Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 308-313. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
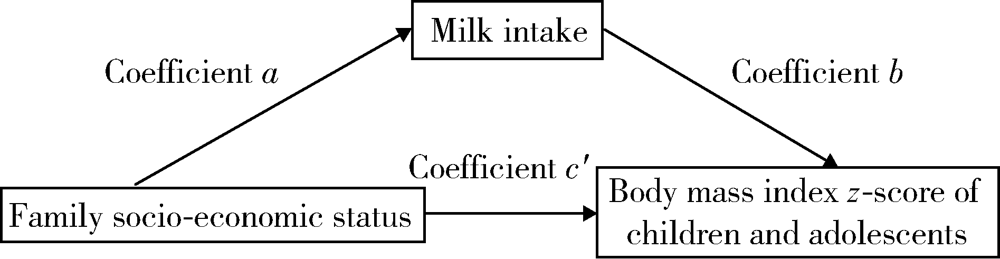
Mediating effect of milk intake between family socioeconomic status and body mass index of children and adolescents
SHI Xin-ran,AN Mei-jing,CHEN Tian-jiao( ),Ma jun
),Ma jun
- Institute of Child and Adolescent Health, Peking University, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R151.3
| [1] | 王烁, 董彦会, 王政和, 等. 1985—2014年中国7~18岁学生超重与肥胖流行趋势[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2017,51(4):300-305. |
| [2] | 刘丹, 房红芸, 赵丽云, 等. 家庭相关因素与中国6~17岁儿童青少年超重肥胖关系的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2018,39(6):720-723. |
| [3] |
Dinsa GD, Goryakin Y, Fumagalli E, et al. Obesity and socio-economic status in developing countries: a systematic review[J]. Obes Rev, 2012,13(11):1067-1079.
pmid: 22764734 |
| [4] | Barriuso L, Miqueleiz E, Albaladejo R, et al. Socioeconomic position and childhood-adolescent weight status in rich countries: a systematic review, 1990—2013[J]. BMC Pediatr, 2015,15(1):129. |
| [5] | Newton S, Braithwaite D, Akinyemiju TF. Socio-economic status over the life course and obesity: Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2017,12(5):e177151. |
| [6] |
Qian L, Zhang F, Newman IM, et al. Effects of selected socio-demographic characteristics on nutrition knowledge and eating behavior of elementary students in two provinces in China[J]. BMC Public Health, 2018,18(1):21.
pmid: 28709414 |
| [7] |
Mielke GI, Brown WJ, Nunes BP, et al. Socioeconomic correlates of sedentary behavior in adolescents: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sports Med, 2017,47(1):61-75.
pmid: 27260683 |
| [8] | Yannakoulia M, Lykou A, Kastorini CM, et al. Socio-economic and lifestyle parameters associated with diet quality of children and adolescents using classification and regression tree analysis: the DIATROFI study[J]. Public Health Nutr, 2016,19(2):339-347. |
| [9] | 杨静, 王丹, 吴萍萍, 等. 家庭因素对学龄前儿童不良进食习惯的影响[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2019,40(1):46-50. |
| [10] | 韩慧, 汤建军, 张勤. 蚌埠市4~6岁儿童饮食行为现状及家庭影响因素分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2016,20(10):1008-1010. |
| [11] | 中国学生体质与健康研究组. 2010年中国学生体质与健康研究报告[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2012: 32-47. |
| [12] | 中国肥胖问题工作组, 季成叶. 中国学龄儿童青少年超重、肥胖筛查体重指数值分类标准[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2004,25(2):97-102. |
| [13] | 温忠麟, 叶宝娟. 中介效应分析: 方法和模型发展[J]. 心理科学进展, 2014(5):731-745. |
| [14] | 杜文雯, 王惠君, 王志宏, 等. 中国九省区1991—2006年7~17岁儿童青少年饮奶状况及变化趋势[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2010,31(12):1349-1352. |
| [15] | 中国营养学会. 中国居民膳食指南(2016)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016: 279. |
| [16] | 聂少萍, 马文军, 徐浩锋, 等. 广东省城市中小学生饮用奶制品状况及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2007(9):774-775. |
| [17] | 赖月云. 我国城乡居民收入食品消费效应动态差异分析[J]. 统计与决策, 2014(12):127-129. |
| [18] | 赵婧洁, 王明利. 居民奶产品消费现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2014,50(20):3-7. |
| [19] |
Keast DR, Hill GK, Albertson AM, et al. Associations between yogurt, dairy, calcium, and vitamin D intake and obesity among U.S. children aged 8-18 years: NHANES, 2005—2008[J]. Nutrients, 2015,7(3):1577-1593.
pmid: 25742042 |
| [20] |
Moore LL, Singer MR, Qureshi MM, et al. Dairy intake and anthropometric measures of body fat among children and adole-scents in NHANES[J]. J Am Coll Nutr, 2008,27(6):702-710.
pmid: 19155429 |
| [21] |
Janne Kunchel L, Sanne N, Jens Juul H, et al. Effect of dairy calcium or supplementary calcium intake on postprandial fat metabolism, appetite, and subsequent energy intake[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2007,85(3):678.
pmid: 17344487 |
| [22] |
O’Dea JA, Wilson R. Socio-cognitive and nutritional factors associated with body mass index in children and adolescents: possibilities for childhood obesity prevention[J]. Health Educ Res, 2006,21(6):796-805.
pmid: 17095571 |
| [23] |
Löffler A, Luck T, Then FS, et al. Effects of psychological eating behaviour domains on the association between socio-economic status and BMI[J]. Public Health Nutr, 2017,20(15):2706-2712.
doi: 10.1017/S1368980017001653 pmid: 28735590 |
| [24] |
Lahelma E, Martikainen P, Laaksonen M, et al. Pathways between socioeconomic determinants of health[J]. J Epidemiol Community Health, 2004,58(4):327-332.
pmid: 15026449 |
| [1] | Weimin LI,Zufeiya TUERDI. Comparative research on the relationship between body mass index and physical fitness index among the Uygur, Kazakh and Han ethnic college students [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 411-417. |
| [2] | Yifan WU,Yingxiang YU,Lan XIE,Zhida ZHANG,Cuiqing CHANG. Characteristics of resting energy expenditure and evaluation of prediction formulas in young men with different body mass indexes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 247-252. |
| [3] | Jing-feng ZHANG,Yin-ji JIN,Hui WEI,Zhong-qiang YAO,Jin-xia ZHAO. Correlation analysis between body mass index and clinical characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [4] | Yang-yang CHEN,Yu-bo ZHOU,Jing YANG,Yu-meng HUA,Peng-bo YUAN,Ai-ping LIU,Yuan WEI. Effects of gestational weight on the association between serum high sensitivity C reaction protein and gestational diabetes mellitus among twin gestations: A cohort study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 427-433. |
| [5] | WANG Li-fang, ZHOU Hong, ZHANG Yan, WANG Yan. Relationship between pre-pregnancy body mass index and preterm birth [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(3): 414-417. |
| [6] | WEI Dong-Mei, WU Li-Jing, GAO Ai-Yu, LI Qin, CHENG Lan, WANG Hai-Jun. Study on the relations among the screen-based sedentary behaviors, family factors and body mass index of children [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(3): 390-394. |
|
||