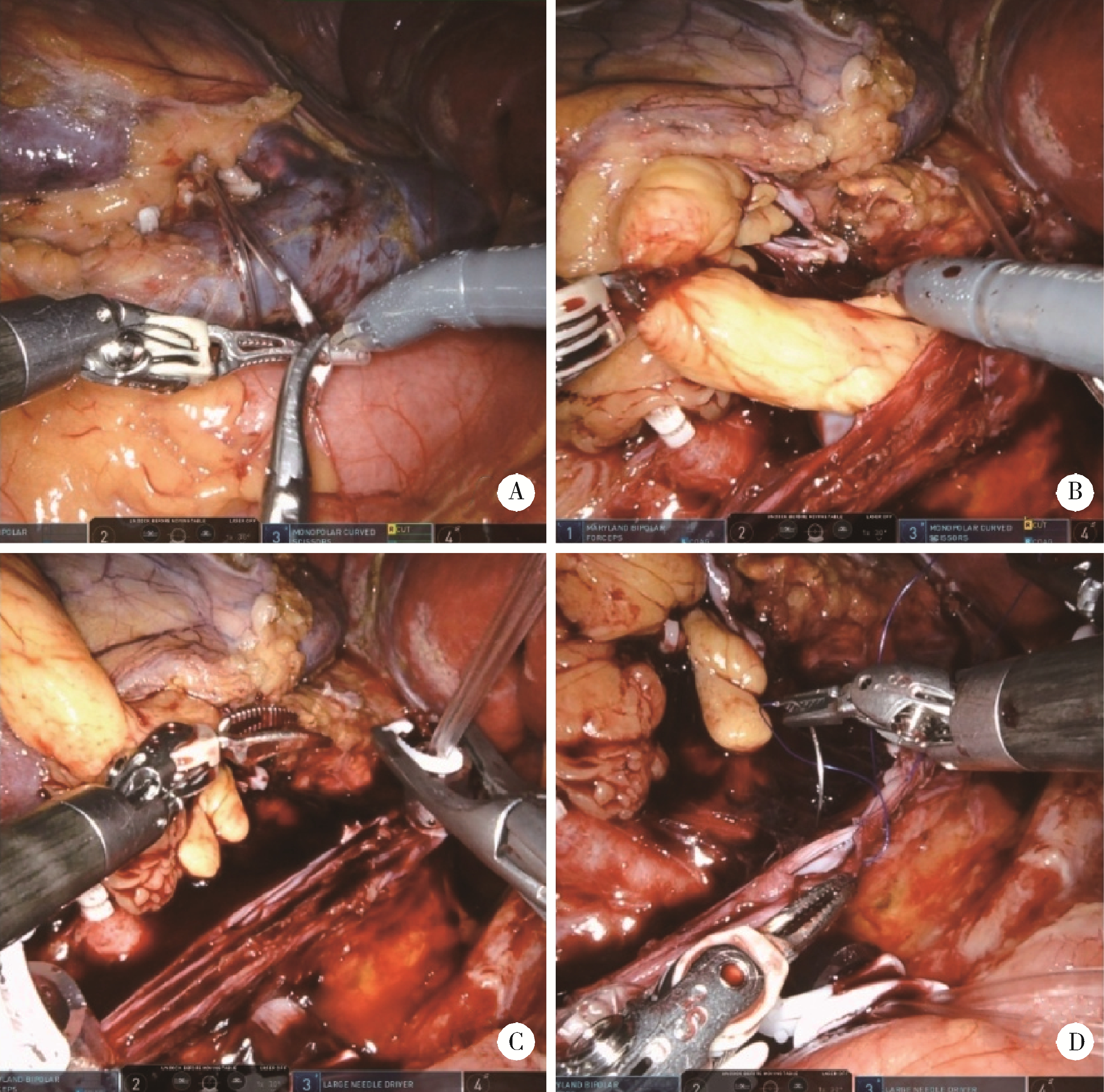
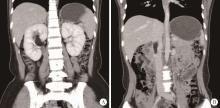
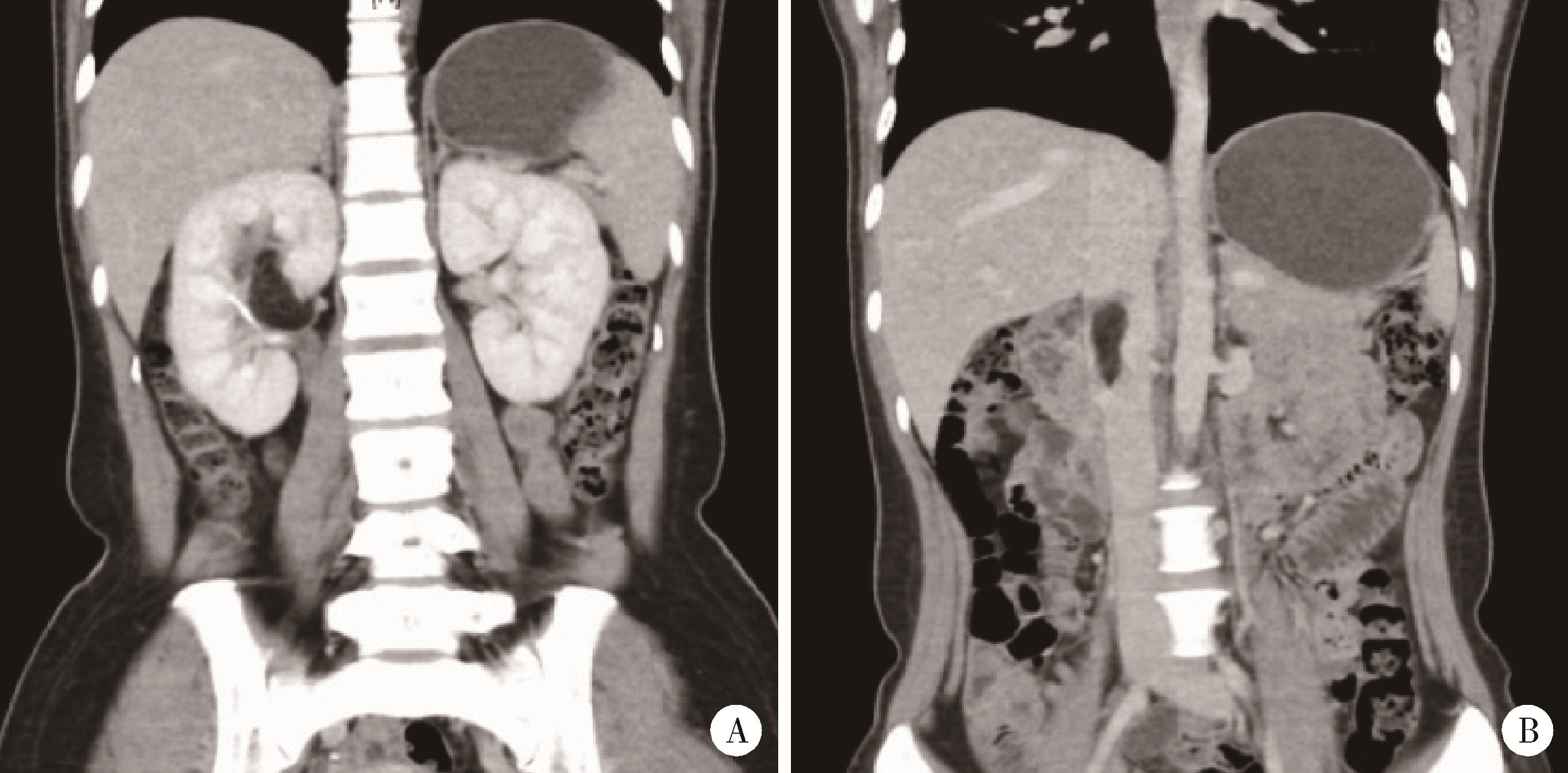
Clinical diagnosis and treatment of renal angiomyolipoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus
Kewei CHEN,Zhuo LIU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Jianfei YE,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG*( )
)
- Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R737.1
| 1 |
Fujii Y , Ajima J , Oka Ke , et al. Benign renal tumors detected among healthy adults by abdominal ultrasonography[J]. Eur Urol, 1995, 27 (2): 124- 127.
doi: 10.1159/000475142 |
| 2 |
Rule AD , Sasiwimonphan K , Lieske JC , et al. Characteristics of renal cystic and solid lesions based on contrast-enhanced computed tomography of potential kidney donors[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2012, 59 (5): 611- 618.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.12.022 |
| 3 |
Sivalingam S , Nakada SY . Contemporary minimally invasive treatment options for renal angiomyolipomas[J]. Curr Urol Rep, 2013, 14 (2): 147- 153.
doi: 10.1007/s11934-013-0311-3 |
| 4 |
Rakowski SK , Winterkorn EB , Paul E , et al. Renal manifestations of tuberous sclerosis complex: Incidence, prognosis, and predictive factors[J]. Kidney Int, 2006, 70 (10): 1777- 1782.
doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5001853 |
| 5 |
Kutcher R , Rosenblatt R , Mitsudo SM , et al. Renal angiomyolipoma with sonographic demonstration of extension into the inferior vena cava[J]. Radiology, 1982, 143 (3): 755- 756.
doi: 10.1148/radiology.143.3.7079506 |
| 6 | Riviere A , Bessede T , Patard JJ . Nephron sparing surgery for renal angiomyolipoma with inferior vena cava thrombus in tuberous sclerosis[J]. Case Rep Urol, 2014, 2014, 285613. |
| 7 |
Cornman-Homonoff J , Li D , Schiffman M . Pre-operative renal artery embolization and suprarenal IVC filter placement for prevention of fat embolization in renal angiomyolipoma with venous extension[J]. Clin Imaging, 2017, 43, 24- 27.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2017.01.012 |
| 8 |
Cittadini G, Jr. , Pozzi-Mucelli F , Danza FM , et al. "Aggressive" renal angiomyolipoma[J]. Acta Radiol, 1996, 37 (6): 927- 932.
doi: 10.3109/02841859609175471 |
| 9 |
Li HM , Yeh LR , Lu K . Renal angiomyolipoma with coexistent hemorrhagic aneurysm formation and fatty thrombus in inferior vena cava: A rare presentation[J]. Abdom Imaging, 2013, 38 (1): 180- 183.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-012-9886-2 |
| 10 |
Tan YS , Yip KH , Tan PH , et al. A right renal angiomyolipoma with IVC thrombus and pulmonary embolism[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2010, 42 (2): 305- 308.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-009-9612-3 |
| 11 |
Blute ML , Leibovich BC , Lohse CM , et al. The Mayo Clinic experience with surgical management, complications and outcome for patients with renal cell carcinoma and venous tumour thrombus[J]. BJU Int, 2004, 94 (1): 33- 41.
doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2004.04897.x |
| 12 |
Davenport DL , Bowe EA , Henderson WG , et al. National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) risk factors can be used to validate American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status Classification (ASA PS) levels[J]. Ann Surg, 2006, 243 (5): 636- 641.
doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000216508.95556.cc |
| 13 |
Liu Z , Hong P , Zhu G , et al. Pure retroperitoneal laparoscopic radical nephrectomy and thrombectomy with delayed occlusion of the proximal inferior vena cava (DOPI) technique for renal tumor with level Ⅱ-Ⅲ venous tumor thrombus[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21 (1): 627.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08392-5 |
| 14 |
Bissler JJ , Kingswood JC . Renal angiomyolipomata[J]. Kidney Int, 2004, 66 (3): 924- 934.
doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00838.x |
| 15 |
Oesterling JE , Fishman EK , Goldman SM , et al. The management of renal angiomyolipoma[J]. J Urol, 1986, 135 (6): 1121- 1124.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)46013-7 |
| 16 | Dickinson M , Ruckle H , Beaghler M , et al. Renal angiomyolipoma: Optimal treatment based on size and symptoms[J]. Clin Nephrol, 1998, 49 (5): 281- 286. |
| 17 |
Que X , Zhu Y , Ye C , et al. Invasive epithelioid angiomyolipoma with tumor thrombus in the inferior vena cava: A case report and literature review[J]. Urol Int, 2017, 98 (1): 120- 124.
doi: 10.1159/000434648 |
| 18 | Byrd GF , Lawatsch EJ , Mesrobian HG , et al. Laparoscopic cryoablation of renal angiomyolipoma[J]. J Urol, 2006, 176 (4 Pt 1): 1512- 1516. |
| 19 |
Simmons MN , Chung BI , Gill IS . Perioperative efficacy of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for tumors larger than 4 cm[J]. Eur Urol, 2009, 55 (1): 199- 207.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2008.07.039 |
| 20 |
Fernandez-Pello S , Gonzalez-Rodriguez I , Villamil LR , et al. Laparoscopic management of right renal angiomyolipoma with involvement of the inferior vena cava: Case report and review of the literature[J]. Scand J Urol, 2013, 47 (4): 340- 344.
doi: 10.3109/00365599.2012.747563 |
| 21 |
Nese N , Martignoni G , Fletcher CD , et al. Pure epithelioid PEComas (so-called epithelioid angiomyolipoma) of the kidney: A clinicopathologic study of 41 cases: detailed assessment of morphology and risk stratification[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2011, 35 (2): 161- 176.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318206f2a9 |
| 22 |
Lei JH , Liu LR , Wei Q , et al. A four-year follow-up study of renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma: A multi-center experience and literature review[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5, 10030.
doi: 10.1038/srep10030 |
| [1] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [2] | Jie YANG,Jieli FENG,Shudong ZHANG,Lulin MA,Qing ZHENG. Clinical effects of transesophageal echocardiography in different surgical methods for nephrectomy combined with Mayo Ⅲ-Ⅳ vena tumor thrombectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [3] | Binshuai WANG,Min QIU,Qianjin ZHANG,Maofeng TIAN,Lei LIU,Guoliang WANG,Min LU,Xiaojun TIAN,Shudong ZHANG. Experience in diagnosis and treatment of 6 cases of renal Ewing's sarcoma with venous thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [4] | Fan SHU,Yichang HAO,Zhanyi ZHANG,Shaohui DENG,Hongxian ZHANG,Lei LIU,Guoliang WANG,Xiaojun TIAN,Lei ZHAO,Lulin MA,Shudong ZHANG. Functional and oncologic outcomes of partial nephrectomy for cystic renal cell carcinoma: A single-center retrospective study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [5] | Kewei CHEN,Shaohui DENG,Zhuo LIU,Hongxian ZHANG,Lulin MA,Shudong ZHANG. Discussion on the surgical timing of rupture and hemorrhage of renal angiomyolipoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 326-331. |
| [6] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [7] | Dong LAN,Zhuo LIU,Yu-xuan LI,Guo-liang WANG,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG,Hong-xian ZHANG. Risk factors for massive hemorrhage after radical nephrectomy and removal of venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 825-832. |
| [8] | Min QIU,You-long ZONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Bin YANG,Chu-xiao XU,Zheng-hui SUN,Min LU,Lei ZHAO,Jian LU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA. Treatment outcome of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in patients with renal tumors of moderate to high complexity [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [9] | Jin-man ZHUANG,Tian-run LI,Xuan LI,Jing-yuan LUAN,Chang-ming WANG,Qi-chen FENG,Jin-tao HAN. Application of Rotarex catheter system in femoropopliteal artery stenosis accompanied with thrombosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 328-332. |
| [10] | ZHUANG Jin-man,LI Tian-run,LI Xuan,LUAN Jing-yuan,WANG Chang-ming,FENG Qi-chen,HAN Jin-tao. Application of Rotarex mechanical thrombectomy system in acute lower limb ische-mia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1159-1162. |
| [11] | Yu TIAN,Xiao-yue CHENG,Hui-ying HE,Guo-liang WANG,Lu-lin MA. Clinical and pathological features of renal cell carcinoma with urinary tract tumor thrombus: 6 cases report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 928-932. |
| [12] | QIU Min,WANG Lu,DENG Shao-hui,TA Peng-fei,GUO Wei,LU Jian,LIU Cheng,MA Lu-lin. Primary application of Gerota’s fascia suspension device in retroperitoneal laparoscopic partial nephrectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 789-792. |
| [13] | ZHUANG Jin-man,LI Tian-run,LI Xuan,LUAN Jing-yuan,WANG Chang-ming,FENG Qi-chen,HAN Jin-tao. Application of Rotarex mechanical thrombectomy system in treating in-stent restenosis of lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 740-743. |
| [14] | ZHAO Xun,YAN Ye,HUANG Xiao-juan,DONG Jing-han,LIU Zhuo,ZHANG Hong-xian,LIU Cheng,MA Lu-lin. Influence of deep invasive tumor thrombus on the surgical treatment and prognosis of patients with non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma complicated with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 665-670. |
| [15] | Shu-dong ZHANG,Peng HONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Shao-hui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Li-yuan TAO,Cai-guang CAO,Zhen-hua HU,Lu-lin MA. Usefulness of the indocyanine green fluorescence imaging technique in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 657-662. |
|
||