Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 596-601. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.03.033
Previous Articles Next Articles
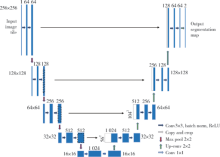
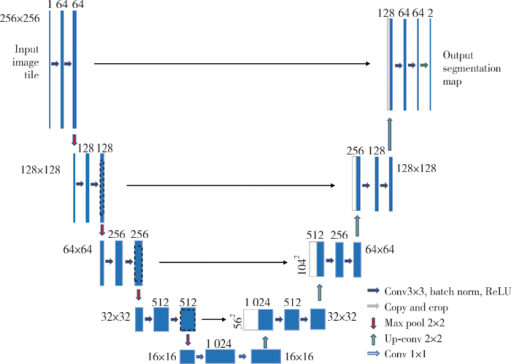
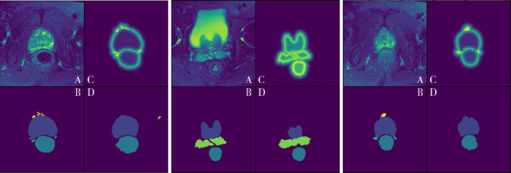
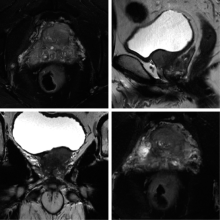
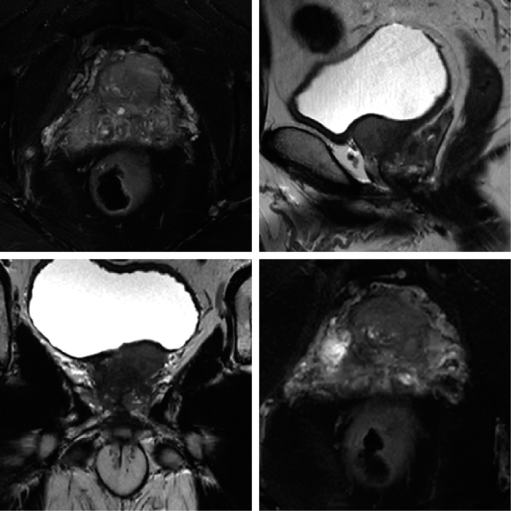
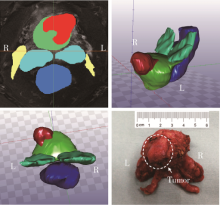
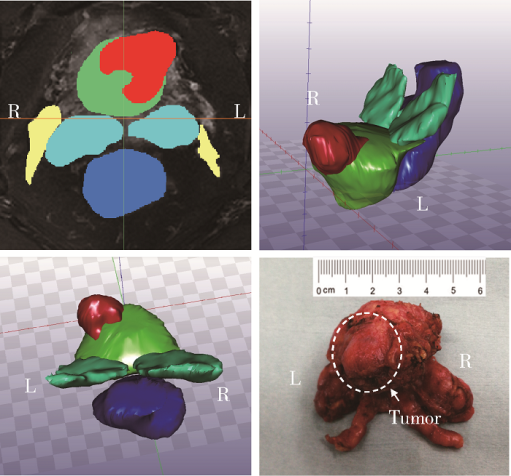
Application of U-shaped convolutional neural network in auto segmentation and reconstruction of 3D prostate model in laparoscopic prostatectomy navigation
Ye YAN1,*,Hai-zhui XIA1,*,Xu-sheng LI2,Wei HE3,Xue-hua ZHU1,Zhi-ying ZHANG1,Chun-lei XIAO1,Yu-qing LIU1,Hua HUANG4,Liang-hua HE2,Jian LU1△( )
)
CLC Number:
- R737.25
| [1] |
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A.Cancer statistics, 2018[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(1): 7-30.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21442 |
| [2] |
Simmons MN, Stephenson AJ, Klein EA.Natural history of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy: risk assessment for secondary therapy[J]. Eur Urol, 2007, 51(5): 1175-1184.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.01.015 |
| [3] | Van den Broeck T, van den Bergh R, Arfi N, et al. Prognostic value of biochemical recurrence following treatment with curative intent for prostate cancer: A systematic review [J/OL]. Eur Urol,(2018-10-17) [2019-02-15]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.10.011. |
| [4] |
Ukimura O, Aron M, Nakamoto M, et al.Three-dimensional surgical navigation model with TilePro display during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy[J]. J Endourol, 2014, 28(6): 625-630.
doi: 10.1089/end.2013.0749 |
| [5] |
Hughes-Hallett A, Mayer EK, Marcus HJ, et al.Augmented rea-lity partial nephrectomy: examining the current status and future perspectives[J]. Urology, 2014, 83(2): 266-273.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2013.08.049 |
| [6] | 王燕, 高旭, 阳青松, 等. 3D打印技术辅助认知融合在前列腺穿刺活检术中的应用[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2016, 31(2): 104-107. |
| [7] | 邵叶秦, 杨新. 基于随机森林的CT前列腺分割[J]. CT理论与应用研究, 2015, 24(5): 647-655. |
| [8] | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T.U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Cham: Springer, 2015: 234-241. |
| [9] | 詹曙, 梁植程, 谢栋栋. 前列腺磁共振图像分割的反卷积神经网络方法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2017, 22(4): 516-522. |
| [10] | Neher PF, Stieltjes B, Reisert M, et al.MITK global tractography[C]. Proceedings of SPIE: The International Society for Optical Engineering, 2012: 83144D. doi: 10.1117/12.911215. |
| [11] |
Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al.Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324.
doi: 10.1109/5.726791 |
| [12] |
Mahapatra D, Buhmann JM.Prostate MRI segmentation using learned semantic knowledge and graph cuts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2014, 61(3): 756-764.
doi: 10.1109/TBME.2013.2289306 |
| [13] | Korez R, Likar B, Pernuš F, et al.Model-based segmentation of vertebral bodies from MR images with 3D CNNs[C]. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Cham: Springer, 2016: 433-441. |
| [14] |
Brosch T, Tang LY, Yoo Y, et al.Deep 3D convolutional encoder networks with shortcuts for multiscale feature integration applied to multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(5): 1229-1239.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2528821 |
| [15] |
Martínez F, Romero E, Dréan G, et al.Segmentation of pelvic structures for planning CT using a geometrical shape model tuned by a multi-scale edge detector[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2014, 59(6): 1471-1484.
doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/6/1471 |
| [16] | 凌彤, 杨琬琪, 杨明. 利用多模态U形网络的CT图像前列腺分割[J]. 智能系统学报, 2018, 13(6): 981-988. |
| [17] | Ebbing J, Jäderling F, Collins JW, et al.Comparison of 3D printed prostate models with standard radiological information to aid understanding of the precise location of prostate cancer: A construct validation study[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(6): e199477. |
| [18] |
Volonté F, Pugin F, Bucher P, et al.Augmented reality and image overlay navigation with OsiriX in laparoscopic and robotic surgery: not only a matter of fashion[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2011, 18(4): 506-509.
doi: 10.1007/s00534-011-0385-6 |
| [19] |
Teber D, Guven S, Simpfendorfer T, et al.Augmented reality: a new tool to improve surgical accuracy during laparoscopic partial nephrectomy? Preliminary in vitro and in vivo results[J]. Eur Urol, 2009, 56(2): 332-338.
doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.05.017 |
| [20] |
Porpiglia F, Fiori C, Checcucci E, et al.Augmented reality robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: Preliminary experience[J]. Urology, 2018, 115(5): 184.
doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2018.01.028 |
| [21] | Porpiglia F, Checcucci E, Amparore D, et al.Augmented-reality robot-assisted radical prostatectomy using hyper-accuracy three-dimensional reconstruction (HA 3DTM) technology: a radiological and pathological study[J]. BJU international, 2018, 123(5): 834-845. |
| [1] | Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG, Qian ZHANG. Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | Yuxuan TIAN,Mingjian RUAN,Yi LIU,Derun LI,Jingyun WU,Qi SHEN,Yu FAN,Jie JIN. Predictive effect of the dual-parametric MRI modified maximum diameter of the lesions with PI-RADS 4 and 5 on the clinically significant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | Kaifeng YAO,Mingjian RUAN,Derun LI,Yuxuan TIAN,Yuke CHEN,Yu FAN,Yi LIU. Diagnostic efficacy of targeted biopsy combined with regional systematic biopsy in prostate cancer in patients with PI-RADS 4-5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [4] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [5] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [6] | Shishi BO,Chengzhi GAO. Tooth segmentation and identification on cone-beam computed tomography with convolutional neural network based on spatial embedding information [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 735-740. |
| [7] | Kewei CHEN,Shaohui DENG,Zhuo LIU,Hongxian ZHANG,Lulin MA,Shudong ZHANG. Discussion on the surgical timing of rupture and hemorrhage of renal angiomyolipoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 326-331. |
| [8] | Liang LYU,Mingjin ZHANG,Aonan WEN,Yijiao ZHAO,Yong WANG,Jing LI,Gengchen YANG,Dawei LIU. Preliminary evaluation of chin symmetry with three dimentional soft tissue spatial angle wireframe template [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [9] | Bochun MAO,Yajing TIAN,Xuedong WANG,Jing LI,Yanheng ZHOU. Soft and hard tissue changes of hyperdivergent class Ⅱ patients before and after orthodontic extraction treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [10] | Xiaotong LING,Liuyang QU,Danni ZHENG,Jing YANG,Xuebing YAN,Denggao LIU,Yan GAO. Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [11] | Silan AN,Qunyi ZHENG,Kai WANG,Shan GAO. Characteristics and influencing factors of early pain in patients after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 167-173. |
| [12] | Yi LIU,Chang-wei YUAN,Jing-yun WU,Qi SHEN,Jiang-xi XIAO,Zheng ZHAO,Xiao-ying WANG,Xue-song LI,Zhi-song HE,Li-qun ZHOU. Diagnostic efficacy of prostate cancer using targeted biopsy with 6-core systematic biopsy for patients with PI-RADS 5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [13] | Hai MAO,Fan ZHANG,Zhan-yi ZHANG,Ye YAN,Yi-chang HAO,Yi HUANG,Lu-lin MA,Hong-ling CHU,Shu-dong ZHANG. Predictive model of early urinary continence recovery based on prostate gland MRI parameters after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 818-824. |
| [14] | Chang-wei YUAN,De-run LI,Zhi-hua LI,Yi LIU,Gang-zhi SHAN,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of dynamic contrast enhanced status in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer with PI-RADS 4 lesion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [15] | Zhan-yi ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Cai-guang CAO,Chang-jian LI,Shao-hui DENG,Yue-hao SUN,Tian-liang HUANG,Yun-he GUAN,Nan LI,Min LU,Zhen-hua HU,Shu-dong ZHANG. Near-infrared targeted probe designed for intraoperative imaging of prostatic neurovascular bundles [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
|
||