Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 126-132. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
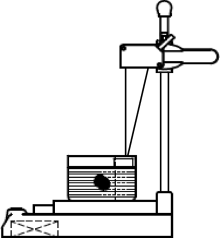
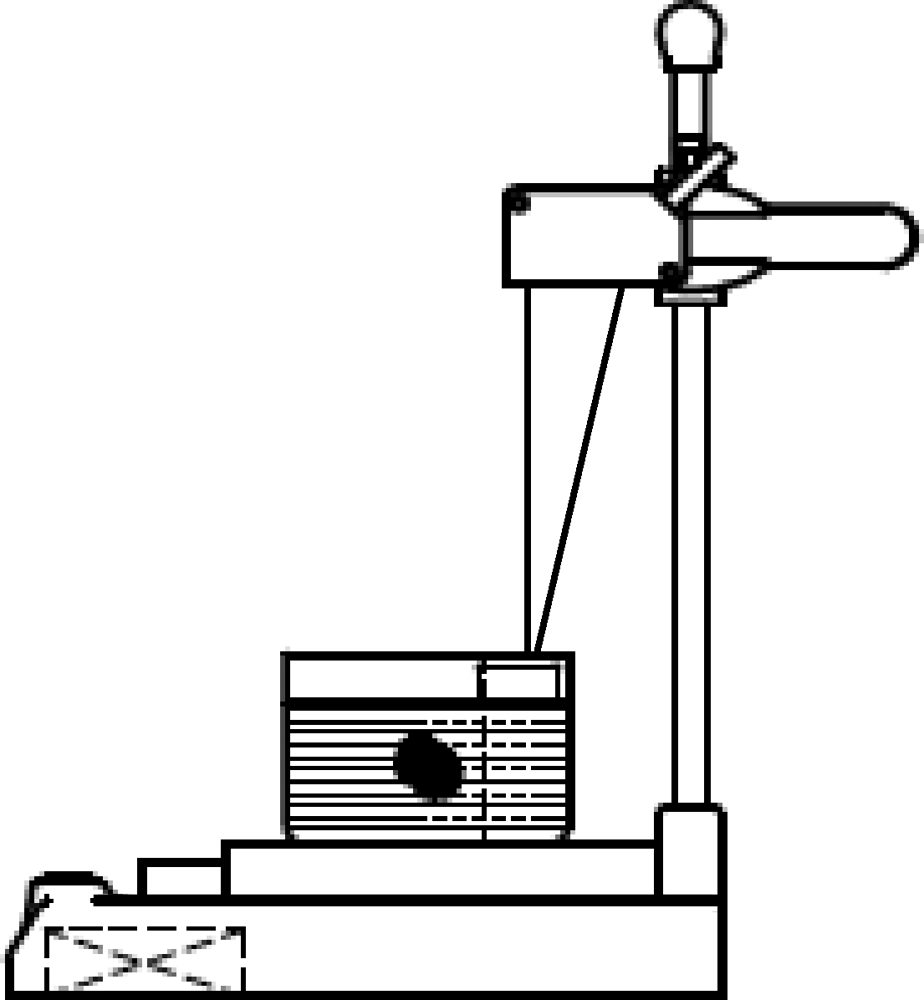
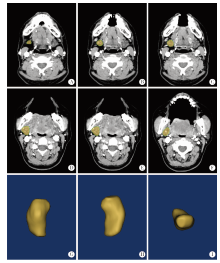
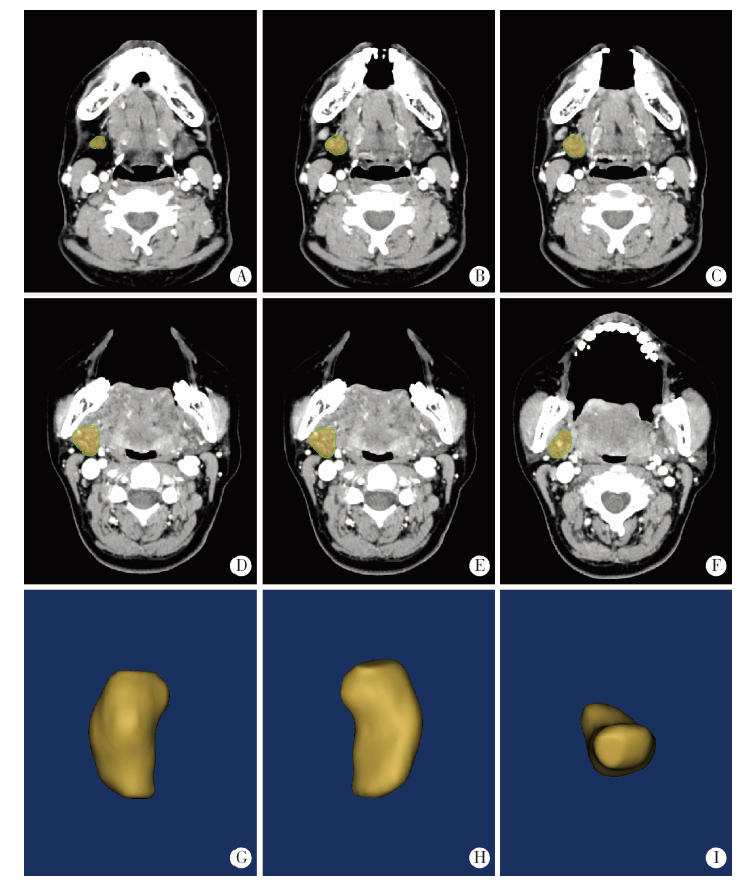
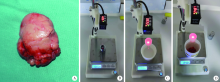
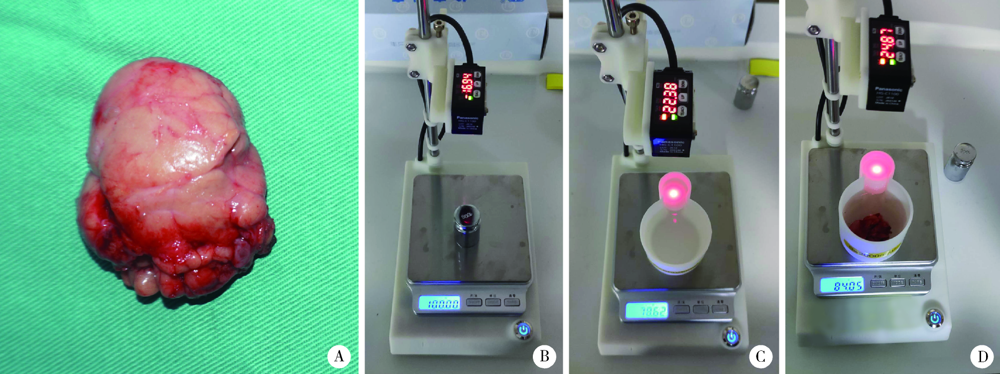
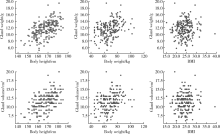
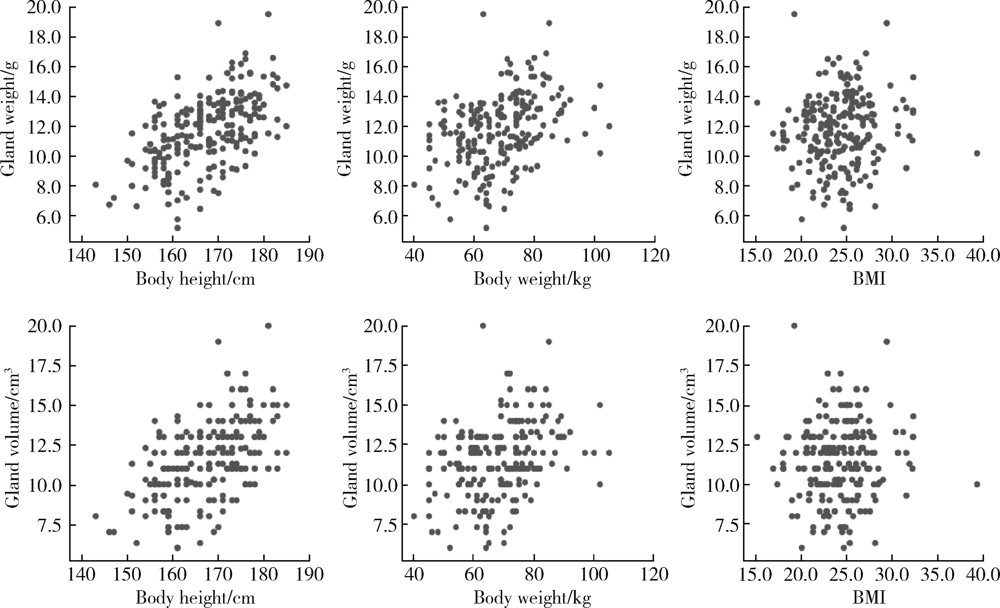
Measurement of the weight and volume of submandibular gland in vitro
WANG Yi-ping1,CAI Zhi-gang1,PENG Xin1,ZHANG Jie1,SUN Zhi-peng2,LI Wei1,ZHANG Lei1,Δ( ),YU Guang-yan1,Δ(
),YU Guang-yan1,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Oral Radiology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R782.7
| [1] | 张震康, 俞光岩. 口腔颌面外科学[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2013: 301. |
| [2] | 赵士杰, 皮昕. 口腔颌面部解剖学[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2014: 66. |
| [3] | 李巍, 孙志鹏, 刘筱菁, 等. 腮腺和颌下腺体积的测量[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014,46(2):288-293. |
| [4] | 潘天鹏, 石津生, 高和. 中华老年医学[M]. 北京: 华夏出版社, 2010: 1079. |
| [5] |
Ying M, Pang BS. Three-dimensional ultrasound measurement of cervical lymph node volume[J]. Br J Radiol, 2009,82(980):617-625.
doi: 10.1259/bjr/17611956 pmid: 19153188 |
| [6] |
Prionas ND, Ray S. Boone JM. Volume assessment accuracy in computed tomography: A phantom study[J]. J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2010,11(2):168-180.
doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v11i2.3037 |
| [7] | 张红丽, 徐亮, 许建铭, 等. 颌下腺增龄性改变的MRI定量分析[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2016,27(2):90-93. |
| [8] |
Lee MK, Sepahdari A, Cohen M. Radiologic measurement of submandibular gland ptosis[J]. Facial Plast Surg, 2013,29(4):316-320.
doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1349356 |
| [9] |
Heo MS, Lee SC, Lee SS, et al. Quantitative analysis of normal major salivary glands using computed tomography[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2001,92(2):240-244.
doi: 10.1067/moe.2001.114756 pmid: 11505274 |
| [10] | 李运成, 鲁际, 李丽亚, 等. 正常人下颌下腺的多层螺旋CT影像解剖研究[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2007,26(6):558-560. |
| [11] |
Stimec BV, Rakocevic Z, Ignjatovic D, et al. Planimetric correlation between the submandibular glands and the pancreas: A postmortem ductographic study[J]. Anat Sci Int, 2018,93(1):114-118.
doi: 10.1007/s12565-016-0382-6 pmid: 27832478 |
| [1] | YU Guang-yan,LIU Deng-gao,LI Wei,HONG Xia,ZHANG Yan-yan,ZHU Wen-xuan,ZHANG Ke-fu,LI Xiao,LI Zhan-guo,LIU Yan-ying,CHEN Yan,GAO Yan,SU Jia-zeng. Studies on newly recognized chronic sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 13-17. |
| [2] | CHEN Chao-lun,SU Jia-zeng,YU Guang-yan. Effects of acid stimulation on saliva flow rate and compositions of human parotid and submandibular glands [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 89-94. |
| [3] | Guo-yong REN,Xue-mei WU, ,Jie-yu LI,Wei-ping SUN,Yi-ning HUANG. Susceptibility vessel sign in subacute stroke patients with large vessel occlusion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1133-1138. |
| [4] | Ya-fei LIU,Lin-lin SONG,Mao-wei XING,Li-xin CAI,Dong-xin WANG. Comparison of pulse pressure variation, stroke volume variation, and plethysmographic variability index in pediatric patients undergoing craniotomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 946-951. |
| [5] | ZHU Yi-ying,MIN Sai-nan,YU Guang-yan. Effect of topical injection of cyclosporine A on saliva secretion and inflammation in the submandibular gland of non-obese diabetic mice [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 750-757. |
| [6] | Hao WANG,Shu-kun JIANG,Ran PENG,Yi HUANG,Ming-qing WANG,Jun-jie WANG,Cheng LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lu-lin MA. Individual control of urine volume to improve stability of bladder volume in radiotherapy of urinary tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 688-691. |
| [7] | Xin CONG,Sai-nan MIN,Li-ling WU,Zhi-gang CAI,Guang-yan YU. Role and mechanism of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in the regulation of submandibular gland secretion [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 390-396. |
| [8] | Guang-ya YU,Xia HONG,Wei LI,Yan-yan ZHANG,Yan GAO,Yan CHEN,Zu-yan ZHANG,Xiao-yan XIE,Zhan-guo LI,Yan-ying LIU,Jia-zeng SU,Wen-xuan ZHU,Zhi-peng SUN. Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of IgG4-related sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 1-3. |
| [9] | LI Jin-yong, SUN Hong-liang, YE Zhi-dong, FAN Xue-qiang, LIU Peng. Carotid plaque composition and volume evaluated by multi-detector computed tomography angiography [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 833-839. |
| [10] | DONG Yan-hui, SONG Yi, DONG Bin, ZOU Zhi-yong, WANG Zheng-he, YANG Zhao-geng, WANG Xi-jie, LI Yan-hui, MA Jun. Association between the blood pressure status and nutritional status among Chinese students aged 7-18 years in 2014: based on the national blood pressure reference for Chinese children and adolescents [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(3): 422-428. |
| [11] | SUN Hai-tao, YANG Rui-jie, JIANG Ping, JIANG Wei-juan, LI Jin-na, MENG Na, WANG Jun-jie. Dosimetric analysis of volumetric modulated arc therapy and intensity modulated radiotherapy for patients undergone breast-conserving operation [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 188-192. |
| [12] | ZHANG Ya-qiong, YE Xin, LIU Deng-gao, ZHAO Ya-ning, XIE Xiao-yan, YU Guang-yan. Endoscopy-assisted sialodochoplasty for the treatment of severe sialoduct stenosis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 160-164. |
| [13] | YU Guang-yan, WU Li-ling, CAI Zhi-gang, LV Lan, CONG Xin. A 20-year study on microvascular autologous transplantation of submandibular gland for treatment of severe dry eye [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 1-4. |
| [14] | CHEN Na, WU Wei, DING Rui-ying, HAN Hao-lun, WANG Hong-nan, LI Bao-wei, WANG Gang. Morphological changes on cochlear hair cells of rats in simulated weightlessness and inboard noise [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(3): 501-500. |
| [15] | CHENG Lan, LI Qin, SONG Yi, MA Jun, WANG Hai-Jun. Association of physical activities, sedentary behaviors with overweight/obesity in 9-11 year-old Chinese primary school students [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(3): 436-441. |
|