Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 959-963. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
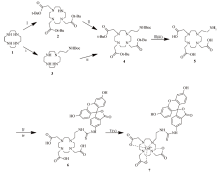
Improved synthesis process of optical-magnetic bimodal probe of Gd-[4,7-Bis-carboxymethyl-10-(2-fluoresceinthioureaethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraaza-cyclododec-1-yl]-acetic acid complexes
Hui SHENG1,2,3,Lei LIANG4,Tong-liang ZHOU4,Yan-xing JIA4,Tong WANG1,2,3,Lan YUAN1,2,∆( ),Hong-bin HAN3,5,∆(
),Hong-bin HAN3,5,∆( )
)
- 1. Department of Chemical Biology, Peking University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Beijng 100191, China
2. Peking University Medical and Health Analysis Center, Beijng 100191, China
3. Beijing Key Lab of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Device and Technique, Beijing 100191, China
4. Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Peking University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Beijng 100191, China
5. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R914
| [1] |
Han HB, Li K, Yan JH, et al. An in vivo study with an MRI tracer method reveals the biophysical properties of interstitial fluid in the rat brain[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2012,55(9):782-787.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-012-4361-4 pmid: 23015126 |
| [2] |
Han H, Shi C, Fu Y, et al. A novel MRI tracer-based method for measuring water diffusion in the extracellular space of the rat brain[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2014,18(3):978-983.
doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2014.2308279 pmid: 24808229 |
| [3] | 和清源, 韩鸿宾, 许方婧伟, 等. Gd-DTPA磁共振成像示踪法对脑细胞外间隙成像与定量分析的初步研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2010,42(2):188-191. |
| [4] | 韩鸿宾. 细胞微环境成像新方法与脑分区稳态的发现[J]. 武警医学, 2016,27(4):325-328. |
| [5] |
Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, et al. Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain[J]. Science, 2013,342(6156):373-377.
doi: 10.1126/science.1241224 |
| [6] |
Mishra A, Pfeuffer J, Mishra R, et al. A new class of Gd-based DO3A- ethylamine-derived targeted contrast agents for MR and optical imaging[J]. Bioconjug Chem, 2006,17(3):773-780.
doi: 10.1021/bc050295b pmid: 16704217 |
| [7] | 李昀倩, 盛荟, 梁磊, 等. 光磁双模态分子探针Gd-DO3A-EA-FITC在脑组织间隙成像分析中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2018,50(2):221-225. |
| [8] |
Laakso J, Rosser GA, Szíjjártó C, et al. Synjournal of chlorin-sensitized near infrared-emitting lanthanide complexes[J]. Inorg Chem, 2012,51(19):10366-10374.
doi: 10.1021/ic3015354 pmid: 22978627 |
| [9] |
Junker AKR, Tropiano M, Faulkner S, et al. Kinetically inert lanthanide complexes as reporter groups for binding of potassium by 18-crown-6[J]. Inorg Chem, 2016,55(23):12299.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.6b02063 pmid: 27934409 |
| [10] | Nicholson C. Factors governing diffusing molecular signals in brain extracellular space[J]. J Neural Transm (Vienna), 2005,112(1):29-44. |
| [11] |
Sherpa AD, Van d NP, Xiao F, et al. Gliotoxin-induced swelling of astrocytes hinders diffusion in brain extracellular space via formation of dead-space microdomains[J]. Glia, 2014,62(7):1053-1065.
doi: 10.1002/glia.22661 |
| [12] |
Saghyan A, Lewis DP, Hrabe J, et al. Extracellular diffusion in laminar brain structures exemplified by hippocampus[J]. J Neurosci Methods, 2012,205(1):110-118.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.12.008 pmid: 22230768 |
| [13] |
李怀业, 赵越, 左龙, 等. 光、磁分子探针在脑组织间隙内的扩散分布规律[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2015,47(4):667-673.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2015.04.024 |
| [14] |
Dmytrenko L, Cicanic M, Anderova M, et al. The impact of alpha-syntrophin deletion on the changes in tissue structure and extracellular diffusion associated with cell swelling under physiological and pathological conditions[J]. PLoS One, 2013,8(7):e68044.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068044 pmid: 23861848 |
| [15] |
Guan X, Wang W, Wang A, et al. Brain interstitial fluid drainage alterations in glioma-bearing rats[J]. Aging Dis, 2018,9(2):228.
doi: 10.14336/AD.2017.0415 |
| [1] | Yuxuan TIAN,Mingjian RUAN,Yi LIU,Derun LI,Jingyun WU,Qi SHEN,Yu FAN,Jie JIN. Predictive effect of the dual-parametric MRI modified maximum diameter of the lesions with PI-RADS 4 and 5 on the clinically significant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [2] | Yi LIU,Chang-wei YUAN,Jing-yun WU,Qi SHEN,Jiang-xi XIAO,Zheng ZHAO,Xiao-ying WANG,Xue-song LI,Zhi-song HE,Li-qun ZHOU. Diagnostic efficacy of prostate cancer using targeted biopsy with 6-core systematic biopsy for patients with PI-RADS 5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [3] | Chang-wei YUAN,De-run LI,Zhi-hua LI,Yi LIU,Gang-zhi SHAN,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of dynamic contrast enhanced status in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer with PI-RADS 4 lesion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [4] | Ying LIU,Ran HUO,Hui-min XU,Zheng WANG,Tao WANG,Hui-shu YUAN. Correlations between plaque characteristics and cerebral blood flow in patients with moderate to severe carotid stenosis using magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [5] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [6] | Shan YE,Ping-ping JIN,Nan ZHANG,Hai-bo WU,Lin SHI,Qiang ZHAO,Kun YANG,Hui-shu YUAN,Dong-sheng FAN. Cortical thickness and cognitive impairment in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1158-1162. |
| [7] | Ying CAI,Qiao-qin WAN,Xian-jie CAI,Ya-juan GAO,Hong-bin HAN. Epidural photobiomodulation accelerates the drainage of brain interstitial fluid and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 1000-1005. |
| [8] | WANG Shu-lei,GAO Yang-xu,ZHANG Hong-wu,YANG Hai-bo,LI Hui,LI Yu,SHEN Li-xue,YAO Hong-xin. Clinical analysis of 30 cases of basal ganglia germinoma in children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 222-226. |
| [9] | ZHANG Fan,CHEN Qu,HAO Yi-chang,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and preoperative/postoperative membranous urethral length [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [10] | Yi-fan WU,Xiao-yuan ZHANG,Shuang REN,Ying-xiang YU,Cui-qing CHANG. Measurement and evaluation of the quadriceps muscle mass in young men based on magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 843-849. |
| [11] | Shi-ming ZHAO,Tie-jun YANG,Chun-miao XU,Xiao-feng GUO,Yong-kang MA,Xue-jun CHEN,Xiang LI,Chao-hong HE. Bladder cancer local staging about muscle invasion: 3.0T MRI performance following transurethral resection [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 701-704. |
| [12] | Yu SONG,Hong-bin HAN,Jun YANG,Ai-bo WANG,Qing-yuan HE,Yuan-yuan LI,Guo-mei ZHAO,Ya-juan GAO,Rui WANG,Yi-xing HAN,Ai-lian LIU,Qing-wei SONG. Effect of convection enhanced delivery on the microstructure of brain extracellular space in aged rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 362-367. |
| [13] | Jing-yun WU,Yue MI,Shui LIU,Lin YAO,Qi TANG,Zhi-song HE,Xiao-ying WANG. Evaluating inferior vena cava wall invasion in renal cell carcinoma tumor thrombus with MRI [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 673-677. |
| [14] | Li XU,Ming-jie HU,Yu-yu LI,Hong-dang QU,Wei-dong QIAN,Xiao-lin LIU. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system caused by myxopapillary ependymoma of conus medullaris and cauda equine: a case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 769-774. |
| [15] | Hong-bin HAN. Discovery of a new division system in brain and the regionalized drainage route of brain interstitial fluid [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 397-401. |
|
||