Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2026, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 153-159. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2026.01.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
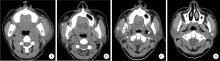
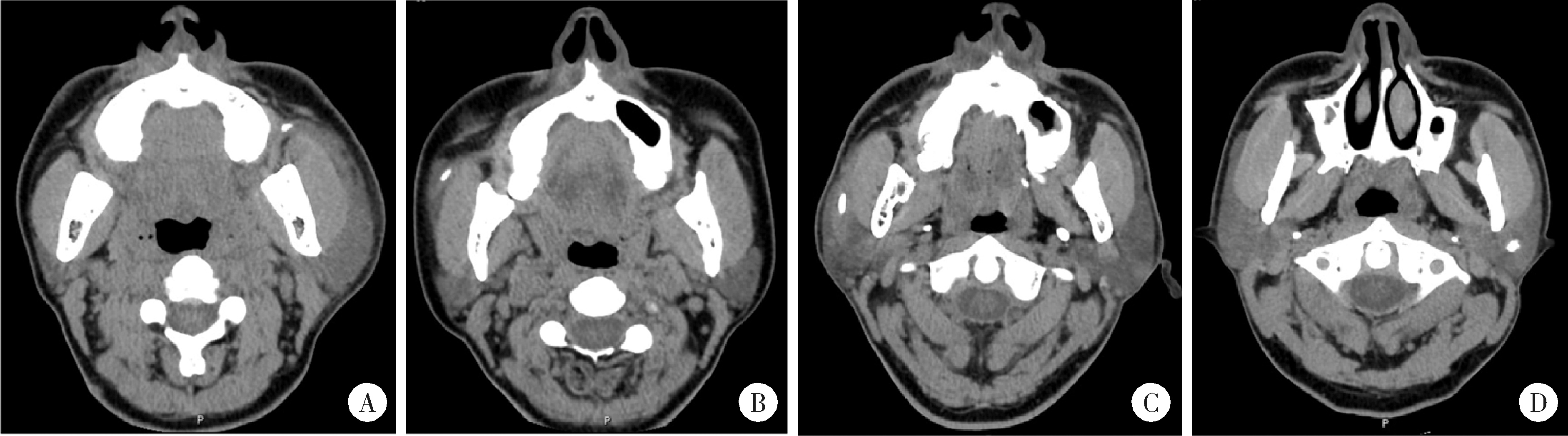
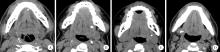
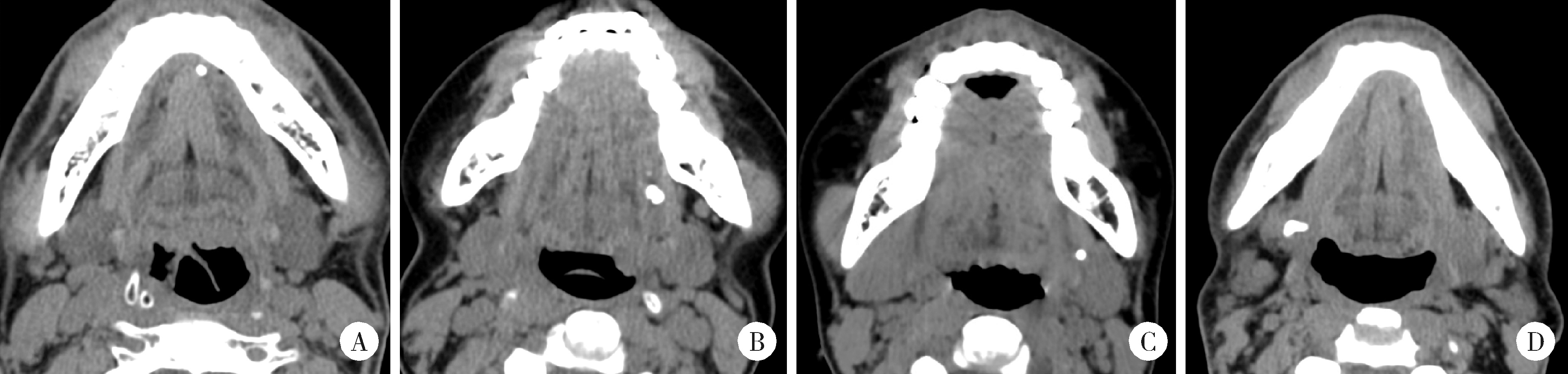
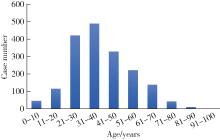
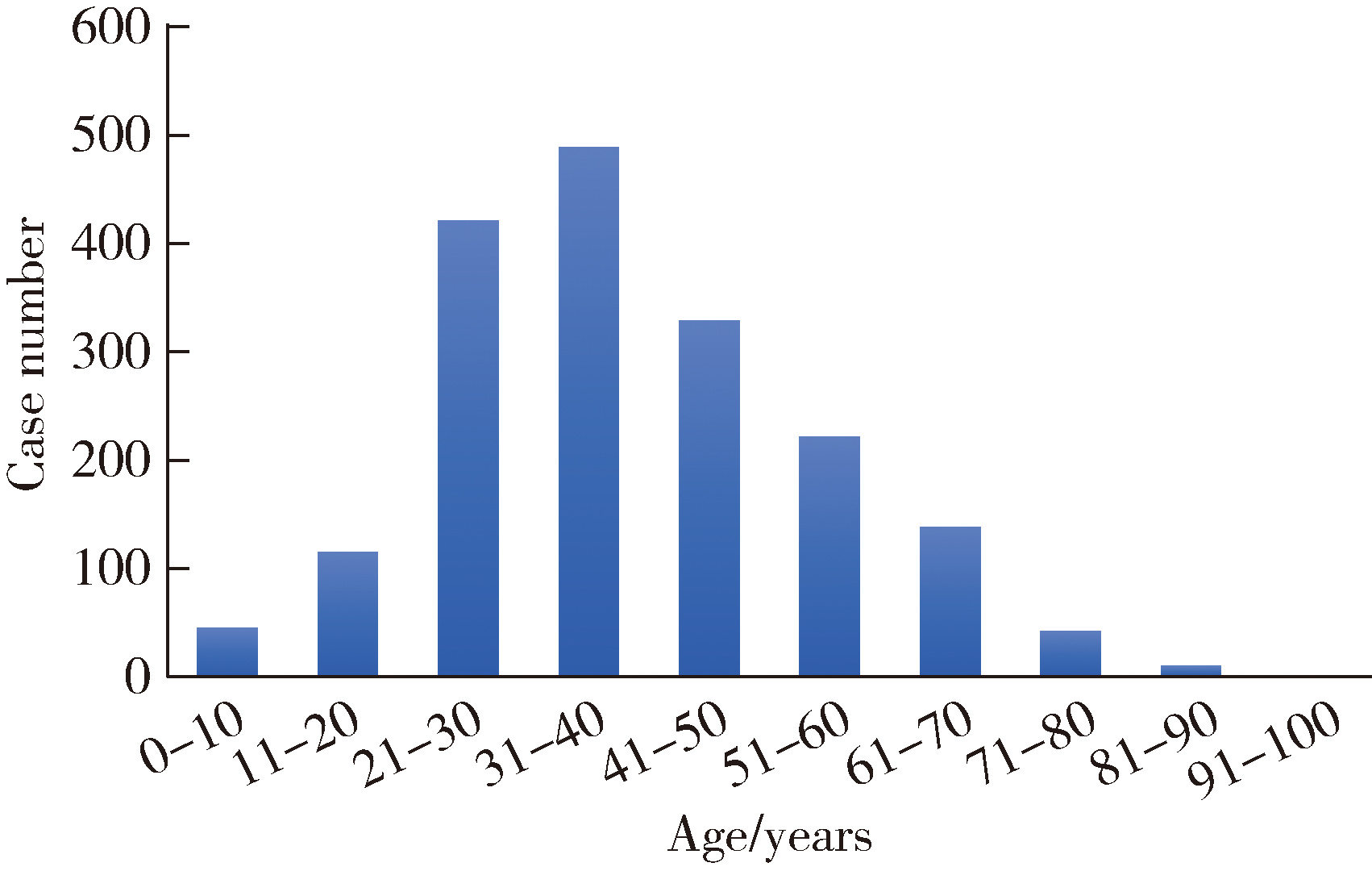
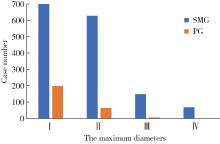
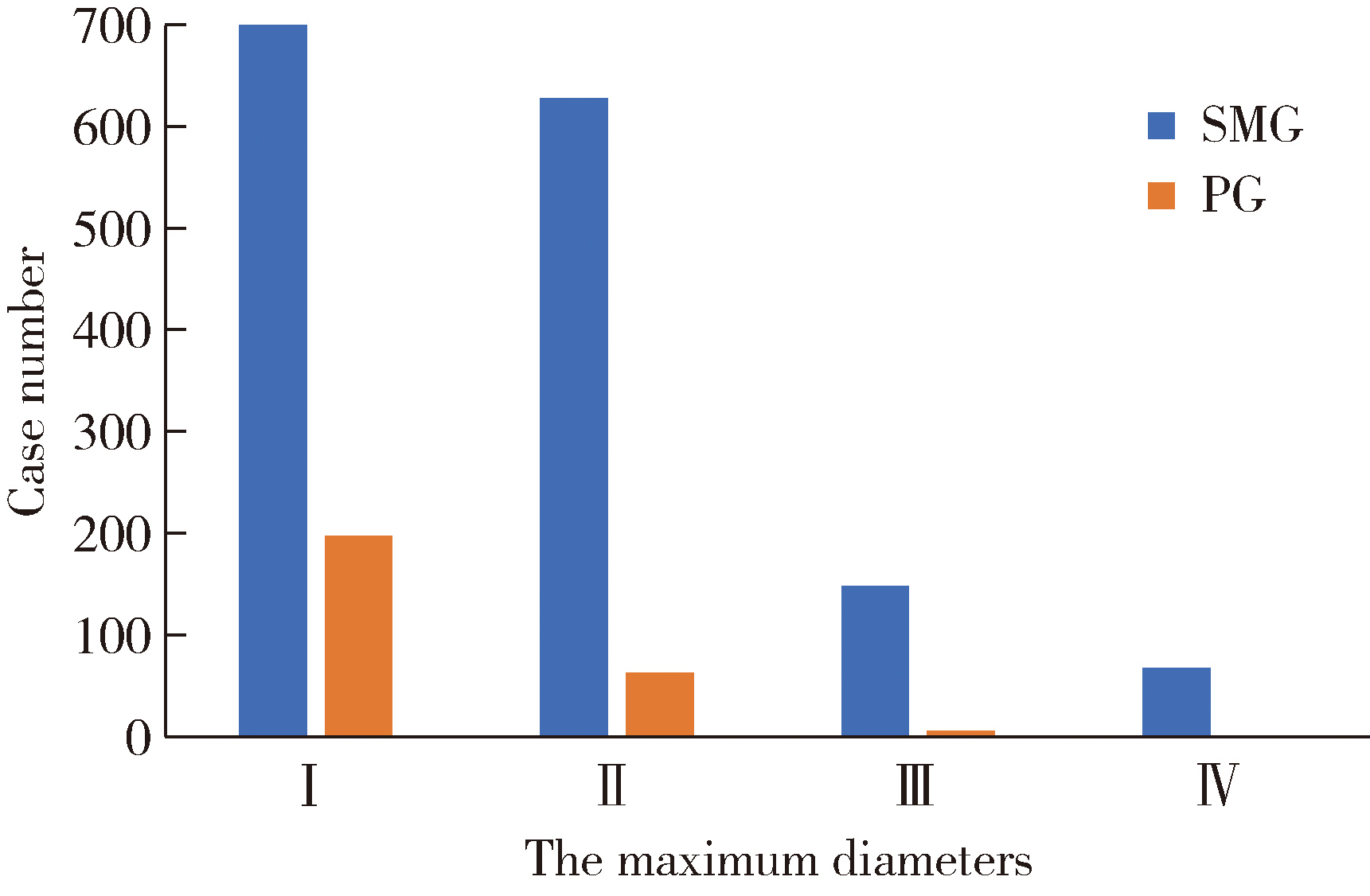
Demographic characteristic and clinical features in 1 812 patients with salivary gland stones
Yuting YANG, Liuyang QU, Danni ZHENG, Xiaotong LING, Xiaoyun XU, Denggao LIU*( )
)
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NHC Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology & NMPA Key Laboratory for Dental Materials, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R781.75
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
doi: 10.1016/S0901-5027(05)80127-4 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4800141a |
| 4 |
doi: 10.1067/moe.2000.109075a |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/S0030-6665(05)70175-4 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2014.1054 |
| 7 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2022.10.007 |
| 8 |
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2023.12.001 |
| 9 |
doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050390017005 |
| 10 |
doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(83)90341-9 |
| 11 |
doi: 10.1002/lary.25377 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.10.063 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1002/bjs.4789 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1007/s001060050476 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.1177/0194599812452837 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2009.08.012 |
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20210361 |
| 19 |
伊里夏提·卡米力. 颌下腺导管腺门结石形成的解剖学因素研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2014.
|
| 20 |
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2022.08.005 |
| 21 |
doi: 10.1016/S0003-9969(02)00211-X |
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
doi: 10.4103/0976-237X.111599 |
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
doi: 10.1001/archotol.127.1.66 |
| 28 |
doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2016.02.008 |
| 29 |
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000851 |
| 30 |
doi: 10.1002/hed.25560 |
| [1] | Yuanyuan YANG, Shanshan ZHANG, Guangyan YU, Huijun YANG, Hongyu YANG. Clinical outcomes of partial sialoadenectomy for the treatment of benign tumors in the submandibular gland [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(2): 334-339. |
| [2] | Deng-gao LIU,Dan-ni ZHENG,Ya-ning ZHAO,Ya-qiong ZHANG,Xin YE,Li-qi ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Lei ZHANG,Zu-yan ZHANG,Guang-yan YU. Recent progress in the treatment of intractable sialolithiasis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 8-12. |
| [3] | Guang-yan YU,Jia-zeng SU,Deng-gao LIU,Li-ling WU,Xin CONG. Establishment and application of new techniques for submandibular gland preservation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 842-845. |
| [4] | CHEN Chao-lun,SU Jia-zeng,YU Guang-yan. Effects of acid stimulation on saliva flow rate and compositions of human parotid and submandibular glands [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 89-94. |
| [5] | YU Guang-yan,LIU Deng-gao,LI Wei,HONG Xia,ZHANG Yan-yan,ZHU Wen-xuan,ZHANG Ke-fu,LI Xiao,LI Zhan-guo,LIU Yan-ying,CHEN Yan,GAO Yan,SU Jia-zeng. Studies on newly recognized chronic sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 13-17. |
| [6] | ZHU Yi-ying,MIN Sai-nan,YU Guang-yan. Effect of topical injection of cyclosporine A on saliva secretion and inflammation in the submandibular gland of non-obese diabetic mice [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 750-757. |
| [7] | WANG Yi-ping,CAI Zhi-gang,PENG Xin,ZHANG Jie,SUN Zhi-peng,LI Wei,ZHANG Lei,YU Guang-yan. Measurement of the weight and volume of submandibular gland in vitro [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 126-132. |
| [8] | Xin CONG,Sai-nan MIN,Li-ling WU,Zhi-gang CAI,Guang-yan YU. Role and mechanism of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in the regulation of submandibular gland secretion [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 390-396. |
| [9] | Qian SU,Xin PENG,Chuan-xiang ZHOU,Guang-yan YU. Clinicopathological features and possible prognostic factors in parotid lymphomas [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 35-42. |
| [10] | Guang-ya YU,Xia HONG,Wei LI,Yan-yan ZHANG,Yan GAO,Yan CHEN,Zu-yan ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Zhan-guo LI,Yan-ying LIU,Jia-zeng SU,Wen-xuan ZHU,Zhi-peng SUN. Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of IgG4-related sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 1-3. |
| [11] | ZHANG Ya-qiong, YE Xin, LIU Deng-gao, ZHAO Ya-ning, XIE Xiao-yan, YU Guang-yan. Endoscopy-assisted sialodochoplasty for the treatment of severe sialoduct stenosis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 160-164. |
| [12] | YU Guang-yan, WU Li-ling, CAI Zhi-gang, LV Lan, CONG Xin. A 20-year study on microvascular autologous transplantation of submandibular gland for treatment of severe dry eye [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 1-4. |
| [13] | CONG Xin, ZHANG Yan, YU Guang-Yan, WU Li-Ling. Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 serves as a novel pathway to modulate secretion in submandibular gland [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(1): 8-12. |
| [14] | LI Wei, SUN Zhi-Peng, LIU Xiao-Jing, YU Guang-Yan. Volume measurements of human parotid and submandibular glands [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2014, 46(2): 288-293. |
|
||