Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 183-187. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.027
Previous Articles Next Articles
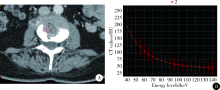
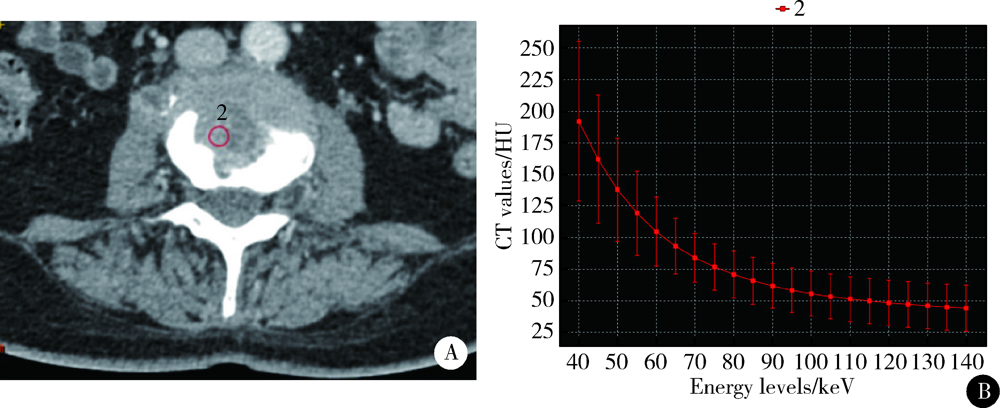
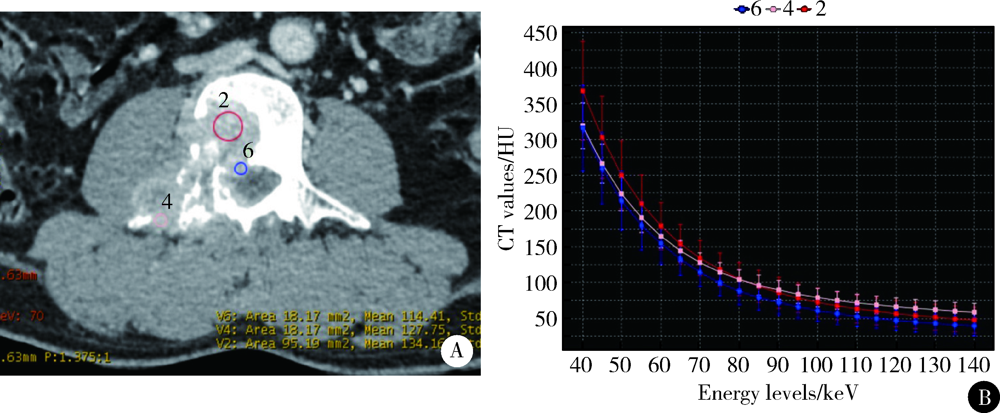
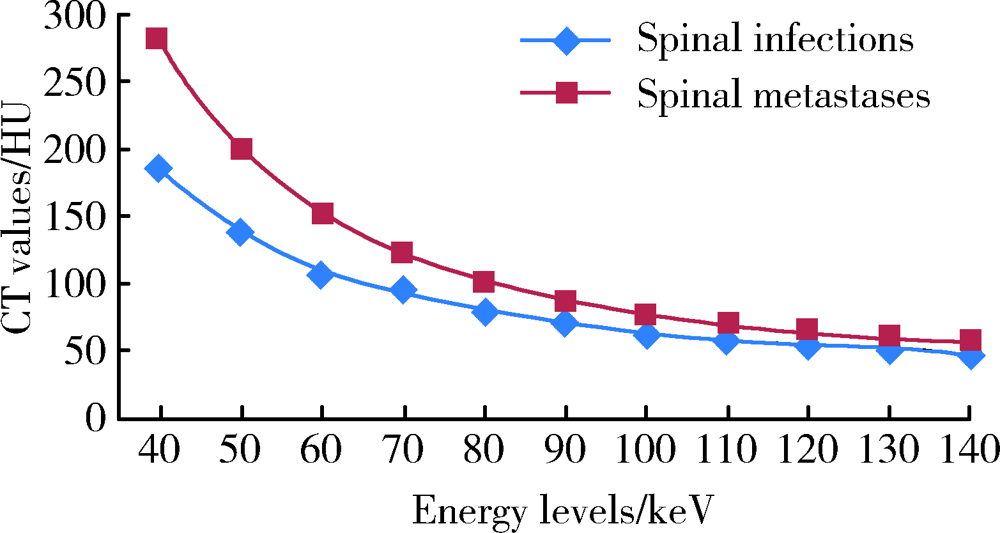
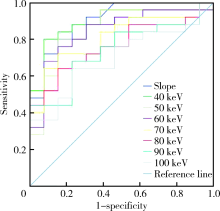
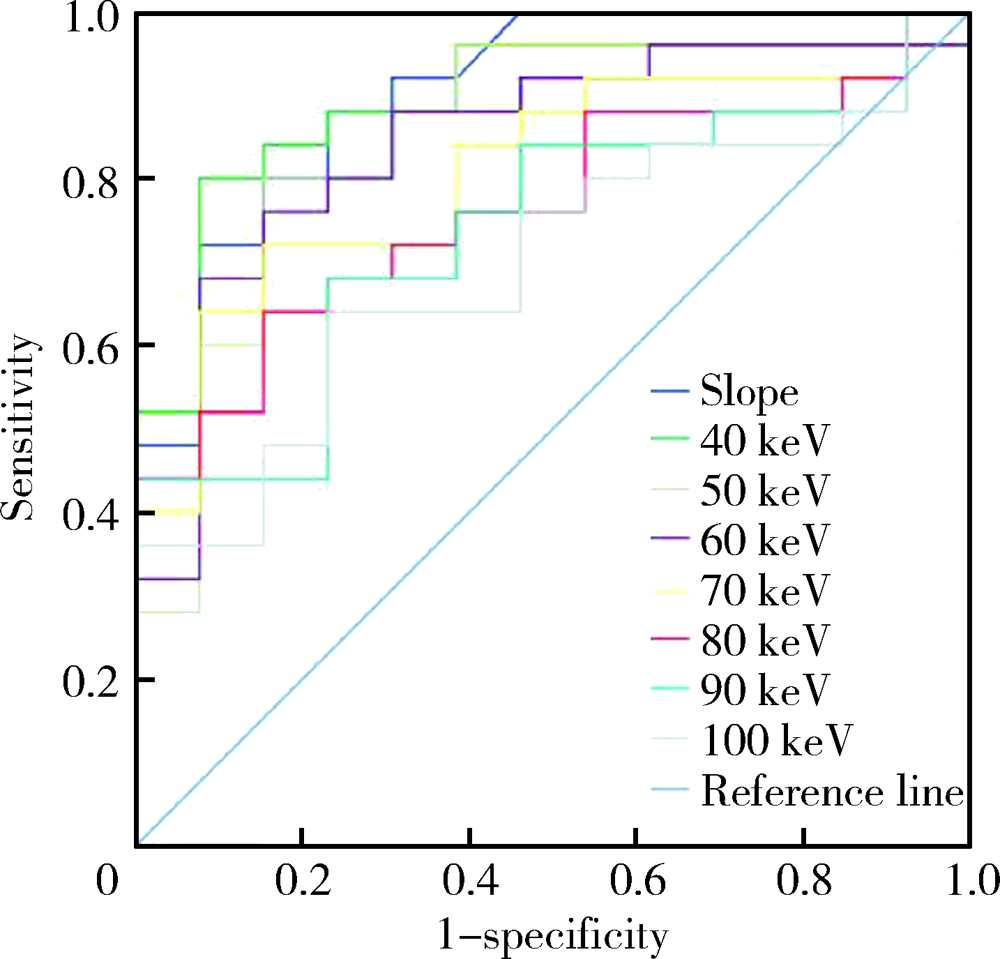
CT spectral curve in differentiating spinal tumor metastasis and infections
YUAN Yuan,LANG Ning,YUAN Hui-shu( )
)
- Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R738.1
| [1] |
Lee SH, Lee JM, Kim KW, et al. Dual-energy computed tomography to assess tumor response to hepatic radiofrequency ablation: potential diagnostic value of virtual noncontrast images and iodine maps[J]. Invest Radiol, 2011,46(2):77-84.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3181f23fcd pmid: 20856125 |
| [2] |
Lang N, Yuan H, Yu HJ, et al. Diagnosis of spinal lesions using heuristic and pharmacokinetic parameters measured by dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI[J]. Acad Radiol, 2017,24(7):867-875.
doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2016.12.014 pmid: 28162875 |
| [3] |
Babic M, Simpfendorfer CS. Infections of the Spine[J]. Infect Dis Clin North Am, 2017,31(2):279-297.
doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2017.01.003 pmid: 28366222 |
| [4] |
Dong Y, Zheng S, Machida H, et al. Differential diagnosis of osteoblastic metastases from bone islands in patients with lung cancer by single-source dual-energy CT: advantages of spectral CT imaging[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2015,84(5):901-907.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.01.007 pmid: 25661696 |
| [5] |
Ko JP, Brandman S, Stember J, et al. Dual-energy computed tomography: concepts, performance, and thoracic applications[J]. J Thorac Imaging, 2012,27(1):7-22.
doi: 10.1097/RTI.0b013e31823fe0e9 pmid: 22189245 |
| [6] |
Flais J, Coiffier G, Brillet E, et al. Atypical presentation of spine bone metastasis in prostate cancer mimicking Pott’s disease[J]. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab, 2017,14(2):239-240.
doi: 10.11138/ccmbm/2017.14.1.239 pmid: 29263741 |
| [7] | 袁源, 张艳, 郎宁, 等. CT能谱曲线鉴别诊断脊柱肿瘤及肿瘤样病变[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2015,31(4):600-603. |
| [8] |
Avrin DE, Macovski A, Zatz LE. Clinical application of Compton and photo-electric reconstruction in computed tomography: preliminary results[J]. Invest Radiol, 1978,13(3):217-222.
doi: 10.1097/00004424-197805000-00007 pmid: 711396 |
| [9] | Dilmanian FA. Computed tomography with monochromatic X rays[J]. Am J Physiol Imaging, 1992,7(3/4):175-193. |
| [10] |
Riederer SJ, Mistretta CA. Selective iodine imaging using K-edge energies in computerized X-ray tomography[J]. Med Phys, 1977,4(6):474-481.
doi: 10.1118/1.594357 pmid: 927384 |
| [11] |
Silva AC, Morse BG, Hara AK, et al. Dual-energy (spectral) CT: applications in abdominal imaging[J]. Radiographics, 2011,31(4):1031-1050.
doi: 10.1148/rg.314105159 pmid: 21768237 |
| [12] | 雷立昌, 陈建宇. 能谱CT的临床应用与研究进展[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2013,29(1):146-149. |
| [13] | 林晓珠, 沈云, 陈克敏. CT能谱成像的基本原理与临床应用研究进展[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2011,45(8):798-800. |
| [14] | 张靖, 周新社. 脊柱肿瘤的诊断和外科分期研究进展[J]. 中华全科医学, 2011,9(2):277-279. |
| [15] |
Go SW, Lee HY, Lim CH, et al. Atypical disseminated skeletal tuberculosis mimicking metastasis on PET-CT and MRI[J]. Intern Med, 2012,51(20):2961-2965.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.51.8347 pmid: 23064577 |
| [16] |
Mittal S, Khalid M, Sabir AB, et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging findings between pathologically proven cases of atypical tubercular spine and tumour metastasis: A retrospective study in 40 patients[J]. Asian Spine J, 2016,10(4):734-743.
doi: 10.4184/asj.2016.10.4.734 pmid: 27559455 |
| [17] |
Sezgin B, Atilganoglu U, Yigit O, et al. Concomitant cutaneous metastatic tuberculous abscesses and multifocal skeletal tuberculosis[J]. Indian J Dermatol, 2008,53(3):149-153.
doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.43208 pmid: 19882018 |
| [18] |
Chang DS, Rafii M, McGuinness G, et al. Primary multifocal tuberculous osteomyelitis with involvement of the ribs[J]. Skeletal Radiol, 1998,27(11):641-645.
doi: 10.1007/s002560050451 pmid: 9867183 |
| [19] |
Lang N, Su MY, Yu HJ, et al. Differentiation of tuberculosis and metastatic cancer in the spine using dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI[J]. Eur Spine J, 2015,24(8):1729-1737.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-3851-z pmid: 25749725 |
| [20] |
Zheng S, Dong Y, Miao Y, et al. Differentiation of osteolytic metastases and Schmorl’s nodes in cancer patients using dual-energy CT: Advantage of spectral CT imaging[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2014,83(7):1216-1221.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.02.003 pmid: 24820064 |
| [21] | Gupta S, Wagner-Bartak N, Jensen CT, et al. Dual-energy CT of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Reproducibility of primary tumor measurements and assessment of tumor conspicuity and margin sharpness[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2016,41(7):1317-1324. |
| [22] |
Ramon A, Bohm-Sigrand A, Pottecher P, et al. Role of dual-energy CT in the diagnosis and follow-up of gout: systematic analysis of the literature[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2018,37(3):587-595.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3976-z pmid: 29350330 |
| [1] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | Zhengfang LI,Cainan LUO,Lijun WU,Xue WU,Xinyan MENG,Xiaomei CHEN,Yamei SHI,Yan ZHONG. Application value of anti-carbamylated protein antibody in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [4] | Shishi BO,Chengzhi GAO. Tooth segmentation and identification on cone-beam computed tomography with convolutional neural network based on spatial embedding information [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 735-740. |
| [5] | Xiaotong LING,Liuyang QU,Danni ZHENG,Jing YANG,Xuebing YAN,Denggao LIU,Yan GAO. Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [6] | Deng-hui DUAN,Hom-Lay WANG,En-bo WANG. Role of collagen membrane in modified guided bone regeneration surgery using buccal punch flap approach: A retrospective and radiographical cohort study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1097-1104. |
| [7] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [8] | Xiang LIU,Hui-hui XIE,Yu-feng XU,Xiao-dong ZHANG,Xiao-feng TAO,Lin LIU,Xiao-ying WANG. Value of artificial intelligence in the improvement of diagnostic consistency of radiology residents [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 670-675. |
| [9] | Ting WANG,Qiao-sheng LI,Hao-ran LIU,Wei-yan JIAN. Urban-rural differentials in the relationship between personality traits and changes in depressive symptoms [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 385-391. |
| [10] | Yan XIONG,Xin LI,Li LIANG,Dong LI,Li-min YAN,Xue-ying LI,Ji-ting DI,Ting LI. Evaluation of accuracy of pathological diagnosis based on thyroid core needle biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [11] | Jin-hua ZHANG,Jie PAN,Zhi-peng SUN,Xiao WANG. Effect of various intracanal materials on the diagnostic accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography in vertical root fractures [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 333-338. |
| [12] | Xue-mei HA,Yong-zheng YAO,Li-hua SUN,Chun-yang XIN,Yan XIONG. Solid placental transmogrification of the lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [13] | Bo-han NING,Qing-xia ZHANG,Hui YANG,Ying DONG. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma with proliferated stromal cells, hyalinization and cord-like formations: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [14] | Jia-xue YE,Yu-hong LIANG. A prevalence survey of cone-beam computed tomography use among endodontic practitioners [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 114-119. |
| [15] | Meng-qiao PAN,Jian LIU,Li XU,Xiao XU,Jian-xia HOU,Xiao-tong LI,Xiao-xia WANG. A long-term evaluation of periodontal phenotypes before and after the periodontal-orthodontic-orthognathic combined treatment of lower anterior teeth in patients with skeletal Angle class Ⅲ malocclusion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 52-61. |
|
||