Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1158-1162. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
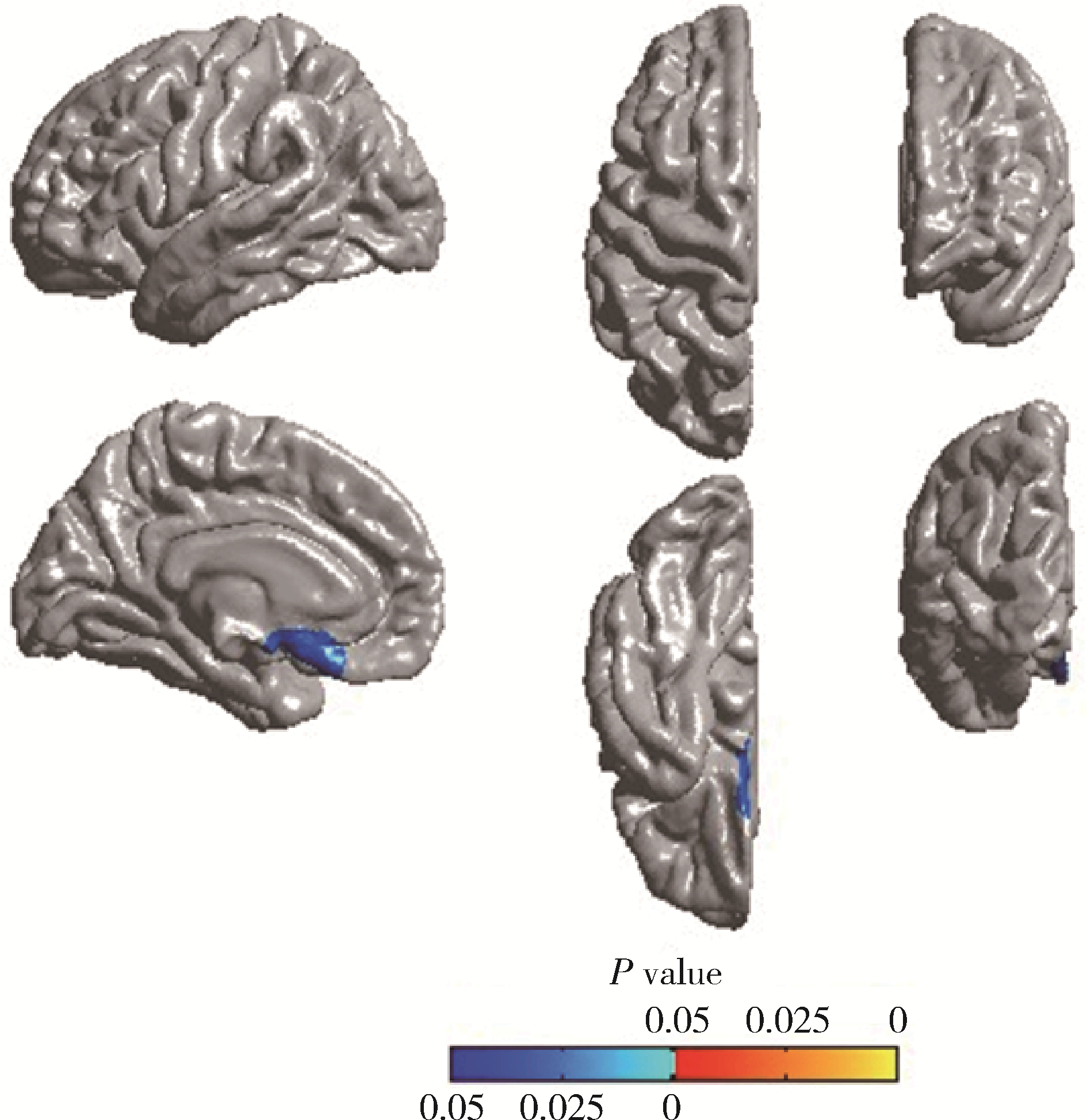
Cortical thickness and cognitive impairment in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Shan YE1,2,Ping-ping JIN1,2,Nan ZHANG1,2,Hai-bo WU3,Lin SHI4,5,Qiang ZHAO3,Kun YANG3,Hui-shu YUAN3,Dong-sheng FAN1,2,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Neurology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Beijing Municipal Key Laboratory of Biomarker and Translational Research in Neurodegenerative Diseases, Beijing 100191, China
3. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
4. Department of Imaging and Interventional Radiology, Prince of Wales Hospital, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region 000852, China
5. BrainNow Research Institute, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong, China
CLC Number:
- R744.8
| 1 | Strong M , Abrahams S , Goldstein L , et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal spectrum disorder (ALS-FTSD): Revised diagnostic criteria[J]. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener, 2017, 18 (3/4): 153- 174. |
| 2 | Hanstock C , Sun K , Choi C , et al. Spectroscopic markers of neurodegeneration in the mesial prefrontal cortex predict survival in ALS[J]. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener, 2020, 21 (3/4): 246- 251. |
| 3 |
Trojsi F , Nardo F , Siciliano M , et al. Frontotemporal degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): A longitudinal MRI one-year study[J]. CNS Spectr, 2021, 26 (3): 258- 267.
doi: 10.1017/S109285292000005X |
| 4 |
Hu T , Hou Y , Wei Q , et al. Patterns of brain regional functional coherence in cognitive impaired ALS[J]. Int J Neurosci, 2020, 130 (8): 751- 758.
doi: 10.1080/00207454.2019.1705806 |
| 5 |
Brooks BR , Miller RG , Swash M , et al. El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord, 2000, 1 (5): 293- 299.
doi: 10.1080/146608200300079536 |
| 6 |
Desikan RS , Segonne F , Fischl B , et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest[J]. Neuroimage, 2006, 31 (3): 968- 980.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021 |
| 7 |
Chiara C , Alessandra D , Stefano FC , et al. Multimodal MRI quantification of the common neurostructural bases within the FTD-ALS continuum[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2018, 62, 95- 104.
doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.09.019 |
| 8 | Verstraete E , Veldink JH , Hendrikse J , et al. Structural MRI reveals cortical thinning in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2011, 83 (4): 383- 388. |
| 9 |
Bergmann M . Motor neuron disease/amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Lessons from ubiquitin[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 1993, 189 (8): 902- 912.
doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)81102-7 |
| 10 | Shen D , Hou B , Cui B , et al. Comparing brain structural and perfusion MRI changes across ALS-FTD continuum[J]. Clin Neurophysiol, 2018, 129, e162. |
| 11 |
Labar KS , Cabeza R . Cognitive neuroscience of emotional memory[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2006, 7 (1): 54- 64.
doi: 10.1038/nrn1825 |
| 12 | Dolcos F , Labar KS , Cabeza R . Dissociable effects of arousal and valence on prefrontal activity indexing emotional evaluation and subsequent memory: An event-related fMRI study[J]. Neuro-image, 2004, 23 (1): 64- 74. |
| 13 |
Lule D , Diekmann V , Anders S , et al. Brain responses to emotional stimuli in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)[J]. J Neurol, 2007, 254 (4): 519- 527.
doi: 10.1007/s00415-006-0409-3 |
| [1] | Yuxuan TIAN,Mingjian RUAN,Yi LIU,Derun LI,Jingyun WU,Qi SHEN,Yu FAN,Jie JIN. Predictive effect of the dual-parametric MRI modified maximum diameter of the lesions with PI-RADS 4 and 5 on the clinically significant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [2] | Yuting LIN,Huali WANG,Yu TIAN,Litong GONG,Chun CHANG. Factors influencing cognitive function among the older adults in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [3] | Yi LIU,Chang-wei YUAN,Jing-yun WU,Qi SHEN,Jiang-xi XIAO,Zheng ZHAO,Xiao-ying WANG,Xue-song LI,Zhi-song HE,Li-qun ZHOU. Diagnostic efficacy of prostate cancer using targeted biopsy with 6-core systematic biopsy for patients with PI-RADS 5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [4] | Chang-wei YUAN,De-run LI,Zhi-hua LI,Yi LIU,Gang-zhi SHAN,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of dynamic contrast enhanced status in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer with PI-RADS 4 lesion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [5] | Ying LIU,Ran HUO,Hui-min XU,Zheng WANG,Tao WANG,Hui-shu YUAN. Correlations between plaque characteristics and cerebral blood flow in patients with moderate to severe carotid stenosis using magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [6] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [7] | Ying CAI,Qiao-qin WAN,Xian-jie CAI,Ya-juan GAO,Hong-bin HAN. Epidural photobiomodulation accelerates the drainage of brain interstitial fluid and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 1000-1005. |
| [8] | WANG Shu-lei,GAO Yang-xu,ZHANG Hong-wu,YANG Hai-bo,LI Hui,LI Yu,SHEN Li-xue,YAO Hong-xin. Clinical analysis of 30 cases of basal ganglia germinoma in children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 222-226. |
| [9] | ZHANG Fan,CHEN Qu,HAO Yi-chang,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and preoperative/postoperative membranous urethral length [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [10] | Yi-fan WU,Xiao-yuan ZHANG,Shuang REN,Ying-xiang YU,Cui-qing CHANG. Measurement and evaluation of the quadriceps muscle mass in young men based on magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 843-849. |
| [11] | Hui SHENG,Lei LIANG,Tong-liang ZHOU,Yan-xing JIA,Tong WANG,Lan YUAN,Hong-bin HAN. Improved synthesis process of optical-magnetic bimodal probe of Gd-[4,7-Bis-carboxymethyl-10-(2-fluoresceinthioureaethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraaza-cyclododec-1-yl]-acetic acid complexes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 959-963. |
| [12] | Shi-ming ZHAO,Tie-jun YANG,Chun-miao XU,Xiao-feng GUO,Yong-kang MA,Xue-jun CHEN,Xiang LI,Chao-hong HE. Bladder cancer local staging about muscle invasion: 3.0T MRI performance following transurethral resection [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 701-704. |
| [13] | Xing-hong ZHOU,Ying HUANG,Chao YUAN,Shu-guo ZHENG,Jie ZHANG,Jian-guo ZHANG. Awareness and knowledge of oral cancer among 1 483 residents in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 323-331. |
| [14] | Yu SONG,Hong-bin HAN,Jun YANG,Ai-bo WANG,Qing-yuan HE,Yuan-yuan LI,Guo-mei ZHAO,Ya-juan GAO,Rui WANG,Yi-xing HAN,Ai-lian LIU,Qing-wei SONG. Effect of convection enhanced delivery on the microstructure of brain extracellular space in aged rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 362-367. |
| [15] | Hong-xia YANG,Xiao-lan TIAN,Wei JIANG,Wen-li LI,Qing-yan LIU,Qing-lin PENG,Guo-chun WANG,Xin LU. Clinical and pathological characteristics of immune mediated necrotizing myopathy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 989-995. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 133
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 405
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cited |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||