Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1167-1171. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
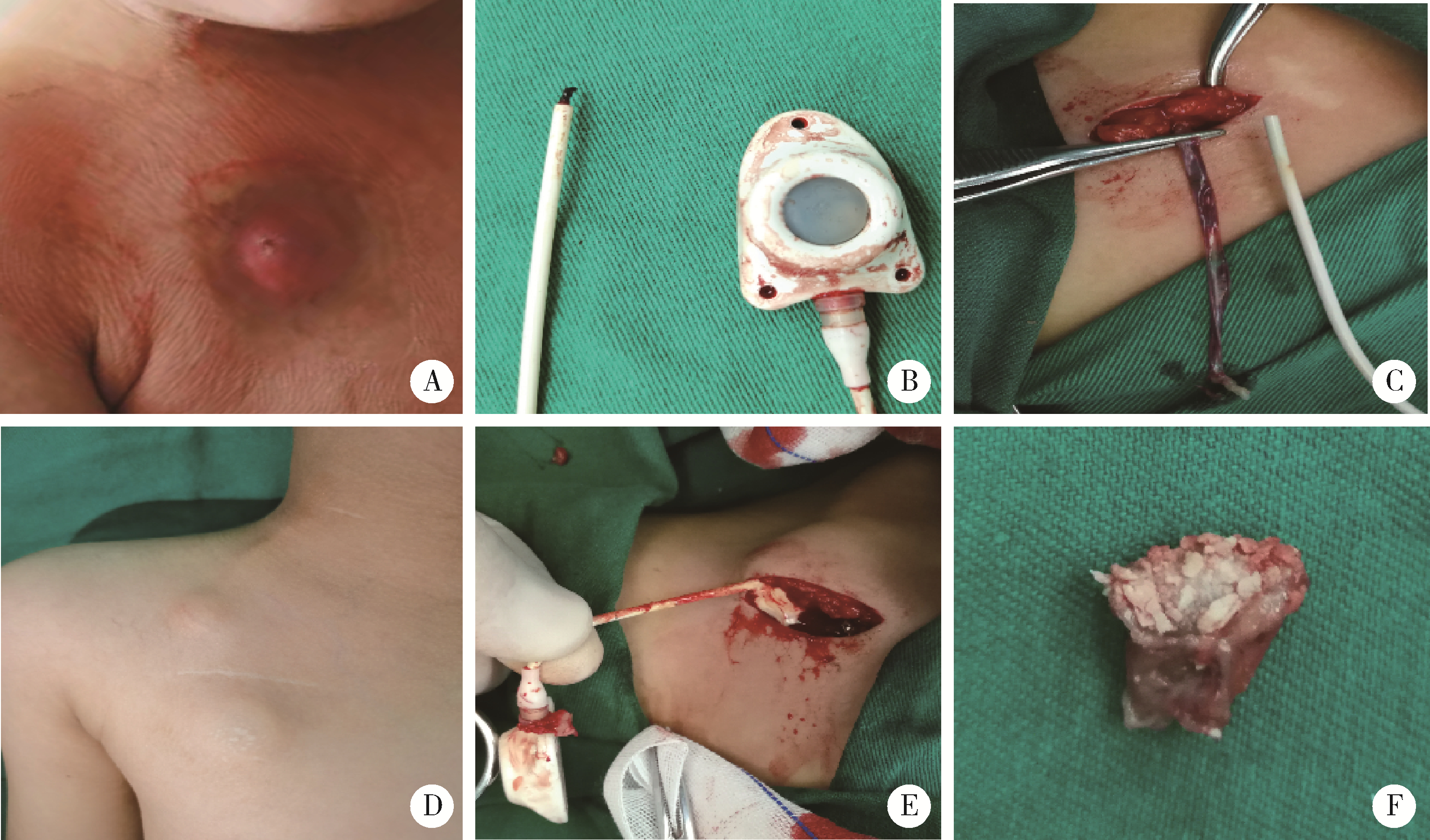
Surgical complications of totally implantable venous access port in children with malignant tumors
Hui LI,Yang-xu GAO,Shu-lei WANG,Hong-xin YAO*( )
)
- Department of Pediatric Surgery, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R726
| 1 |
Zhang P , Du J , Fan CS , et al. Utility of totally implantable venous access ports in patients with breast cancer[J]. Breast J, 2020, 26 (2): 333- 334.
doi: 10.1111/tbj.13595 |
| 2 |
Xu HP , Chen R , Jiang CJ , et al. Implanting totally implantable venous access ports in the upper arm is feasible and safe for patients with early breast cancer[J]. J Vasc Access, 2020, 21 (5): 609- 614.
doi: 10.1177/1129729819894461 |
| 3 |
余磊, 张英妹, 黄种文, 等. 经颈静脉及锁骨下静脉输液港植入术并发症的比较分析[J]. 当代医学, 2021, 27 (3): 112- 114.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2021.03.044 |
| 4 |
李颖, 姜浩, 韩哲洙, 等. 颈内静脉与锁骨下静脉植入输液港并发症发生率的对比分析[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2020, 36 (9): 1496- 1499.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2020.09.035 |
| 5 |
Sundaram J , Agarwal P , Ramasundaram M , et al. Implantable venous access devices in pediatric malignancies: Institutional expe-rience in a developing nation[J]. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg, 2020, 25 (5): 286- 290.
doi: 10.4103/jiaps.JIAPS_121_19 |
| 6 |
Zhang KC , Chen L , Chinese Research Hospital Association Digestive Tumor Committee , et al. Chinese expert consensus and practice guideline of totally implantable access port for digestive tract carcinomas[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26 (25): 3517- 3527.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i25.3517 |
| 7 |
中国医师协会介入医师分会. 植入式给药装置介入专家共识[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2019, 99 (7): 484- 490.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2019.07.002 |
| 8 | 周涛, 唐甜甜, 耿翠芝, 等. 植入式静脉输液港植入手术2007例分析[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2014, 34 (4): 348- 350. |
| 9 |
Caterina G , Maria A , Alessandro C , et al. Totally implantable venous access devices in children with medical complexity: Preliminary data from a tertiary care hospital[J]. J Vasc Access, 2017, 18 (5): 426- 429.
doi: 10.5301/jva.5000727 |
| 10 |
Philomena CD , Shiyam K , Annupam K , et al. Complications and management of totally implantable central venous access ports in cancer patients at a university hospital in Oman[J]. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J, 2021, 21 (1): e103- e109.
doi: 10.18295/squmj.2021.21.01.014 |
| 11 | 黄一敏, 徐伟珏, 吴一波, 等. 小儿完全植入式静脉输液港导管相关性血流感染的诊治——附4例报道[J]. 临床小儿外科杂志, 2020, 19 (10): 939- 942. |
| 12 |
Taveira MRV , Lima LS , Araújo CC , et al. Risk factors for central line-associated bloodstream infection in pediatric oncology patients with a totally implantable venous access port: A cohort study[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2017, 64 (2): 336- 342.
doi: 10.1002/pbc.26225 |
| 13 |
Choksi A , Finnegan K , Etezadi V . Does systemic antibiotic prophylaxis prior to the placement of totally implantable venous access devices reduce early infection? A retrospective study of 1 485 cases at a large academic institution[J]. Am J Infect Control, 2020, 48 (1): 95- 99.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2019.06.028 |
| 14 | 周荻, 葛峰, 缪长虹, 等. 复旦大学附属中山医院完全植入式静脉输液港植入与维护规范(v1.2020)[J]. 中国临床医学, 2020, 27 (4): 697- 703. |
| 15 |
余超, 葛坤元, 蒋晓东, 等. 3种不同途径植入静脉输液港的临床应用比较[J]. 复旦学报(医学版), 2021, 48 (2): 229- 234.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2021.02.013 |
| 16 |
Ding XY , Ding F , Wang YG , et al. Shanghai expert consensus on totally implantable access ports 2019[J]. J Intervent Med, 2019, 2 (4): 141- 145.
doi: 10.1016/j.jimed.2019.10.008 |
| 17 |
Chou PL , Fu JY , Cheng CH , et al. Current port maintenance strategies are insufficient: View based on actual presentations of implanted ports[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98 (44): e17757.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017757 |
| [1] | Shuangyun ZHAO, Siyu ZOU, Xueying LI, Lijuan SHEN, Hong ZHOU. Evaluation of reliability and validity of Chinese version of a short-form of Health Literacy Dental scale (HeLD-14) in the application among parents of preschool children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [2] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [3] | Li WAN, Zhoucang ZHANG, Jiaxiang DING, Mei WANG. Venous air embolism following removal of central venous catheters: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 938-941. |
| [4] | Zhihan YUE,Na HAN,Zheng BAO,Jinlang LYU,Tianyi ZHOU,Yuelong JI,Hui WANG,Jue LIU,Haijun WANG. A prospective cohort study of association between early childhood body mass index trajectories and the risk of overweight [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [5] | Xiuwen FEI,Si LIU,Bo WANG,Aimei DONG. Clinical characteristics and treatment in adults and children with histiocytic necroti-zing lymphadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 533-540. |
| [6] | Xiao-jin YAN,Yun-fei LIU,Ning MA,Jia-jia DANG,Jing-shu ZHANG,Pan-liang ZHONG,Pei-jin HU,Yi SONG,Jun MA. Assessment of prevalence of malnutrition among Chinese primary and secondary school students and analysis of policy effect during the period of the Program for the Development of Chinese Children 2011-2020 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [7] | Su-huan XU,Bei-bei WANG,Qiu-ying PANG,Li-jun ZHONG,Yan-ming DING,Yan-bo HUANG,Xin-yan CHE. Effect of equal temperature bladder irrigation in patients with transurethral resection of prostate: A meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 676-683. |
| [8] | Xiao-yi MI,Shan-shan HOU,Zi-yuan FU,Mo ZHOU,Xin-xuan LI,Zhao-xue MENG,Hua-fang JIANG,Hong Zhou. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of adverse childhood experiences international questionnaire in parents of preschool children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 408-414. |
| [9] | Meng-jie CUI,Qi MA,Man-man CHEN,Tao MA,Xin-xin WANG,Jie-yu LIU,Yi ZHANG,Li CHEN,Jia-nuo JIANG,Wen YUAN,Tong-jun GUO,Yan-hui DONG,Jun MA,Yi XING. Association between different growth patterns and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents aged 7 to 17 years [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [10] | Jia-jia DANG,Shan CAI,Pan-liang ZHONG,Ya-qi WANG,Yun-fei LIU,Di SHI,Zi-yue CHEN,Yi-hang ZHANG,Pei-jin HU,Jing LI,Jun MA,Yi SONG. Association of outdoor artificial light at night exposure with overweight and obesity among children and adolescents aged 9 to 18 years in China [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [11] | Jing LIU,Ai-dong LU,Ying-xi ZUO,Jun WU,Zhi-zhuo HUANG,Yue-ping JIA,Ming-ming DING,Le-ping ZHANG,Jiong QIN. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of seizures in 75 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [12] | Ya-xi CUI,Jun-bao DU,Qing-you ZHANG,Ying LIAO,Ping LIU,Yu-li WANG,Jian-guang QI,Hui YAN,Wen-rui XU,Xue-qin LIU,Yan SUN,Chu-fan SUN,Chun-yu ZHANG,Yong-hong CHEN,Hong-fang JIN. A 10-year retrospective analysis of spectrums and treatment options of orthostatic intolerance and sitting intolerance in children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 954-960. |
| [13] | Tao MA,Yan-hui LI,Man-man CHEN,Ying MA,Di GAO,Li CHEN,Qi MA,Yi ZHANG,Jie-yu LIU,Xin-xin WANG,Yan-hui DONG,Jun MA. Associations between early onset of puberty and obesity types in children: Based on both the cross-sectional study and cohort study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 961-970. |
| [14] | Yan-yan DU,Jian WANG,Lan HE,Li-na JI,Xi-wei XU. Kawasaki disease complicated with mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 756-761. |
| [15] | Yun-fei LIU,Jia-jia DANG,Pan-liang ZHONG,Ning MA,Di SHI,Yi SONG. Injury mortality among Chinese aged 5 to 24 years from 1990 to 2019 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 498-504. |
|
||