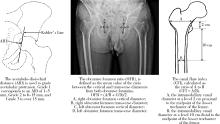
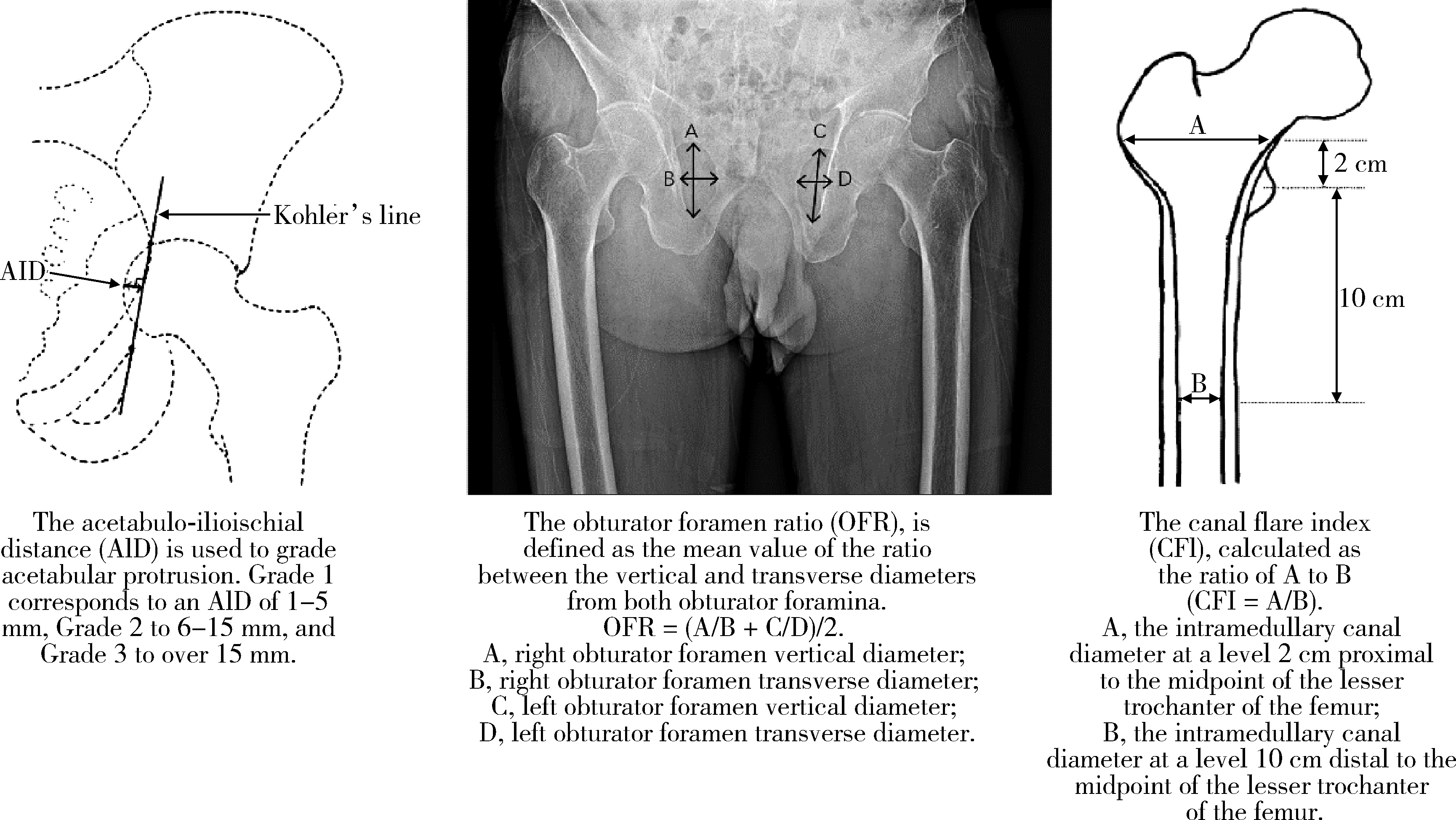
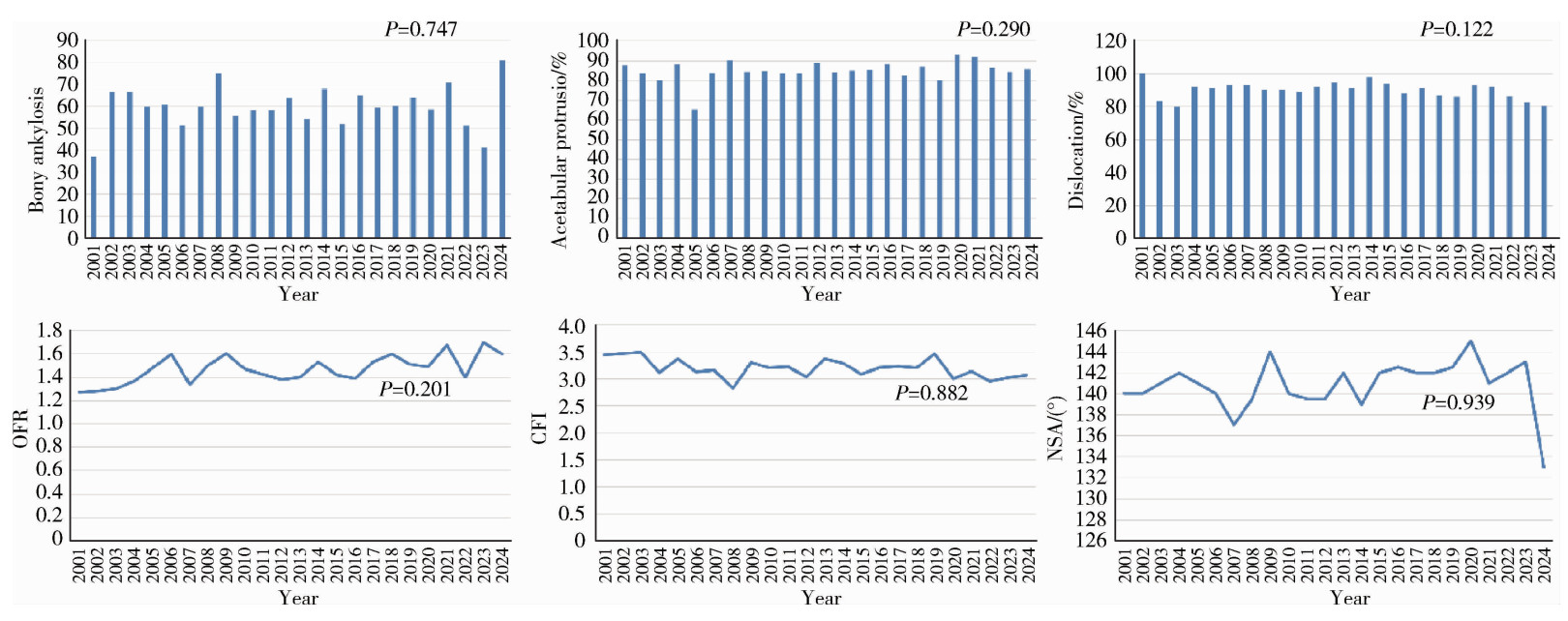
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (6): 1089-1095. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.06.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
A long-term review for radiographic parameters of hips in axial spondyloarthritis patients with end-stage hip involvement: A 24-year trend analysis from a single high-volume tertiary center
Xinfeng WU1, Siliang MAN2, Dazhao CHEN3, Yong HUA4, Xijie WEN5, Yingyue DING2, Liang ZHANG3,*( ), Xiujuan HOU6,*(
), Xiujuan HOU6,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Spine Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100035, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100035, China
3. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100035, China
4. Department of Orthopedics, Gaotang County Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Liaocheng 252800, Shandong, China
5. Department of Orthopedics, Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine of Hebei Province, Cangzhou 061000, Hebei, China
6. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100078, China
CLC Number:
- R593.23
| 1 |
马祝一, 张亮, 满斯亮, 等. 强直性脊柱炎全髋关节置换术治疗最新研究进展[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2021, 14 (12): 1039- 1045.
|
| 2 |
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221035 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1007/s11926-023-01097-7 |
| 4 |
于志永, 张亮, 边涛, 等. 全髋关节置换术治疗强直性脊柱炎合并髋关节骨性融合的中期随访研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2023, 16 (8): 706- 712.
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07338-7 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.108233 |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2007.06.002 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1097/00003086-197805000-00005 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/S0883-5403(00)91155-0 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1097/00003086-198810000-00015 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1002/art.38384 |
| 15 |
马远, 张亮, 郭邵逸, 等. 强直性脊柱炎全髋关节置换术患者基线数据特征分析[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2022, 15 (12): 939- 944.
|
| 16 |
张亮, 李宏超, 张浩天, 等. 类风湿关节炎髋关节终末期受累髋臼内陷临床特征和相关因素分析[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2022, 15 (8): 619- 625.
|
| 17 |
doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001792 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2575-5 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key128 |
| [1] | Xiaolin WANG, Shaoyi GUO, Dazhao CHEN, Xijie WEN, Yong HUA, Liang ZHANG, Qin ZHANG. A follow-up study on total hip arthroplasty in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus combined with osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(6): 1081-1088. |
| [2] | Qiwei WANG, Pengyu BAO, Shihao HONG, Xin YANG, Yu WANG, Yongping CAO. Therapeutic effect of modified femoral neck osteotomy on the surgical treatment of ankylosing spondylitis with severe flexion deformity [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 884-889. |
| [3] | KE Yan,ZHANG Qiang,MA Yun-qing,LI Ru-jun,TAO Ke,GUI Xian-ge,LI Ke-peng,ZHANG Hong,LIN Jian-hao. Short-term outcomes of total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of Tönnis grade 3 hip osteoarthritis in patients with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 175-182. |
| [4] | Sen-lei LI,Xian-teng YANG,Xiao-bin TIAN,Li SUN. Early functional recovery of direct anterior approach versus anterolateral approach for total hip arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 268-272. |
| [5] | Cui-ping ZHANG,Pei-pei LIU,Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Li-gang CUI,Yan XU,Jian-quan WANG. Application of ultrasound-guided hip joint drug injection in the postoperative rehabilitation of arthroscopie repair of acetabular labral tears [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 265-267. |
| [6] | LIU Rui, SUN Lin, LI Chang-hong, ZHAI Jia-yu, LIU Xiang-yuan. Cause analysis of spinal surgery in ankylosing spondylitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 835-839. |
| [7] | LV Ming, ZHANG Jin-qing, WANG Xing-shan, HUANG Ye, LI Wei, ZHANG Chun-yu. Surgical technique and early clinical outcomes of direct anterior approach to total hip arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 206-213. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yong-jin, LI Jia, QI Ke, XUE Chen-chen, XU Wei-dong. Comparison of efficacy and safety between the anterior and the posterior approaches to total hip arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 201-205. |
|
||