Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1183-1187. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.06.029
Previous Articles Next Articles
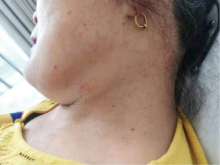
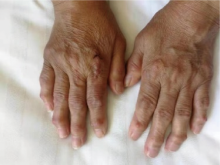
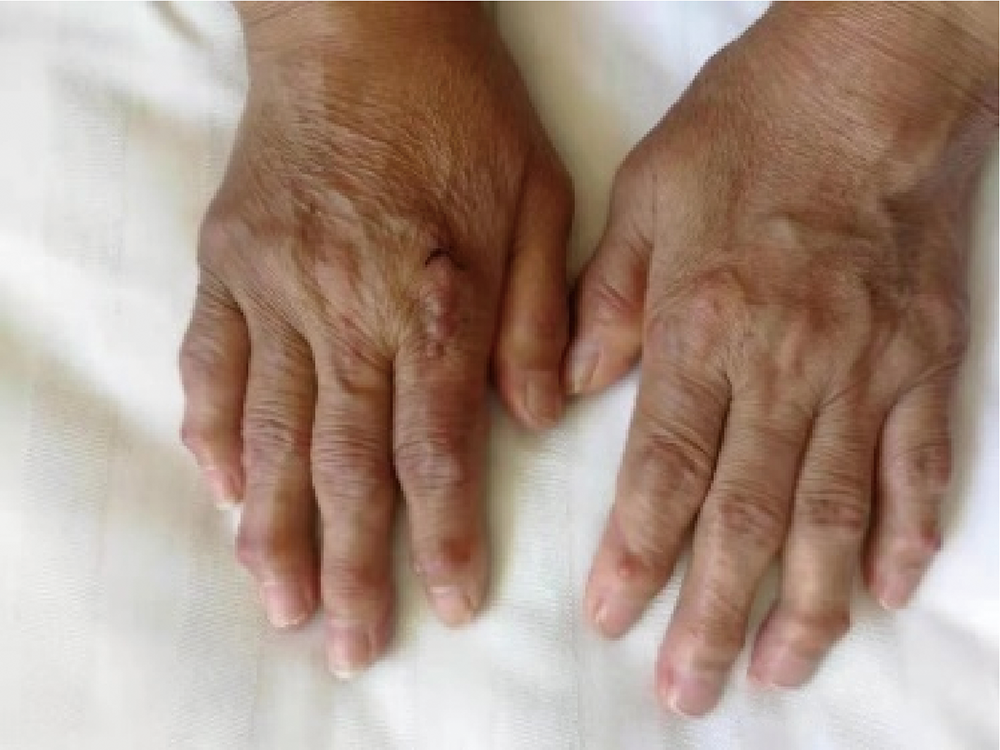
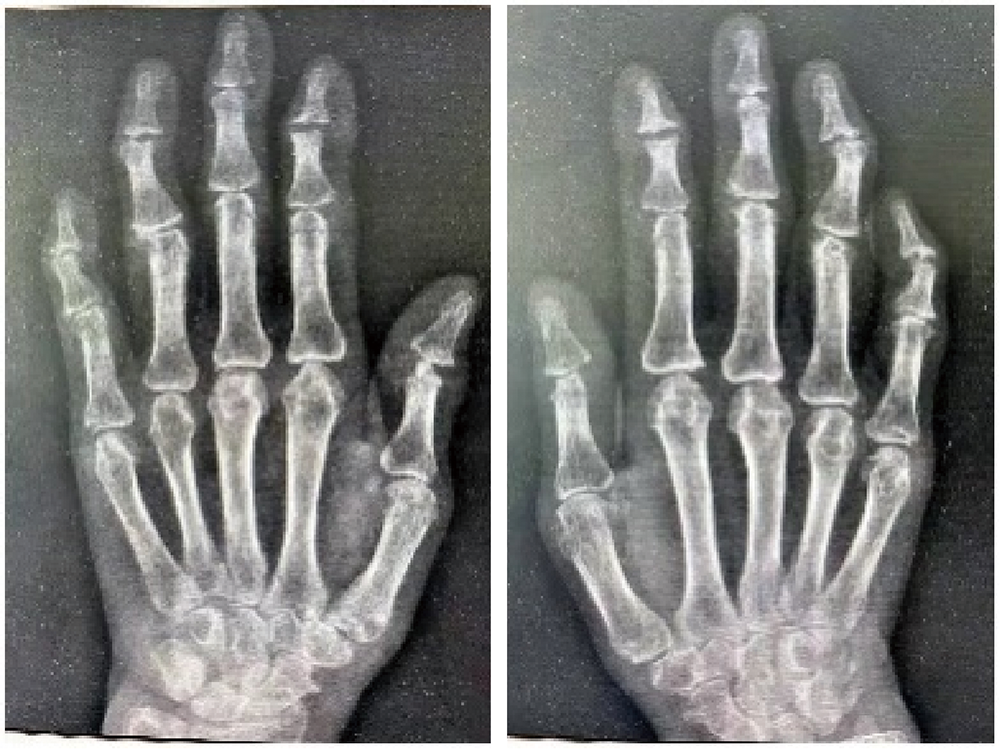
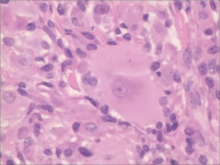
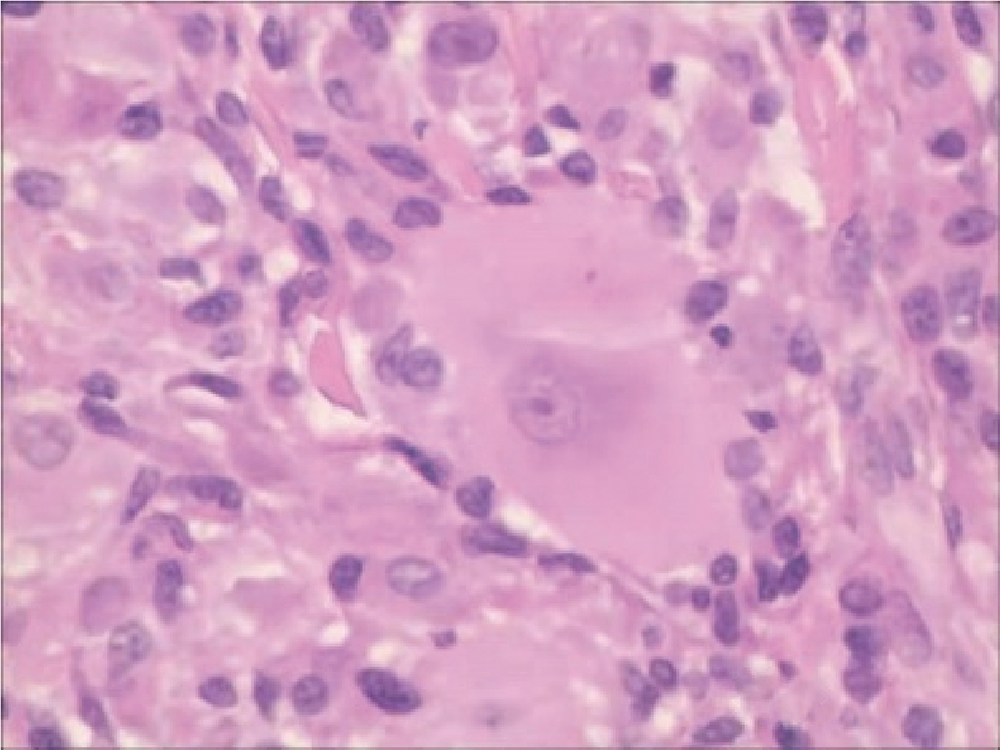
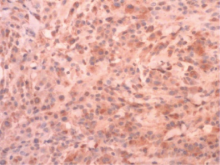
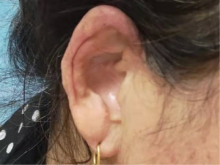
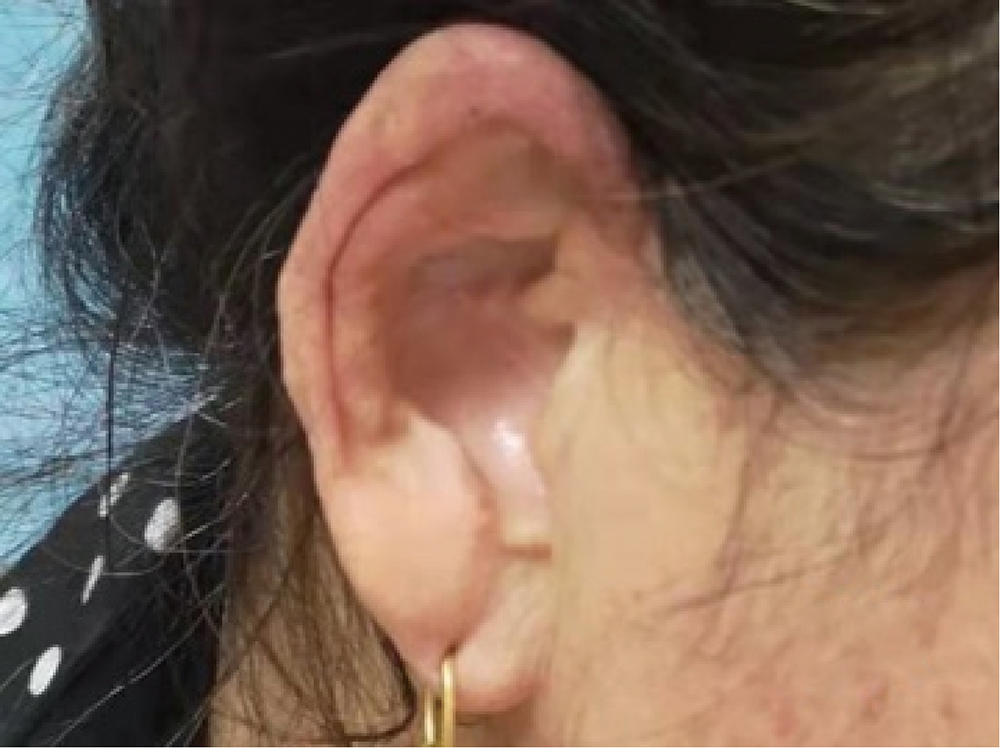
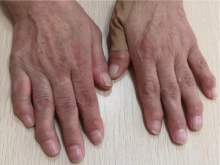
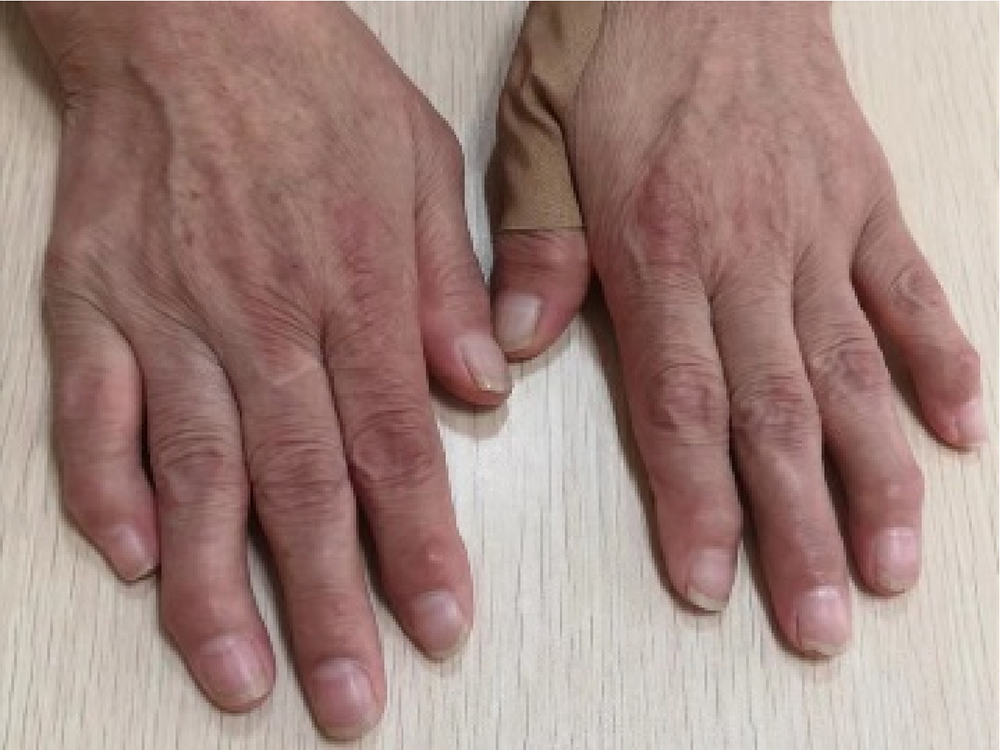
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: A case report
ZHAI Li1,QIU Nan1,SONG Hui2,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The 960th Hospital of the PLA Joint Logistics Support Force, Tai’an 271000, Shandong, China
2. Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Taian City Central Hospital, Tai’an 271000, Shandong, China
CLC Number:
- R59
| [1] | 王白鹤, 惠云, 苑春雨, 等. 多中心网状组织细胞增生症一例[J]. 中国麻风皮肤病杂志, 2018, 34(9):550-552. |
| [2] |
Luz FB, Gaspar TAP, Kalil-Gaspar N, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2001, 15(6):524-531.
pmid: 11843211 |
| [3] |
Tajirian AL, Malik MK, Robinson-Bostom L, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis[J]. Clin Dermatol, 2006, 24(6):486-492.
pmid: 17113966 |
| [4] |
Tariq S, Hugenberg ST, Hirano-Ali SA, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (MRH): Case report with review of literature between 1991 and 2014 with in depth analysis of various treatment regimens and outcomes[J]. Springerplus, 2016, 5(1):180.
doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-1874-5 |
| [5] |
Sanchez-Alvarez C, Sandhu AS, Crowson CS, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: The Mayo clinic experience (1980-2017)[J]. Rheumatology(Oxford), 2020, 59(8):1898-1905.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez555 |
| [6] | 李慧娟, 王立, 侯勇, 等. 多中心网状组织细胞增生症8例临床特征[J]. 中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志, 2015, 9(3):213-217. |
| [7] |
Lu YY, Lu CC, Wu CH. Leonine facies in the cutaneous form of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis[J]. Intern Med, 2012, 51(15):2069-2070.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.51.8119 |
| [8] |
Islam AD, Naguwa SM, Cheema GS, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: A rare yet challenging disease[J]. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, 2013, 45(2):281-289.
doi: 10.1007/s12016-013-8362-2 |
| [9] |
Gorman JD, Danning C, Schumacher HR, et al. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: Case report with immunohistochemical analysis and literature review[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2000, 43(4):930-938.
doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<930::AID-ANR27>3.0.CO;2-A |
| [10] | Yamamoto T. Skin manifestation associated with multicentric reticulohistiocytosis[J/OL]. J Clin Rheumatol, 2020(2020-12-15)[2021-08-01]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33337805/. |
| [11] |
El-Haddad B, Hammoud D, Shaver T, et al. Malignancy-associated multicentric reticulohistiocytosis[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2011, 31(9):1235-1238.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-009-1287-7 pmid: 20012625 |
| [12] | 白丽杰, 李鸿斌, 徐晓艳. 多中心网状组织细胞增多症1例并文献复习[J]. 临床荟萃, 2015, 30(7):831-832. |
| [13] |
Zhao H, Wu C, Wu M, et al. Tumor necrosis factor antagonists in the treatment of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis: Current clinical evidence[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 14(1):209-217.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5253 |
| [14] | Lim K, D’Souza J, Vasquez JB, et al. Looks can be deceiving: A case report on multicentric reticulohistiocytosis successfully treated with rituximab[J]. Cureus, 2017, 9(5):e1220. |
| [15] |
Pacheco-Tena C, Reyes-Cordero G, Ochoa-Albíztegui R, et al. Treatment of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis with tocilizumab[J]. J Clin Rheumatol, 2013, 19(5):272-276.
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e31829cf32b pmid: 23872542 |
| [16] |
Aouba A, Leclerc-Mercier S, Fraitag S, et al. Assessment and effective targeting of Interleukin-1 in multicentric reticulohistyo-cytosis[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2015, 82(4):280-283.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.02.003 |
| [1] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [2] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [3] | Zhengfang LI,Cainan LUO,Lijun WU,Xue WU,Xinyan MENG,Xiaomei CHEN,Yamei SHI,Yan ZHONG. Application value of anti-carbamylated protein antibody in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [4] | Wenjing LI,Baozhou ZHANG,Heng LI,Liangpeng LAI,Hui DU,Ning SUN,Xiaofeng GONG,Ying LI,Yan WANG,Yong WU. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis for end-stage ankle and hindfoot arthropathy: Short- and mid-term clinical outcomes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [5] | Qichen FENG,Shuo GAI,Changming WANG,Xuan LI. Application of iliac vein molding and stent implantation through the ipsilateral great saphenous vein approach in daytime treatment mode [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 322-325. |
| [6] | Bochun MAO,Yajing TIAN,Xuedong WANG,Jing LI,Yanheng ZHOU. Soft and hard tissue changes of hyperdivergent class Ⅱ patients before and after orthodontic extraction treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [7] | Xunmin XU,Xiao SHAO,Aiping JI. Analysis of death cases in the oral emergency department [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 185-189. |
| [8] | Xiaomeng REN,Kaiyi LI,Chunlei LI. Detection of molecular affecting sensitivity to local glucocorticoid therapy in oral lichen planus through transcriptome sequencing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 32-38. |
| [9] | Ying ZHOU,Ning ZHAO,Hongyuan HUANG,Qingxiang LI,Chuanbin GUO,Yuxing GUO. Application of double-layer soft tissue suture closure technique in the surgical treatment of patients with mandible medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw of early and medium stages [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 51-56. |
| [10] | Xue ZOU,Xiao-juan BAI,Li-qing ZHANG. Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [11] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [12] | Min QIU,You-long ZONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Bin YANG,Chu-xiao XU,Zheng-hui SUN,Min LU,Lei ZHAO,Jian LU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA. Treatment outcome of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in patients with renal tumors of moderate to high complexity [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [13] | Ming-rui WANG,Jia-xiang JI,Jin-hui LAI,Xin-wei TANG,Hao-pu HU,Qi WANG,Ke-xin XU,Tao XU,Hao HU. Choice of medical treatment for renal colic: A survey of Chinese urologists [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 871-875. |
| [14] | Bin CHEN,Chao WU,Bin LIU,Tao YU,Zhen-yu WANG. Prognosis of patients with spinal intramedullary cavernous hemangioma by different treatments [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 652-657. |
| [15] | Lei WANG,Tian-dong HAN,Wei-xing JIANG,Jun LI,Dao-xin ZHANG,Ye TIAN. Comparison of safety and effectiveness of active migration technique and in situ lithotripsy technique in the treatment of 1-2 cm upper ureteral calculi by flexible ure-teroscopy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 553-557. |
|
||