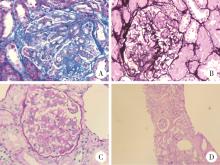
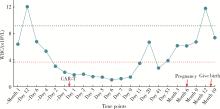
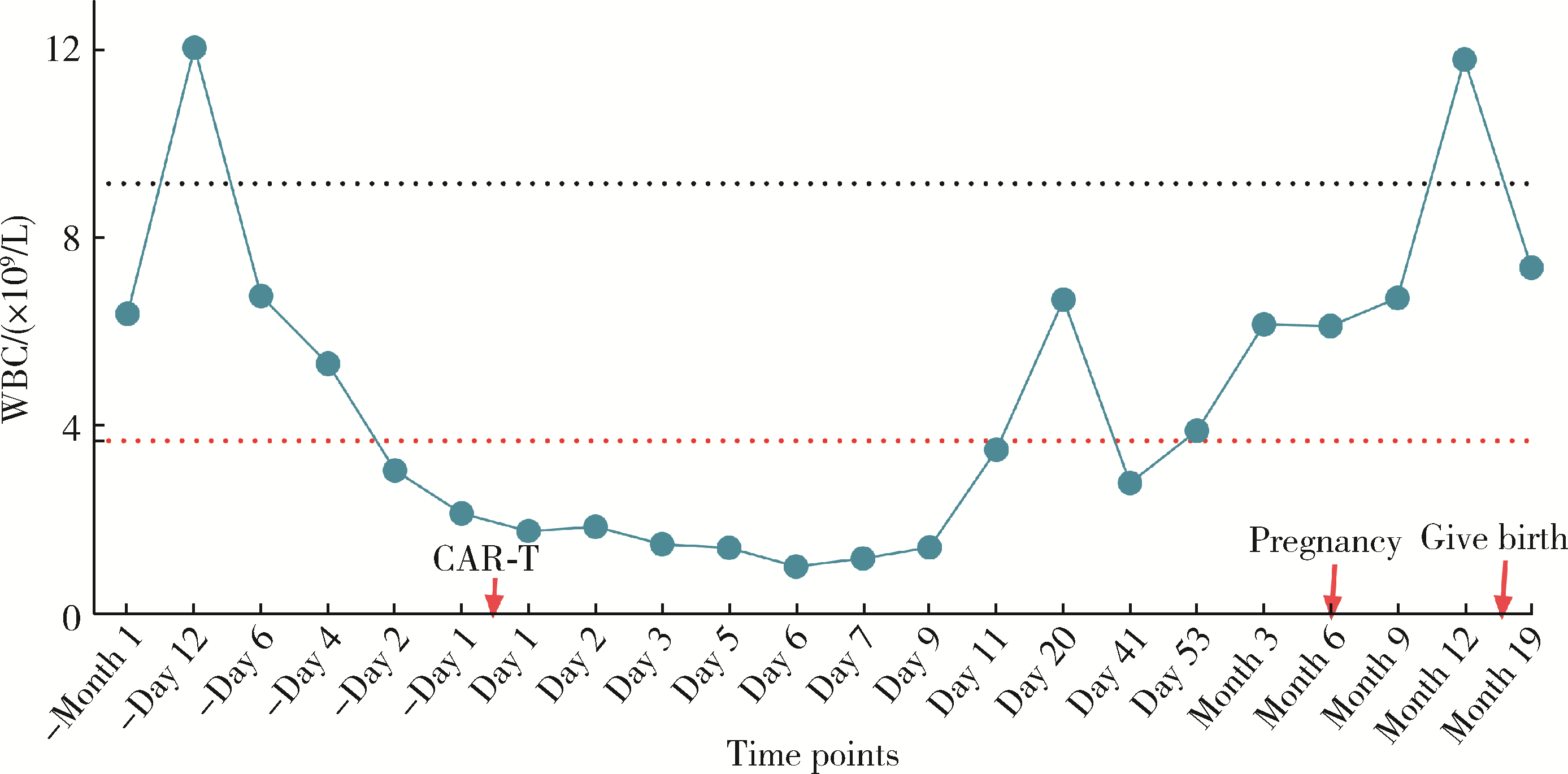
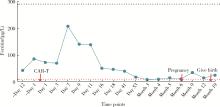
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 1119-1125. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.029
Previous Articles Next Articles
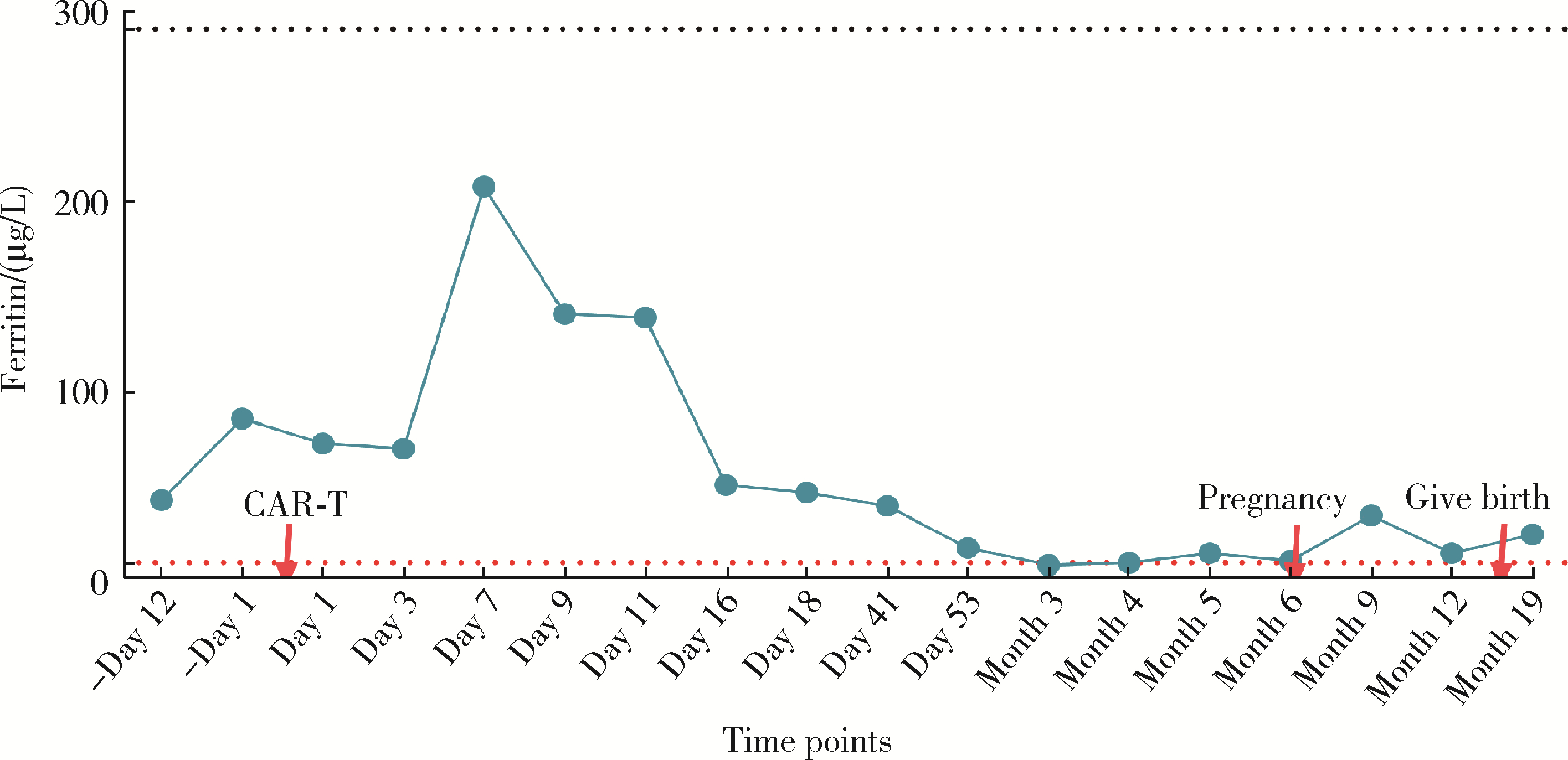
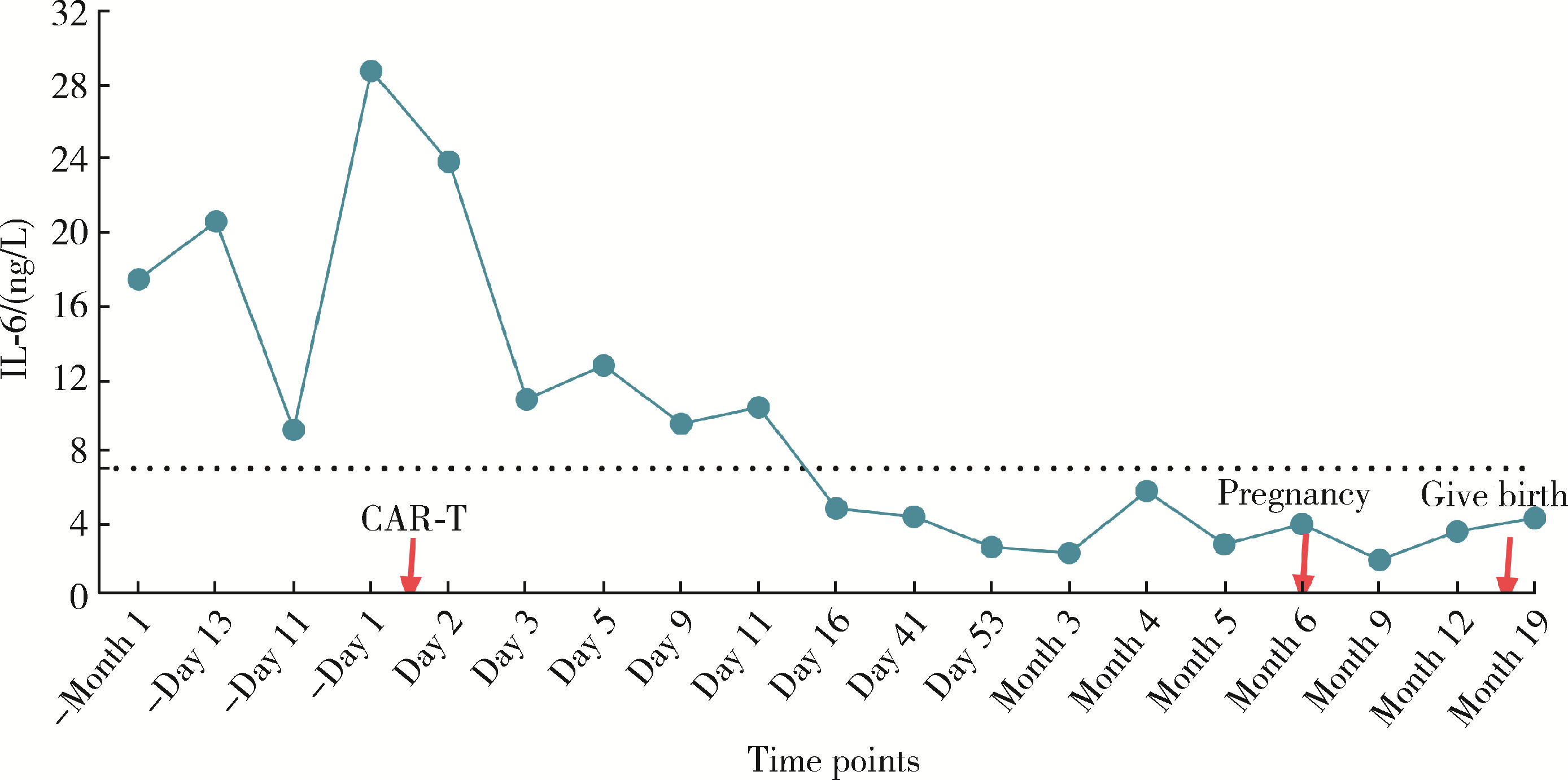
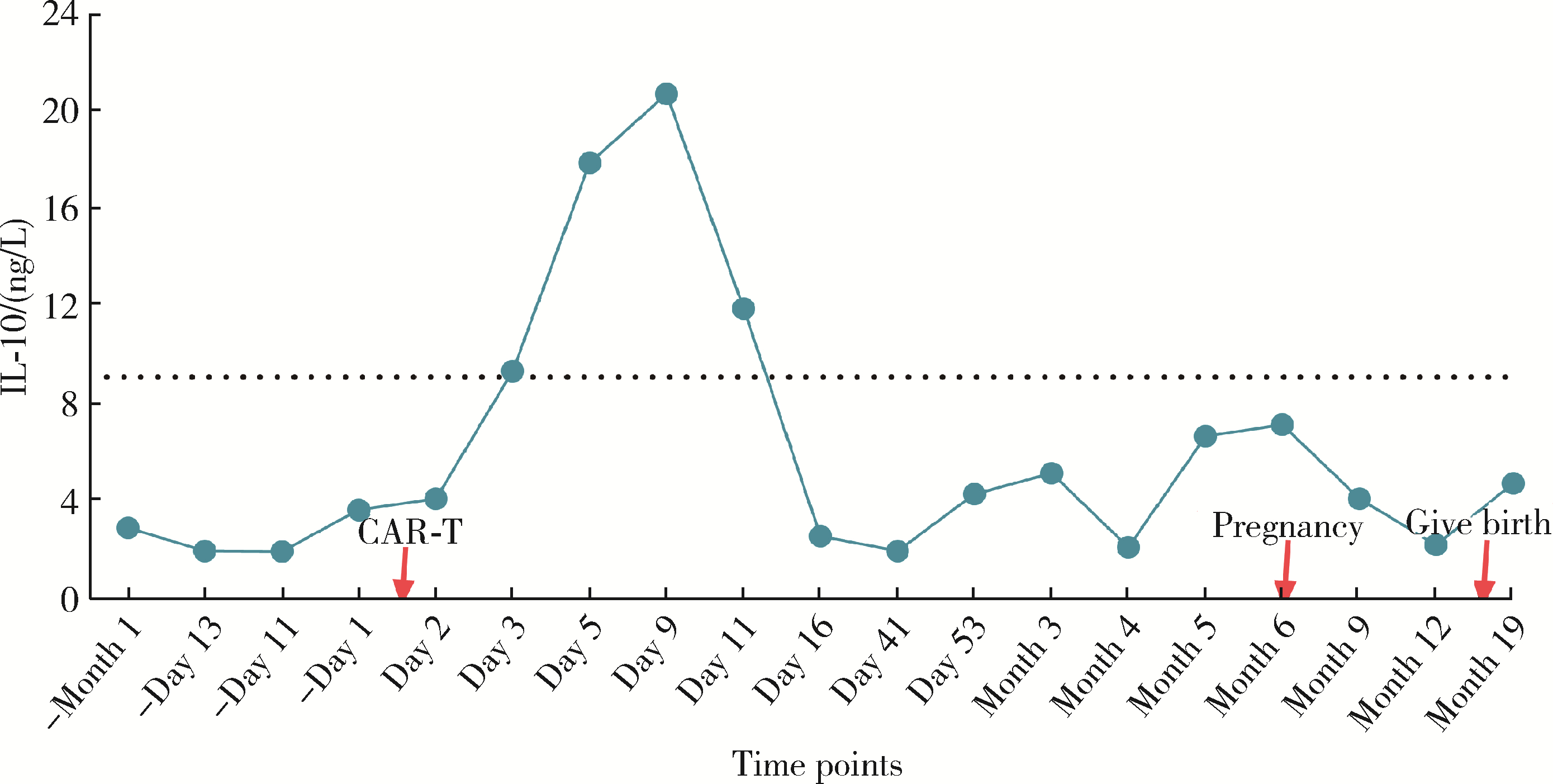
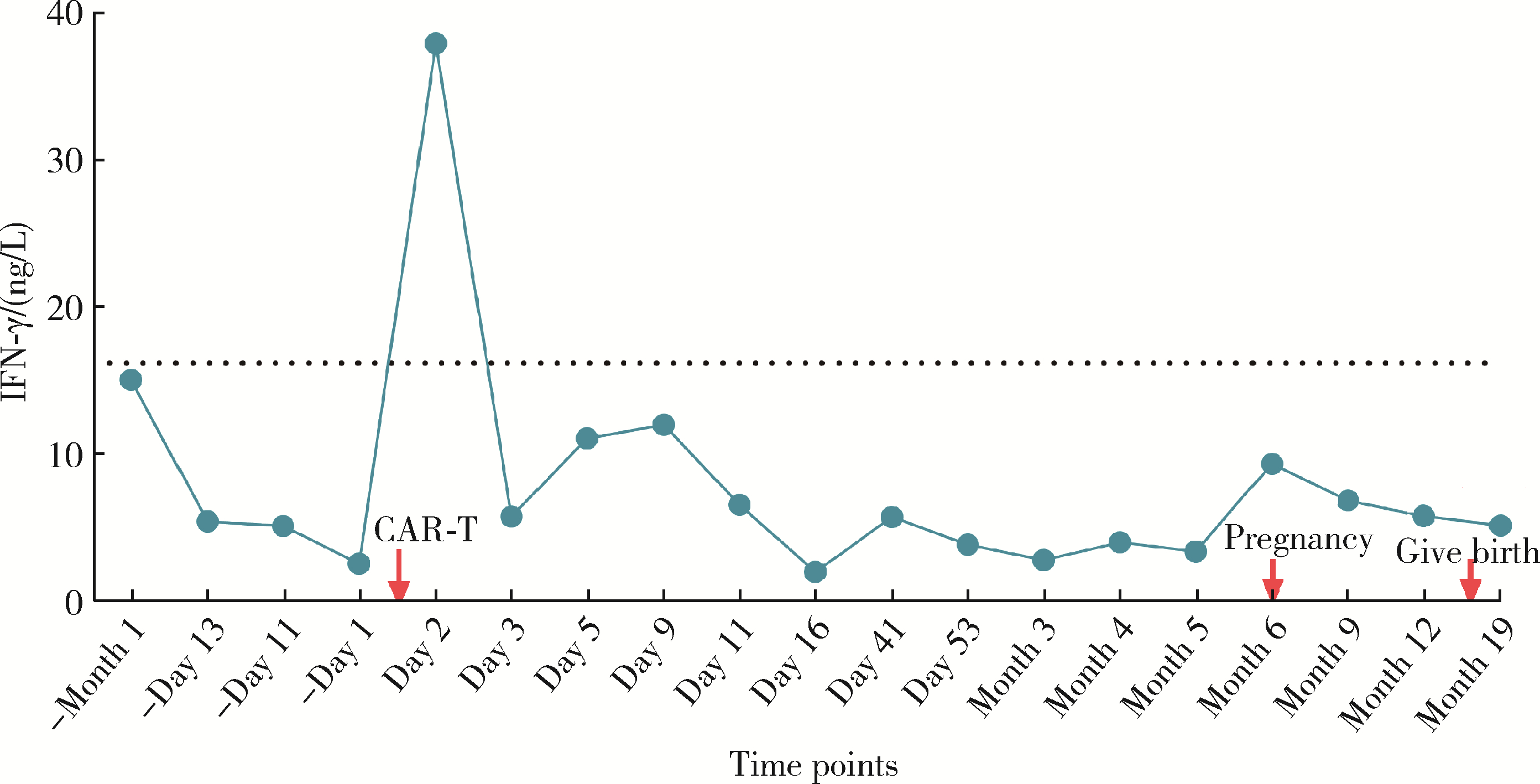
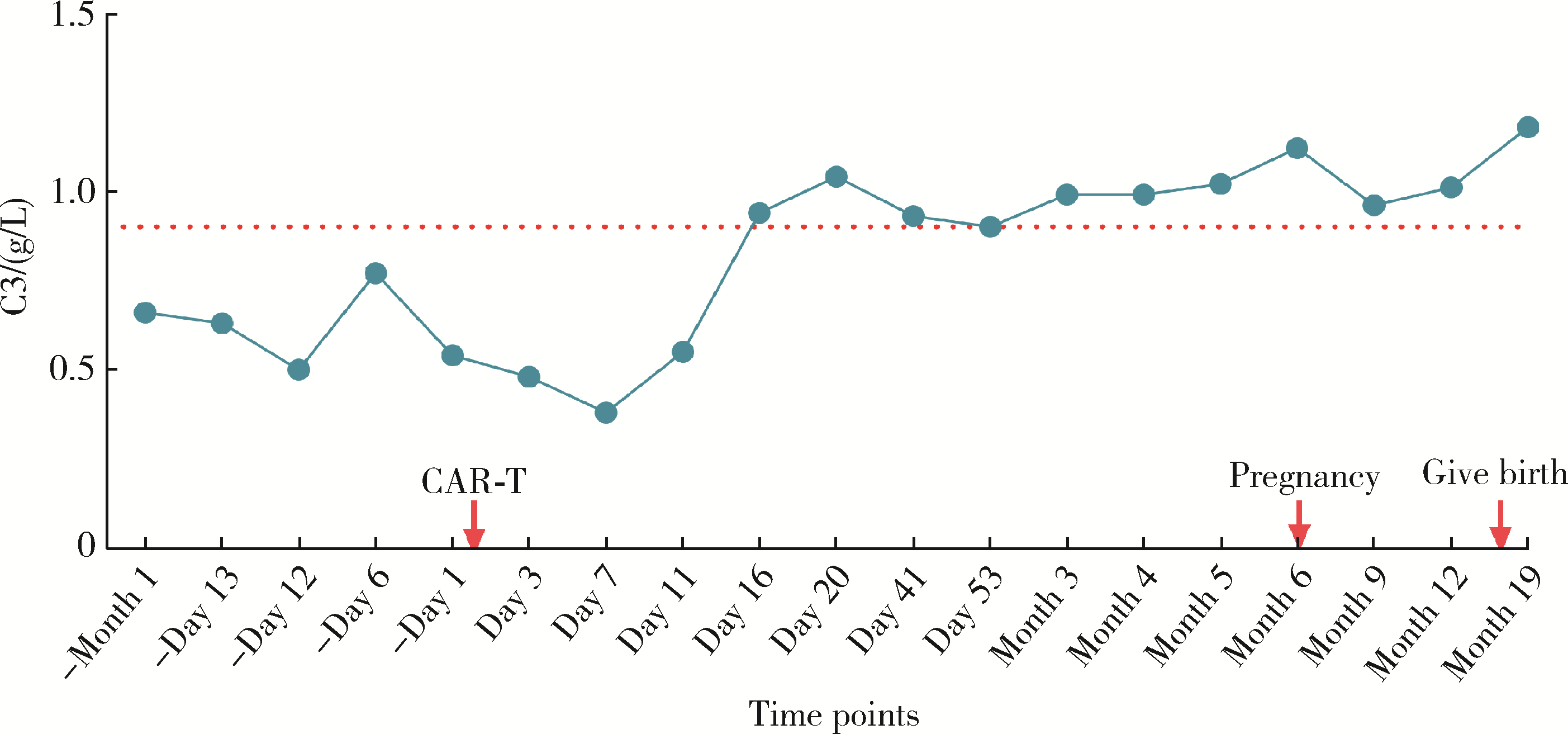
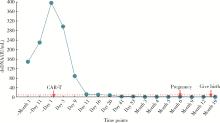
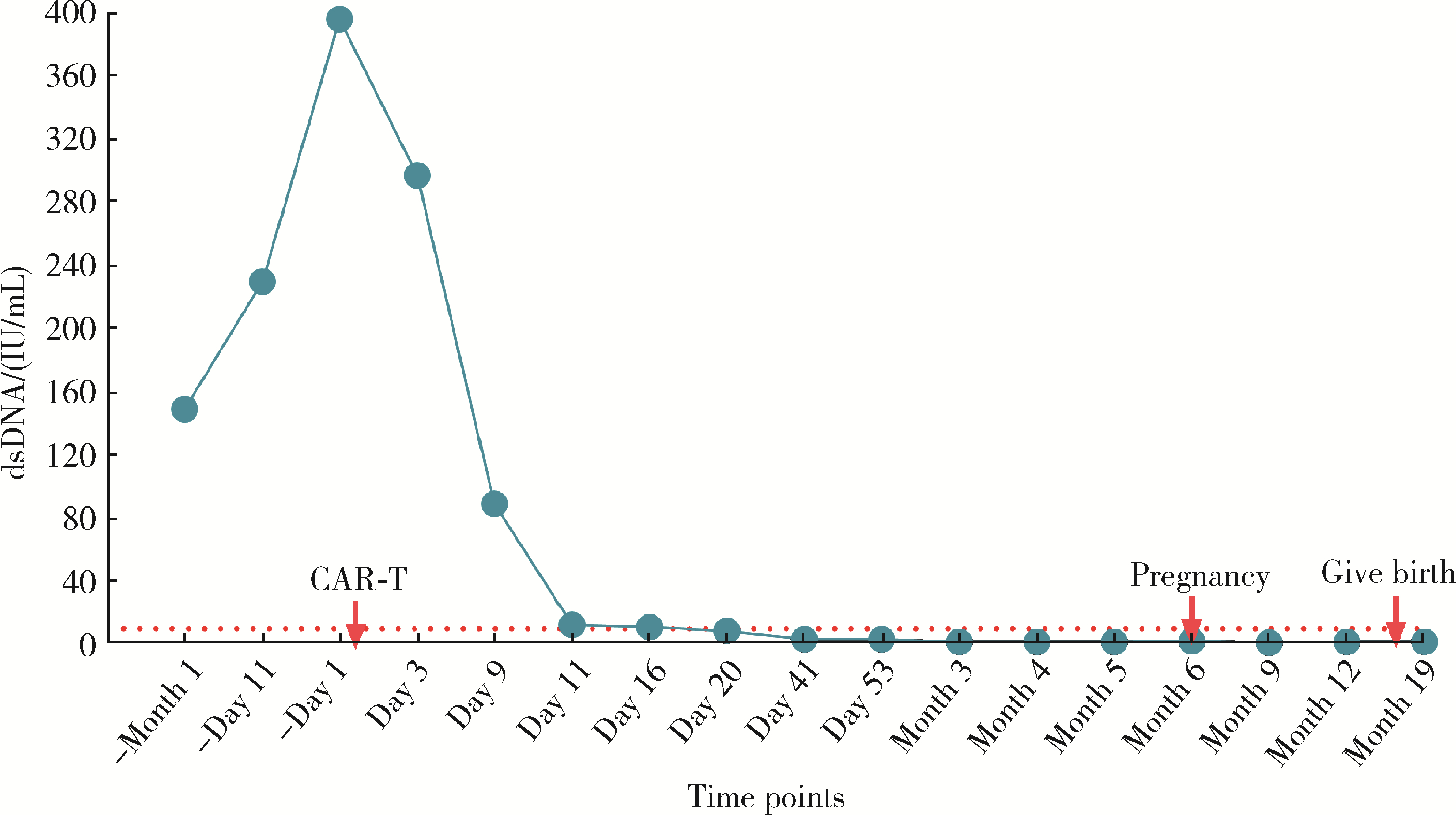
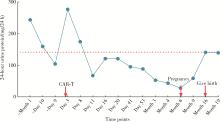
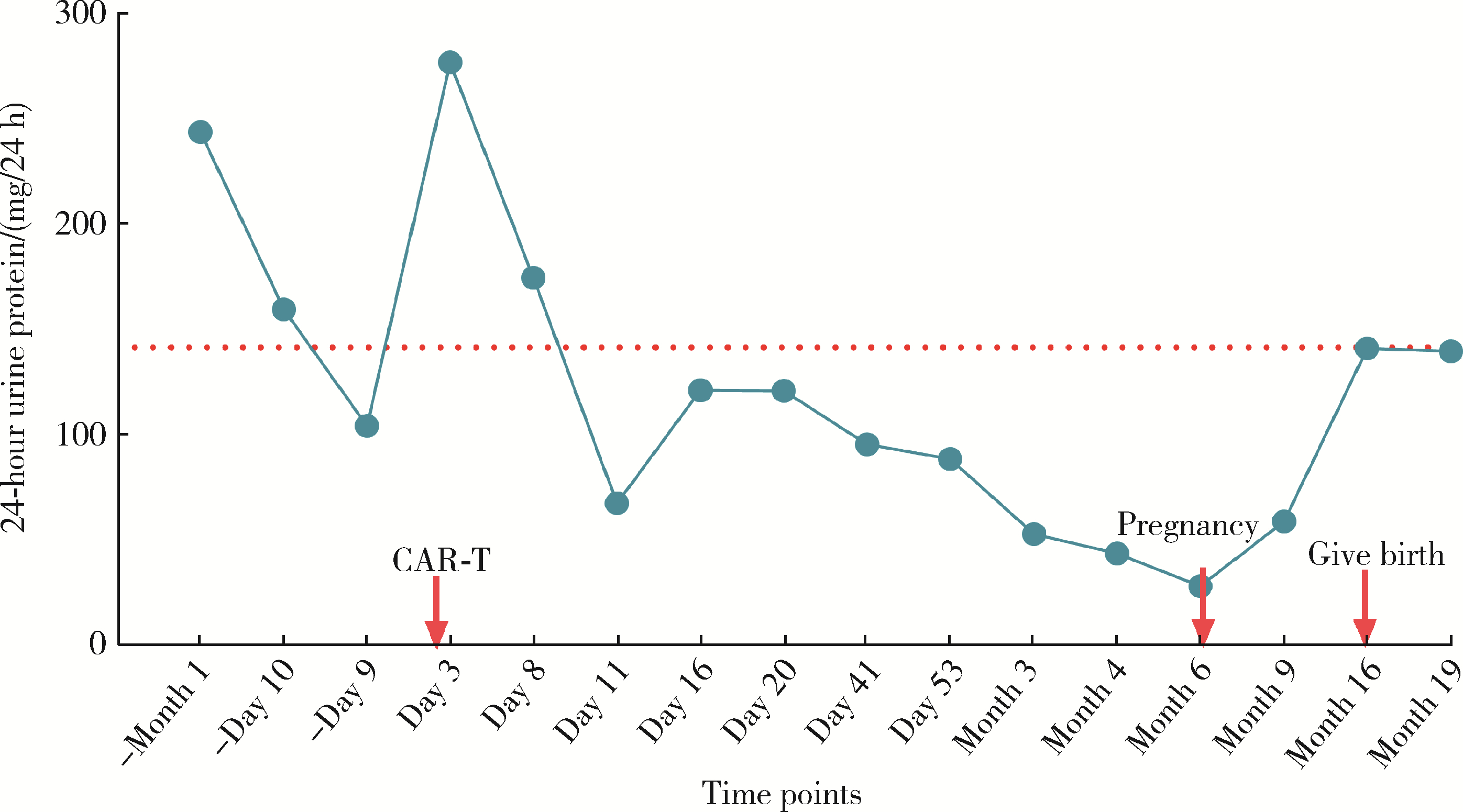
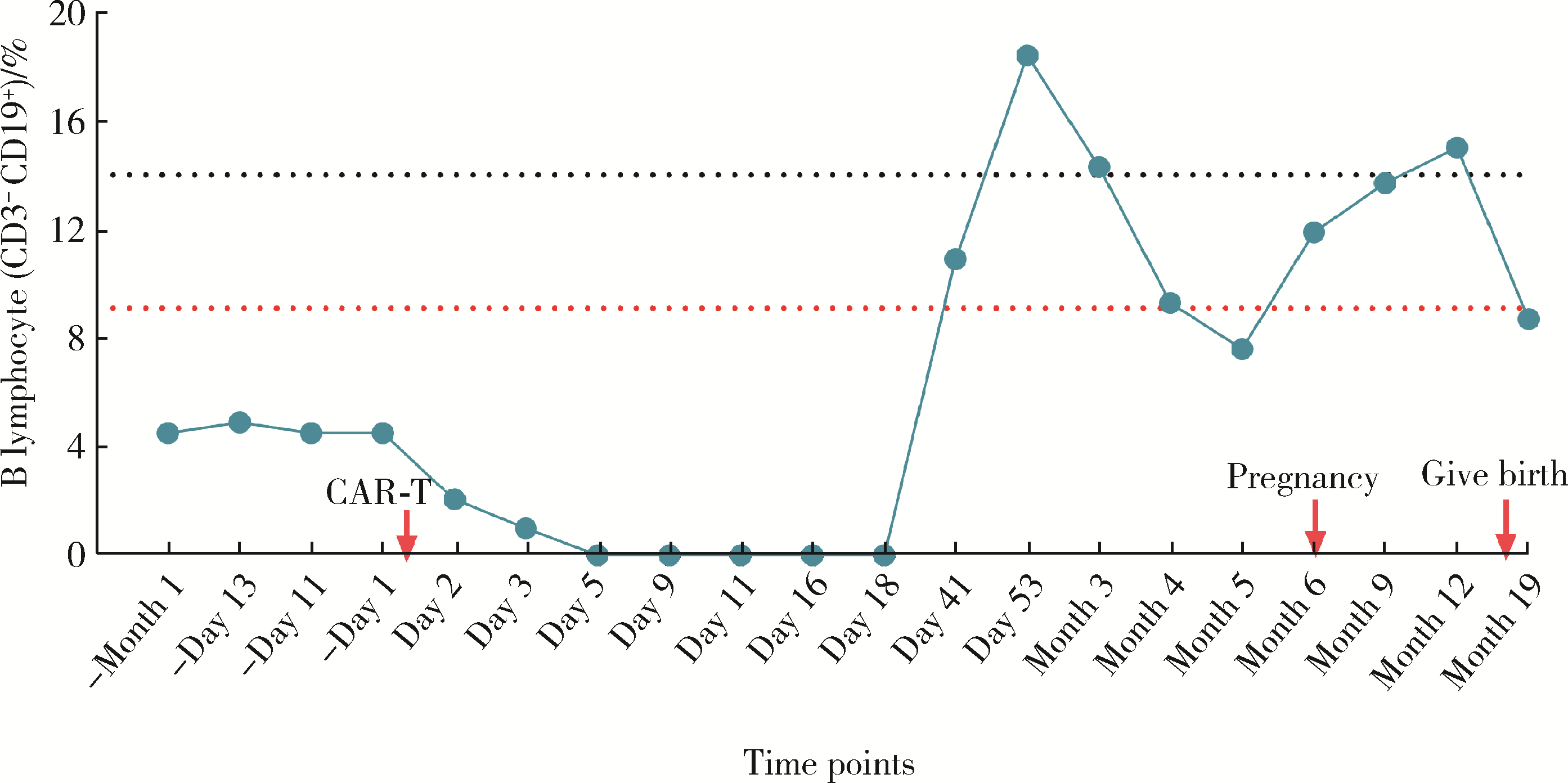
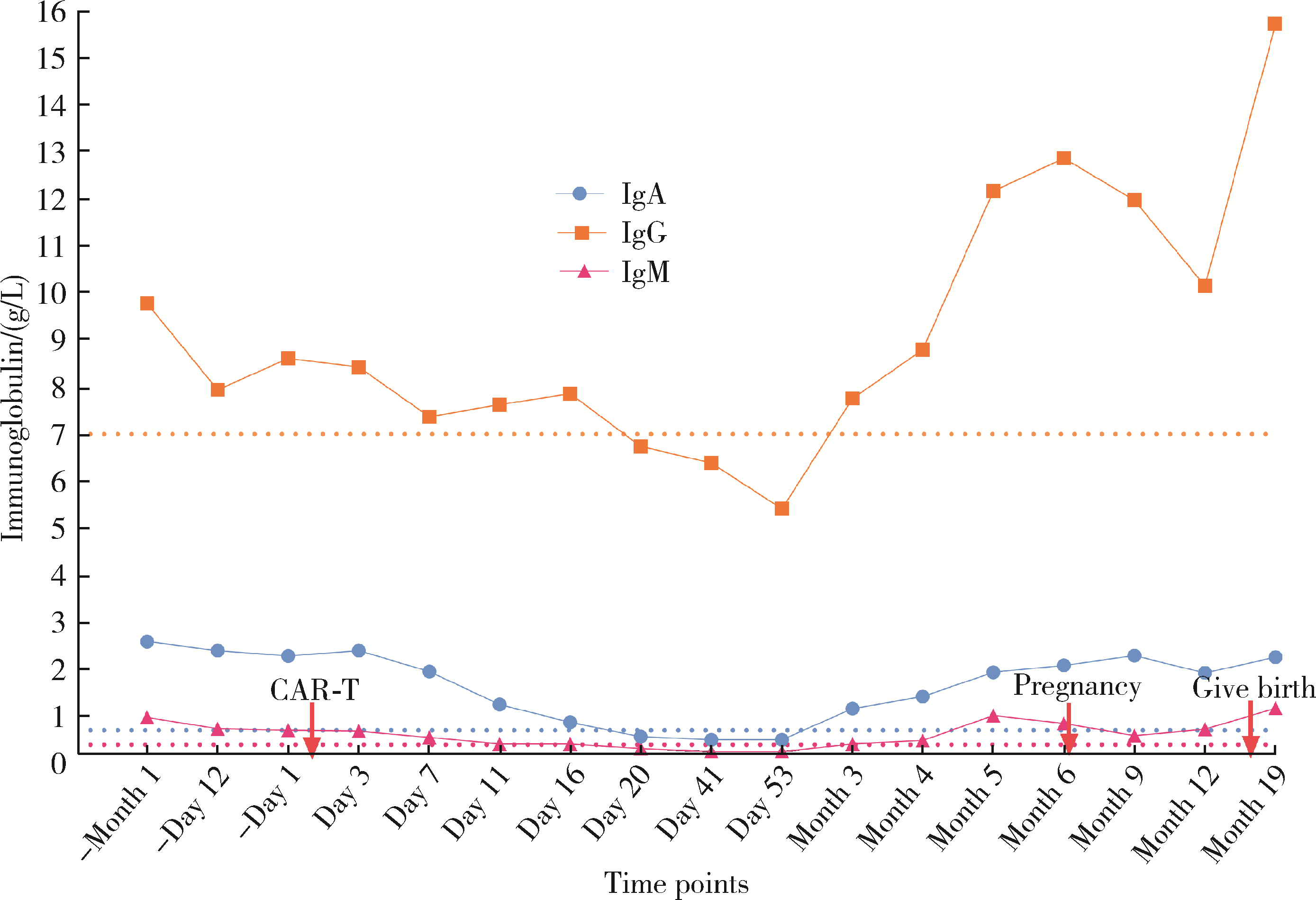
Safe pregnancy and delivery in a female patient with systemic lupus erythematosus after discontinuation of dual-target chimeric antigen receptor T cells therapy
Mingxia WANG1, Ling DING1, Min WANG1, Chanjuan ZOU1, Siyu YAN1, Yingwen LIANG2, Weijia WANG2, Shanzhi HE1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Zhong-shan People' s Hospital, Zhongshan 528403, Guangdong, China
2. Department of Advanced Diagnostic and Clinical Medicine, Zhong-shan People' s Hospital, Zhongshan 528403, Guangdong, China
CLC Number:
- R593.241
| 1 |
Zen M , Gatto M , Depascale R , et al. Early and late response and glucocorticoid-sparing effect of belimumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with joint and skin manifestations: Results from the belimumab in real life setting study-joint and skin (BeRLiSS-JS)[J]. J Pers Med, 2023, 13 (4): 691.
doi: 10.3390/jpm13040691 |
| 2 |
Van Schaik M , Arends EJ , Soonawala D , et al. Efficacy of belimumab combined with rituximab in severe systemic lupus erythematosus: Study protocol for the phase 3, multicenter, randomized, open-label synbiose 2 trial[J]. Trials, 2022, 23 (1): 939.
doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06874-w |
| 3 |
Schuster SJ , Svoboda J , Chong EA , et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells in refractory B-cell lymphomas[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377 (26): 2545- 2554.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1708566 |
| 4 |
Müller F , Taubmann J , Bucci L , et al. CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in autoimmune disease: A case series with follow-up[J]. N Engl J Med, 2024, 390 (8): 687- 700.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2308917 |
| 5 |
Salazar-Camarena DC , Ortiz-Lazareno PC , Cruz A , et al. Asso-ciation of BAFF, APRIL serum levels, BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA expression on peripheral B-cell subsets with clinical manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2016, 25 (6): 582- 592.
doi: 10.1177/0961203315608254 |
| 6 |
Wang W , He S , Zhang W , et al. BCMA-CD19 compound CAR T cells for systemic lupus erythematosus: A phase 1 open-label clinical trial[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2024, 83 (10): 1304- 1314.
doi: 10.1136/ard-2024-225785 |
| 7 |
Wang JY , Wang L . CAR-T cell therapy: Where are we now, and where are we heading?[J]. Blood Sci, 2023, 5 (4): 237- 248.
doi: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000173 |
| 8 |
Mackensen A , Müller F , Mougiakakos D , et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Nat Med, 2022, 28 (10): 2124- 2132.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02017-5 |
| [1] | Hongyan WANG, Xinming LI, Kechi FANG, Huaqun ZHU, Rulin JIA, Jing WANG. Analysis of characteristics related to the disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus and construction of an evaluation model [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1017-1022. |
| [2] | Dandan CHEN, Yun LI, Qingyi LU, Xiaohong XIANG, Feng SUN, Yingni LI, Jing ZHAO, Hongyan WANG, Chun LI. Ovarian function in patients of childbearing age with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1023-1028. |
| [3] | Li WANG, Chao GAO, Huanhuan REN, Yanping SHEN, Xiaowei HUANG, Hong YAO, Dandan HAN. Current status and influential factors of self-management ability in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1029-1035. |
| [4] | Jing CHAI, Yue WANG, Rong MU, Jinxia ZHAO. Systemic lupus erythematosus involving the fornix column leading to hyponatremia: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1115-1118. |
| [5] | Zhihui WU, Mingzhi HU, Qiaoying ZHAO, Fengfeng LV, Jingying ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Yongfu WANG, Xiaolin SUN, Hui WANG. Immunomodulatory mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-125b-5p in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [6] | Limin REN,Chuchu ZHAO,Yi ZHAO,Huiqiong ZHOU,Liyun ZHANG,Youlian WANG,Lingxun SHEN,Wenqiang FAN,Yang LI,Xiaomei LI,Jibo WANG,Yongjing CHENG,Jiajing PENG,Xiaozhen ZHAO,Miao SHAO,Ru Li. Low disease activity and remission status of systemic lupus erythematosus in a real-world study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [7] | Xiang-ge ZHAO,Jia-qing LIU,Hui-na HUANG,Zhi-min LU,Zi-ran BAI,Xia LI,Jing-jing QI. Interferon-α mediating the functional damage of CD56dimCD57+natural killer cells in peripheral blood of systemic lupus erythematosuss [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 975-981. |
| [8] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [9] | Zhi-jun LUO,Jia-jia WU,You SONG,Chun-li MEI,Rong DU. Systemic lupus erythematosus associated macrophage activation syndrome with neuropsychiatric symptoms: A report of 2 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1111-1117. |
| [10] | Miao SHAO,Hui-fang GUO,Ling-yan LEI,Qing ZHAO,Yan-jie DING,Jin LIN,Rui WU,Feng YU,Yu-cui LI,Hua-li MIAO,Li-yun ZHANG,Yan DU,Rui-ying JIAO,Li-xia PANG,Li LONG,Zhan-guo LI,Ru LI. A multicenter study on the tolerance of intravenous low-dose cyclophosphamide in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1112-1116. |
| [11] | Min LI,Lin-qing HOU,Yue-bo JIN,Jing HE. Clinical and immunological characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus with retinopathy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1106-1111. |
| [12] | Lin-qi ZHANG,Jing ZHAO,Hong-yan WANG,Zong-yi WANG,Ying-ni LI,Ji-yang TANG,Si-ying LI,Jin-feng QU,Ming-wei ZHAO. Relationship between anti-ENO1 antibody and systemic lupus erythematosus patients with retinopathy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1099-1105. |
| [13] | Jian-mei ZOU,Li-jun WU,Cai-nan LUO,Ya-mei SHI,Xue WU. Relationship of serum 25- hydroxy vitamin D and systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 938-941. |
| [14] | XIA Fang-fang,LU Fu-ai,LV Hui-min,YANG Guo-an,LIU Yuan. Clinical characteristics and related factors of systemic lupus erythematosus with interstitial pneumonia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 266-272. |
| [15] | Yan GENG,Bo-rui LI,Zhuo-li ZHANG. Musculoskeletal ultrasound findings of symptomatic joints in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2020, 52(1): 163-168. |
|
||