Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 875-883. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
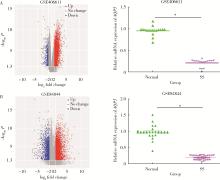
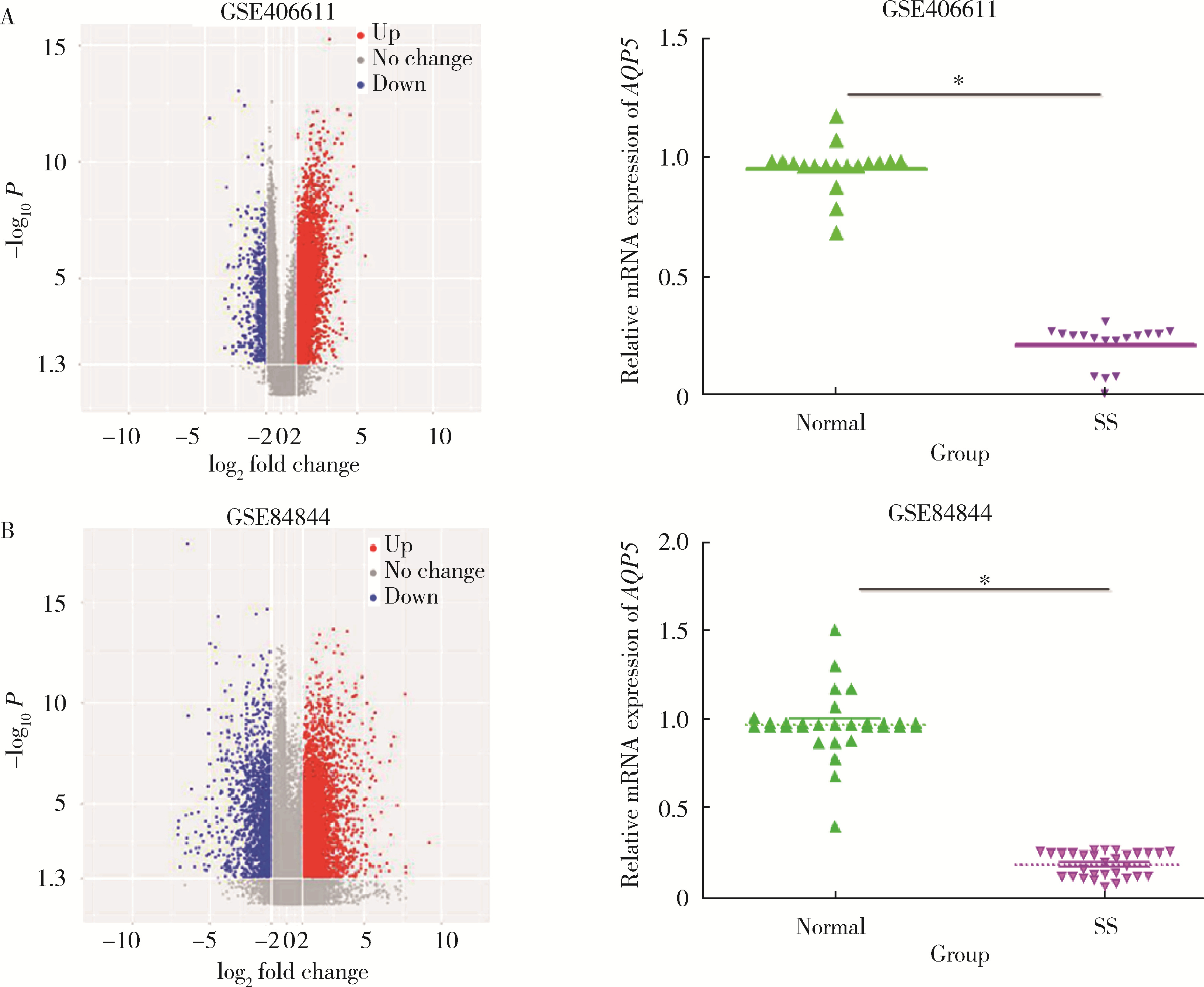
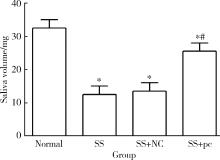
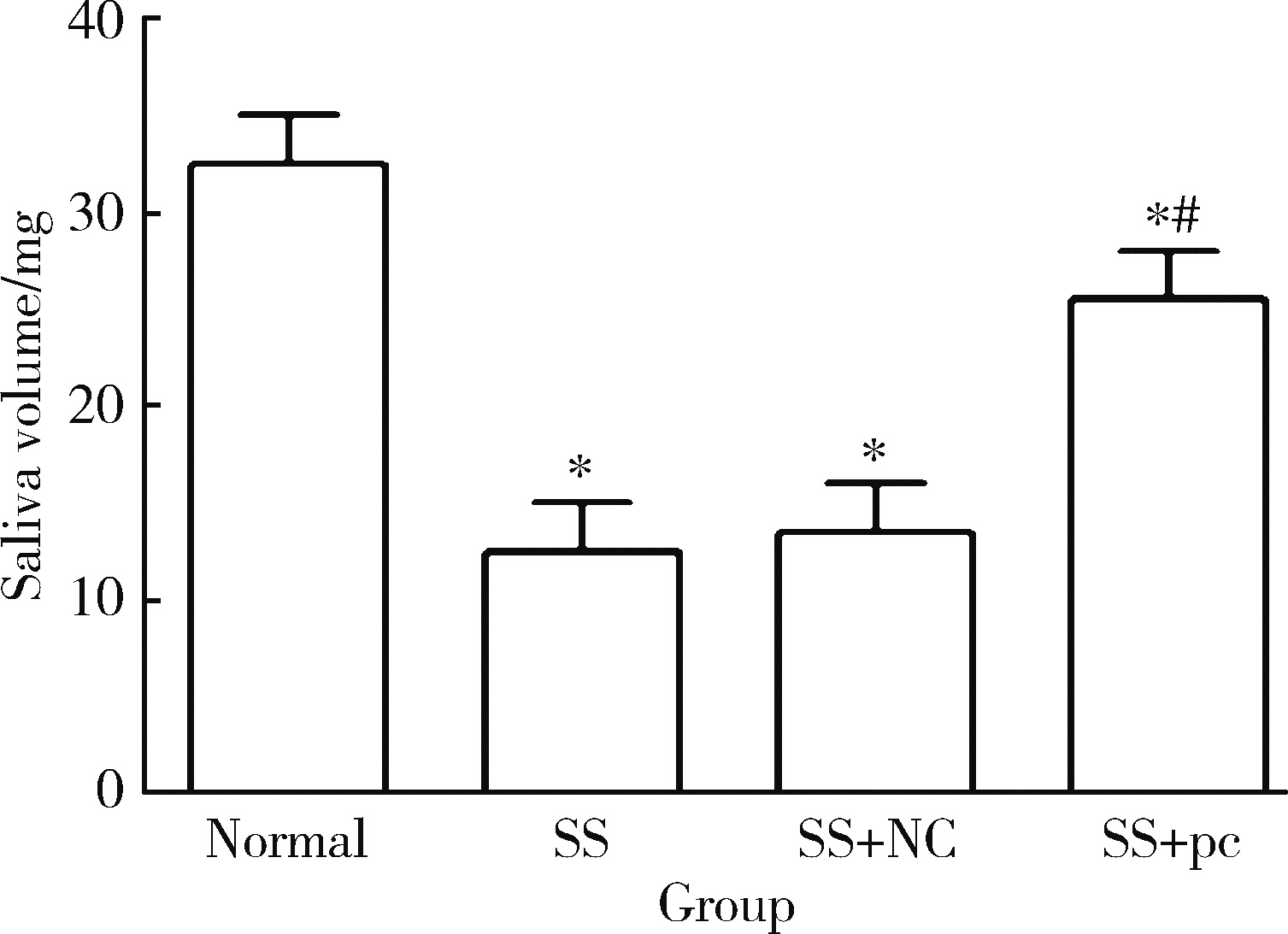
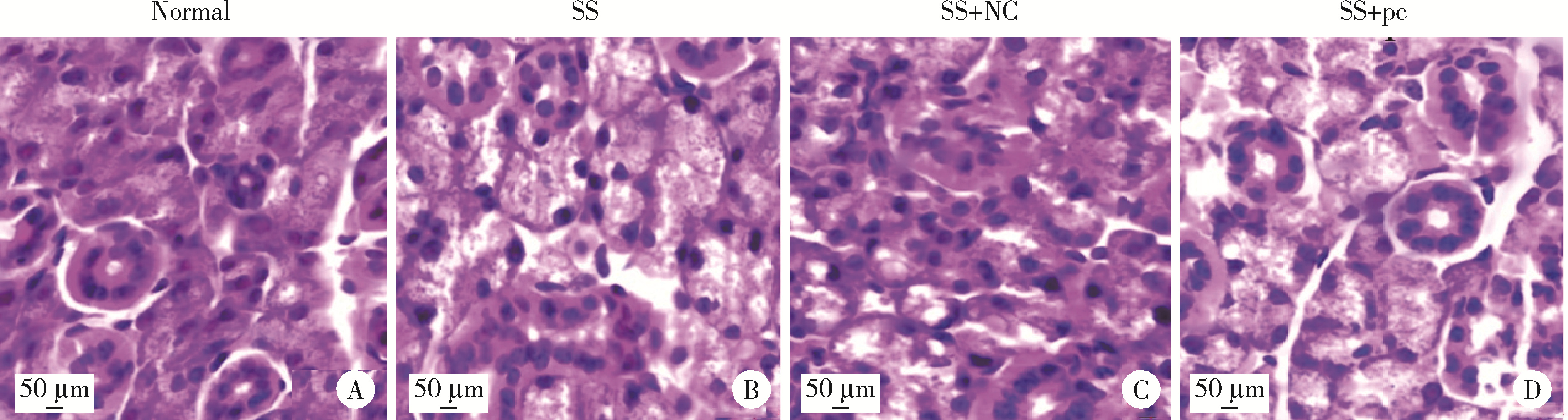
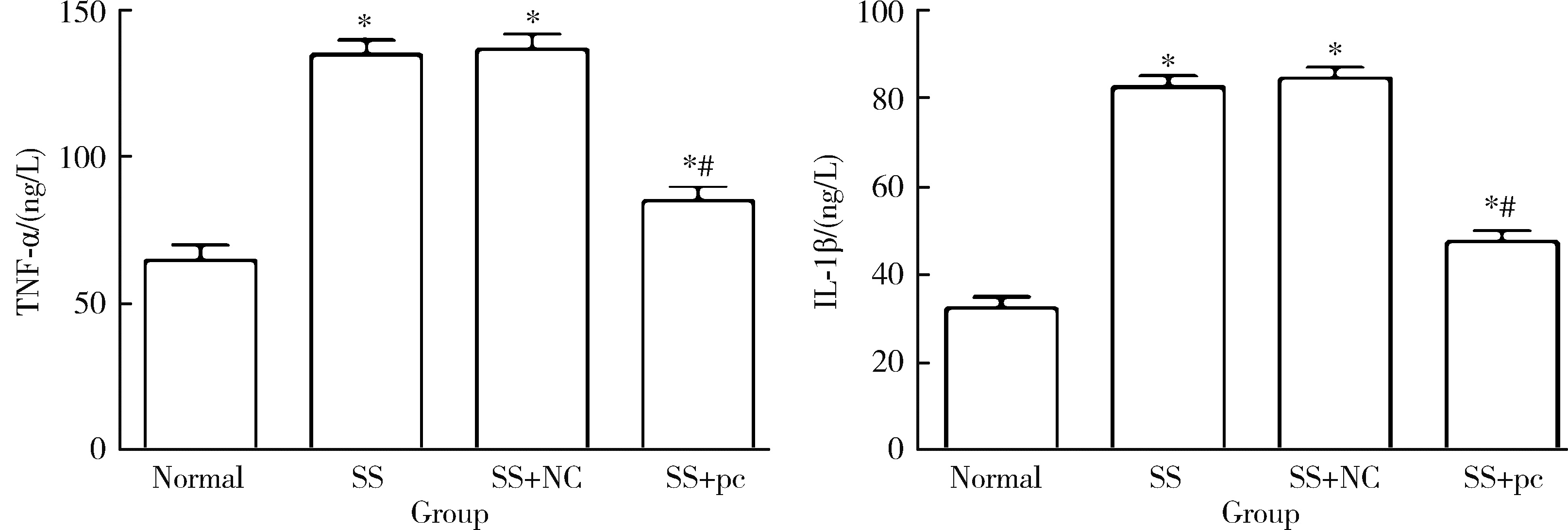
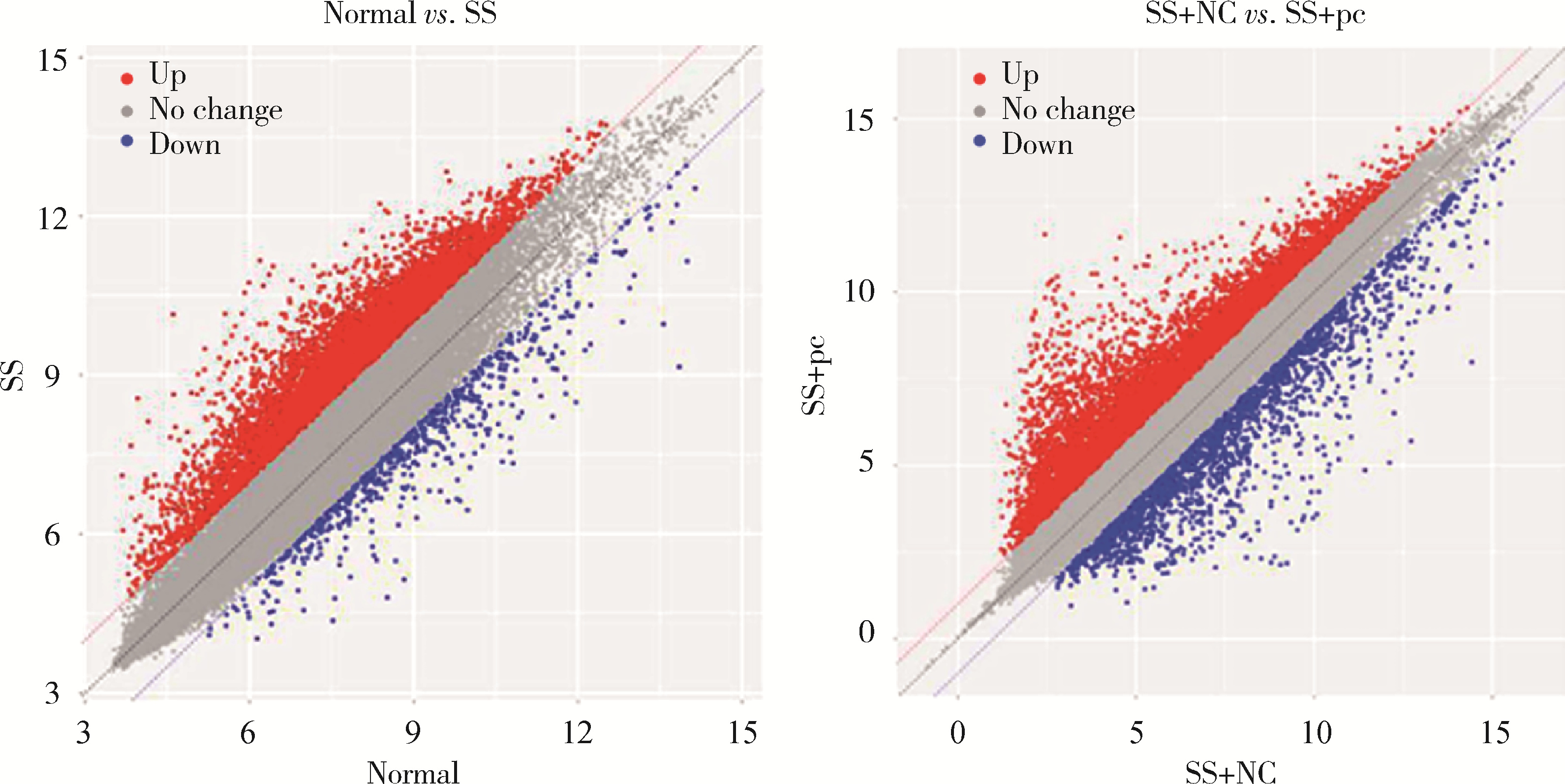
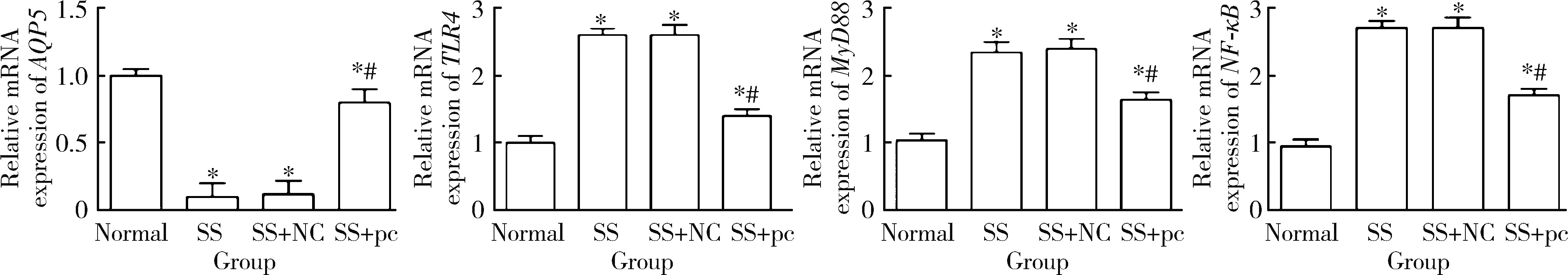
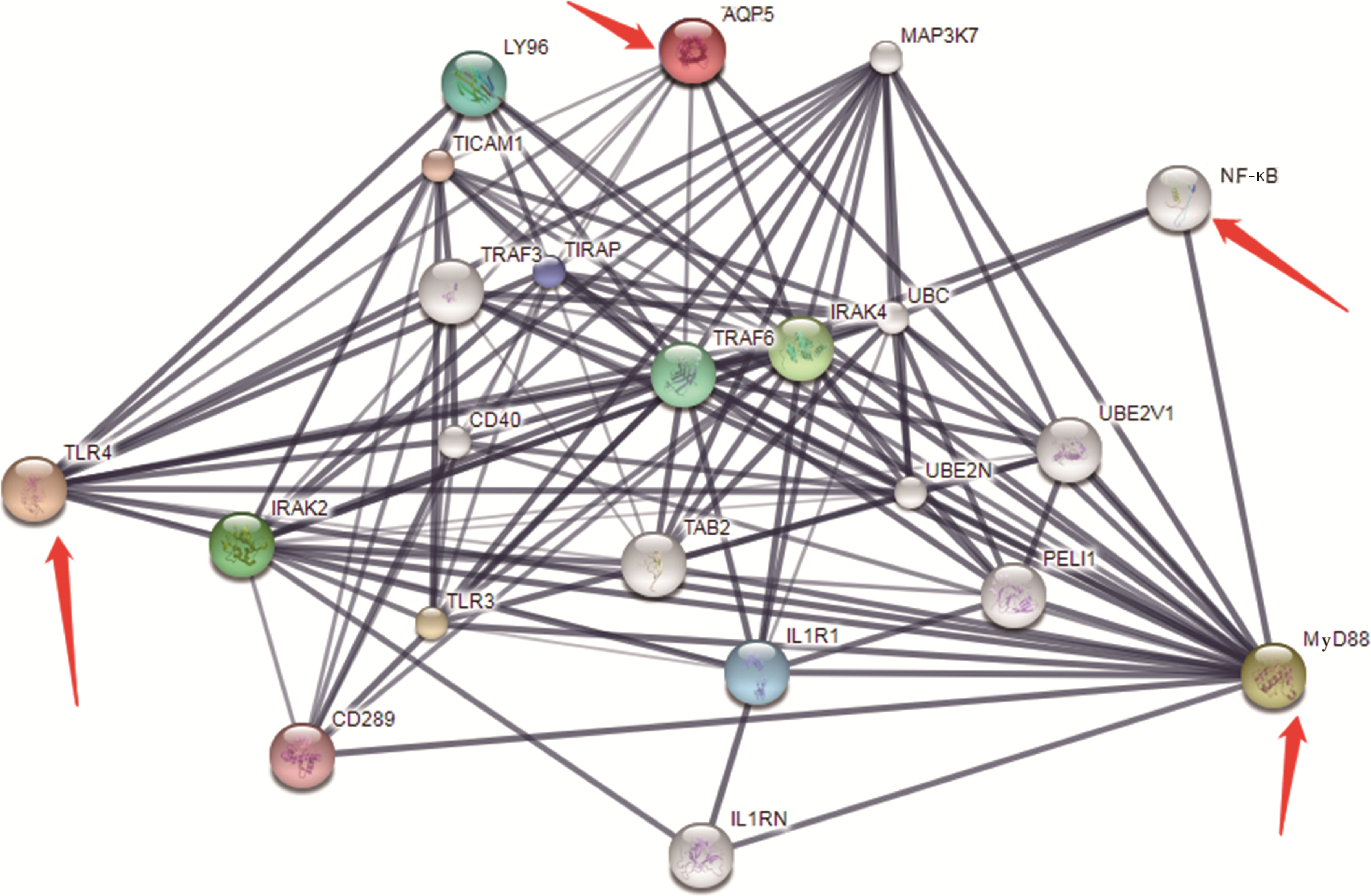
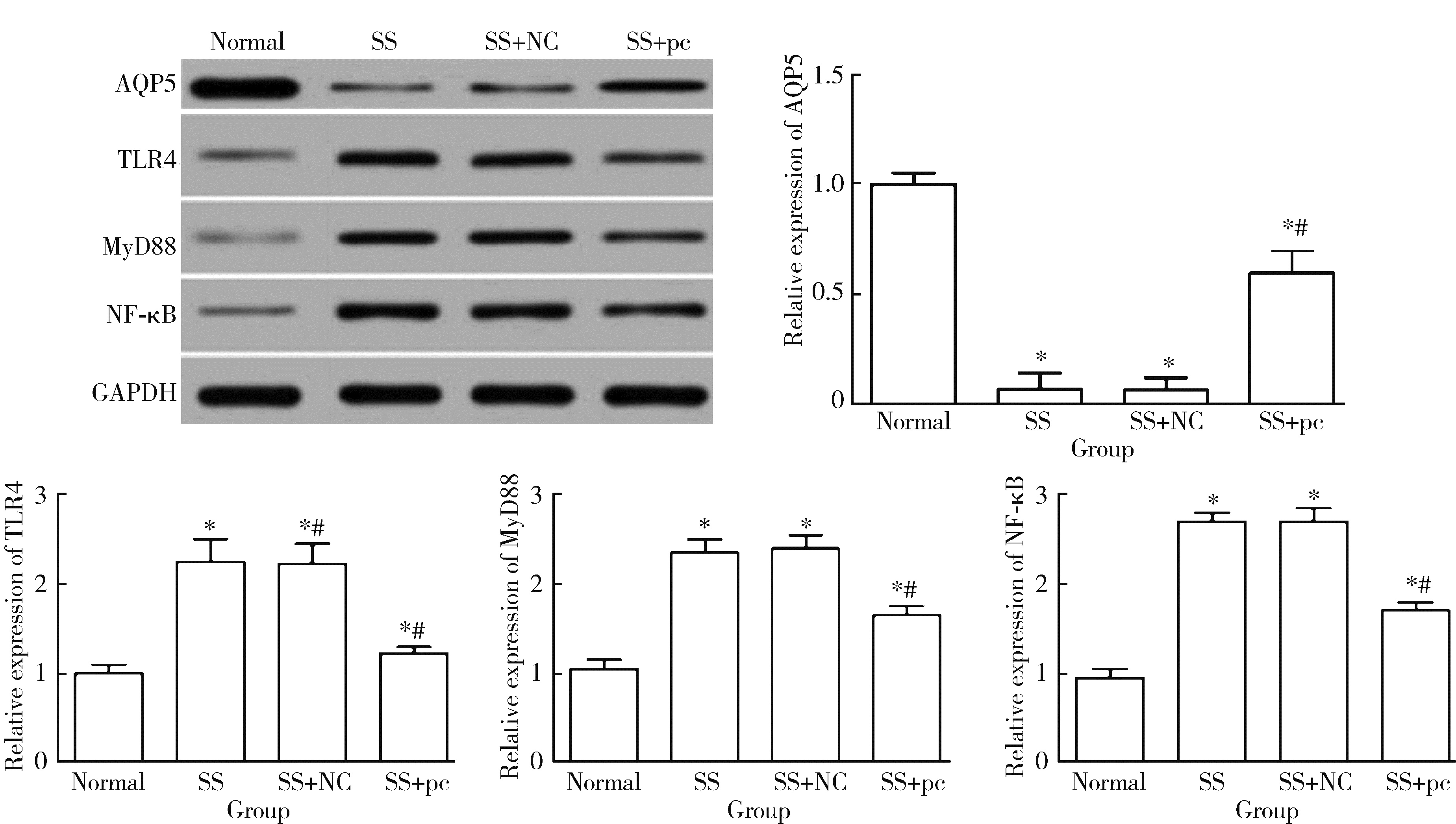
Effect of aquaporin 5 on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in Sjögren syndrome rats
Lixiu ZHU1, Renli CHEN1,*( ), Sujuan ZHOU2, Ye LIN1, Yirong TANG1, Zhen YE1
), Sujuan ZHOU2, Ye LIN1, Yirong TANG1, Zhen YE1
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Ningde Hospital Affiliated to Ningde Normal University/Ningde Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Ningde 352100, Fujian, China
2. Department of Pathology, Ningde Hospital Affiliated to Ningde Normal University/Ningde Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Ningde 352100, Fujian, China
CLC Number:
- R593.2
| 1 |
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key329 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key330 |
| 3 |
李永明, 薛鸾. AQP5在干燥综合征发病机制中的作用[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2019, 37(10): 2369- 2372.
|
| 4 |
doi: 10.3390/ijms22179213 |
| 5 |
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102756 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00605-2 |
| 7 |
梅寒颖, 刘炬, 汤曾耀. 基于TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路探讨白芍总苷抑制干燥综合征模型小鼠炎症的作用机制[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2021, 32(9): 1293- 1299.
|
| 8 |
宋维海, 李琴, 茅建春. 一贯煎对干燥综合征模型大鼠及颌下腺PI3K/Akt/eNOS通路的影响[J]. 中药材, 2020, 43(7): 1721- 1725.
|
| 9 |
王信, 王健, 郭文静, 等. 原发性干燥综合征患者肠道菌群特点分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(7): 949- 957.
|
| 10 |
黄诗怡, 周广文, 朱伟, 等. 补肾化痰方对OVX诱导的骨质疏松大鼠血清LPS及TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2021, 27(9): 70- 76.
|
| 11 |
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa410 |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00812-z |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1177/00220345211003490 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1007/s11655-020-3205-5 |
| 15 |
doi: 10.3390/cells10082108 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102867 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.1007/s12016-020-08793-7 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2019-0337 |
| [1] | Tianjiao HOU,Zhibo ZHOU,Zhuqing WANG,Mengying WANG,Siyue WANG,Hexiang PENG,Huangda GUO,Yixin LI,Hanyu ZHANG,Xueying QIN,Yiqun WU,Hongchen ZHENG,Jing LI,Tao WU,Hongping ZHU. Gene-gene/gene-environment interaction of transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway and the risk of non-syndromic oral clefts [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 384-389. |
| [2] | Jing ZHANG,Jia-gui SONG,Zhen-bin WANG,Yu-qing GONG,Tian-zhuo WANG,Jin-yu ZHOU,Jun ZHAN,Hong-quan ZHANG. Kindlin-2 regulates endometrium development via mTOR and Hippo signaling pathways in mice [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 846-852. |
| [3] | Meng-ying WANG,Wen-yong LI,Ren ZHOU,Si-yue WANG,Dong-jing LIU,Hong-chen ZHENG,Zhi-bo ZHOU,Hong-ping ZHU,Tao WU,Yong-hua HU. Association study between haplotypes of WNT signaling pathway genes and nonsyndromic oral clefts among Chinese Han populations [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 394-399. |
| [4] | Meng-ying WANG,Wen-yong LI,Ren ZHOU,Si-yue WANG,Dong-jing LIU,Hong-chen ZHENG,Jing LI,Nan LI,Zhi-bo ZHOU,Hong-ping ZHU,Tao WU,Yong-hua HU. Evaluating the effect of WNT pathway genes considering interactions on the risk of non-syndromic oral clefts among Chinese populations [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 815-820. |
| [5] | Yan XUAN,Yu CAI,Xiao-xuan WANG,Qiao SHI,Li-xin QIU,Qing-xian LUAN. Effect of Porphyromonas gingivalis infection on atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein-E knockout mice [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 743-749. |
| [6] | Nan WU,Xiu-li ZHANG,Yun HOU,Li-xing LIN,Xiao-bing ZHANG. Effect of methyl eugenol on nasal mucosal aquaporin 5 in rats with allergic rhinitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1036-1041. |
| [7] | WANG Hao, CHEN Liang, YE Xiao-yun. Triptolide induces oxidative stress and apoptosis and activates PIK3/Akt signaling pathway in TM4 sertoli cells [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 607-612. |
| [8] | ZHU Yan,SHI Yong-jin,ZHAO Yu-liang, ZHU Ping. Topoisomerase inhibitor upregulates MICA/B expression in breast cancer cells through ATM/ATR and NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 318-325. |
| [9] | HU Xiao-sheng, HUANG Yun-hui, LIU Xiao-song, HUA Hong. Expression and significance of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell cacinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 310-315. |
|
||