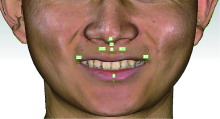
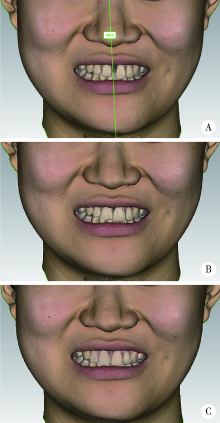
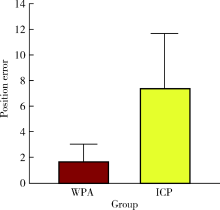
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 193-199. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.01.031
Preliminary clinical application verification of complete digital workflow of design lips symmetry reference plane based on posed smile
QIU Shu-ting1,ZHU Yu-jia1,2,WANG Shi-min3,WANG Fei-long1,YE Hong-qiang1,ZHAO Yi-jiao1,2,△( ),LIU Yun-song1,△(
),LIU Yun-song1,△( ),WANG Yong1,2,ZHOU Yong-sheng1
),WANG Yong1,2,ZHOU Yong-sheng1
- 1. Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Center of Digital Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
3. Center of Dental Laboratory, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R783
| [1] |
Havens DC, Mcnamara JA, Sigler LM, et al. The role of the posed smile in overall facial esthetics[J]. Angle Orthod, 2010, 80(2):322-328.
doi: 10.2319/040409-194.1 pmid: 19905858 |
| [2] |
van der Geld P, Oosterveld P, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM. Age-related changes of the dental aesthetic zone at rest and during spontaneous smiling and speech[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2008, 30(4):366-373.
doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjn009 |
| [3] |
Kokich V. Esthetics and anterior tooth position: An orthodontic perspective. Part Ⅲ: Mediolateral relationships[J]. J Esthet Dent, 1993, 5(5):200-207.
pmid: 8037970 |
| [4] |
Haraguchi S, Iguchi Y, Takada K. Asymmetry of the face in orthodontic patients[J]. Angle Orthod, 2008, 78(3):421-426.
doi: 10.2319/022107-85.1 pmid: 18416611 |
| [5] |
O’Grady KF, Antonyshyn OM. Facial asymmetry: Three-dimensional analysis using laser surface scanning[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1999, 104(4):928-937.
doi: 10.1097/00006534-199909020-00006 |
| [6] |
Momi ED, Chapuis J, Pappas I, et al. Automatic extraction of the mid-facial plane for cranio-maxillofacial surgery planning[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2006, 35(7):636-642.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2006.01.028 |
| [7] |
Du S, Xu Y, Wan T, et al. Robust iterative closest point algorithm based on global reference point for rotation invariant registration[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(11):e0188039.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188039 |
| [8] |
Verhoeven TJ, Nolte JW, Maal TJJ, et al. Unilateral condylar hyperplasia: A 3-dimensional quantification of asymmetry[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(3):e59391.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059391 |
| [9] |
Gateno J, Jajoo A, Nicol M, et al. The primal sagittal plane of the head: A new concept[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016, 45(3):399-405.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2015.11.013 |
| [10] |
Chetverikov D, Stepanov D, Krsek P. Robust Euclidean alignment of 3D point sets: The trimmed iterative closest point algorithm[J]. Image Vis Comput, 2005, 23(3):299-309.
doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2004.05.007 |
| [11] | 朱玉佳, 赵一姣, 郑盛文, 等. 基于赋权形态学分析的三维面部对称参考平面构建方法[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53(1):220-226. |
| [12] | 李立美, 李风兰, 杨红霞. 140名山西籍青年人微笑美学定性指标初步分析[J]. 口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2021, 22(2):129-133. |
| [13] | 徐成华, 王蕴红, 谭铁牛. 三维人脸建模与应用[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2004, 9(8):1-11. |
| [14] | 刘云松, 叶红强, 谷明, 等. 患者参与的数字化设计在前牙美学修复中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46(1):90-94. |
| [15] |
Zhao JM, Ji LL, Han MQ, et al. Lip morphology estimation models based on three-dimensional images in a modern adult population from China[J]. Int J Legal Med, 2021, 135(5):1887-1901.
doi: 10.1007/s00414-021-02559-2 |
| [16] |
Zhu Y, Zheng S, Yang G, et al. A novel method for 3D face symmetry reference plane based on weighted Procrustes analysis algorithm[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2020, 20(1):319.
doi: 10.1186/s12903-020-01311-3 |
| [17] | 叶红强, 柳玉树, 王冠博, 等. 三维数字化仿真设计与实现技术在前牙美学修复中的应用[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2020, 55(10):729-736. |
| [18] | 骆小平. 数字化技术在牙科全瓷美学修复中的应用[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志, 2017, 10(8):449-451. |
| [19] |
McNamara L, McNamara JA Jr, Ackerman MB, et al. Hard- and soft-tissue contributions to the esthetics of the posed smile in growing patients seeking orthodontic treatment[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2008, 133(4):491-499.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.05.042 |
| [20] | 王时敏, 李峥, 王冠博, 等. 全程数字化夜磨牙保护牙合垫的制作和初步应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019, 51(1):105-110. |
| [21] |
Sun KM, Joo LE, Song IJ, et al. The location of midfacial landmarks according to the method of establishing the midsagittal reference plane in three-dimensional computed tomography analysis of facial asymmetry[J]. Imaging Sci Dent, 2015, 45(4):227-232.
doi: 10.5624/isd.2015.45.4.227 |
| [22] |
Young CK. Analysis of facial asymmetry[J]. Arch Craniofac Surg, 2015, 16(1):1-10.
doi: 10.7181/acfs.2015.16.1.1 pmid: 28913211 |
| [23] | 黄佳梦, 李娟, 林军. 面部不对称畸形评估的研究进展[J]. 中国医疗美容, 2019, 9(6):121-128. |
| [24] | 米雁翎, 西文琼, 邓延伟, 等. 骨性Ⅲ类错伴骨性偏颌的正畸-正颌联合治疗[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2019, 54(6):391-395. |
| [25] | 胡祥莹, 肖燕, 王璧霞, 等. 成人错牙合畸形患者正颌手术治疗决策的质性研究[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2019, 28(5):513-517. |
| [26] |
Silva BP, Jiménez-Castellanos E, Finkel S, et al. Layperson’s preference regarding orientation of the transverse occlusal plane and commissure line from the frontal perspective[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2016, 117(4):513-516.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2016.07.027 |
| [27] |
Silva BP, Mahn E, Stanley K, et al. The facial flow concept: An organic orofacial analysis, the vertical component[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2018, 121(2):189-194.
doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2018.03.023 |
| [28] | Koseoglu M, Bayindir F. Effect of variations in facial flow curves on the perceptions of smile esthetics by laypeople [J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2021, S0022-3913(21)00320-6. |
| [29] |
Gibelli D, Pucciarelli V, Poppa P, et al. Three-dimensional facial anatomy evaluation: Reliability of laser scanner consecutive scans procedure in comparison with stereophotogrammetry[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2018, 46(10):1807-1813.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2018.07.008 |
| [30] |
Wu J, Heike C, Birgfeld C, et al. Measuring symmetry in children with unrepaired cleft lip: Defining a standard for the three-dimensional midfacial reference plane[J]. Cleft Palate Craniofac J, 2016, 53(6):695-704.
doi: 10.1597/15-053 |
| [31] | 卢长宝, 黄桂艳. 过多选择效应:概念演化、发生前提及行为决策机制[J]. 北京工商大学学报(社会科学版), 2017, 32(5):108-117. |
| [1] | Yuxuan TIAN,Mingjian RUAN,Yi LIU,Derun LI,Jingyun WU,Qi SHEN,Yu FAN,Jie JIN. Predictive effect of the dual-parametric MRI modified maximum diameter of the lesions with PI-RADS 4 and 5 on the clinically significant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [2] | Liang LYU,Mingjin ZHANG,Aonan WEN,Yijiao ZHAO,Yong WANG,Jing LI,Gengchen YANG,Dawei LIU. Preliminary evaluation of chin symmetry with three dimentional soft tissue spatial angle wireframe template [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 106-110. |
| [3] | Bochun MAO,Yajing TIAN,Xuedong WANG,Jing LI,Yanheng ZHOU. Soft and hard tissue changes of hyperdivergent class Ⅱ patients before and after orthodontic extraction treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [4] | Xiaotong LING,Liuyang QU,Danni ZHENG,Jing YANG,Xuebing YAN,Denggao LIU,Yan GAO. Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [5] | Xinyu XU,Ling WU,Fengqi SONG,Zili LI,Yi ZHANG,Xiaojing LIU. Mandibular condyle localization in orthognathic surgery based on mandibular movement trajectory and its preliminary accuracy verification [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [6] | Sui LI,Wenjie MA,Shimin WANG,Qian DING,Yao SUN,Lei ZHANG. Trueness of different digital design methods for incisal guidance of maxillary anterior implant-supported single crowns [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 81-87. |
| [7] | Yi LIU,Chang-wei YUAN,Jing-yun WU,Qi SHEN,Jiang-xi XIAO,Zheng ZHAO,Xiao-ying WANG,Xue-song LI,Zhi-song HE,Li-qun ZHOU. Diagnostic efficacy of prostate cancer using targeted biopsy with 6-core systematic biopsy for patients with PI-RADS 5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [8] | Chang-wei YUAN,De-run LI,Zhi-hua LI,Yi LIU,Gang-zhi SHAN,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of dynamic contrast enhanced status in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer with PI-RADS 4 lesion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [9] | Zhan-yi ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Cai-guang CAO,Chang-jian LI,Shao-hui DENG,Yue-hao SUN,Tian-liang HUANG,Yun-he GUAN,Nan LI,Min LU,Zhen-hua HU,Shu-dong ZHANG. Near-infrared targeted probe designed for intraoperative imaging of prostatic neurovascular bundles [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [10] | Zhuo-hua LIN,Ru-yi CAI,Yang SUN,Rong MU,Li-gang CUI. Methodology and clinical use of superb microvascular imaging in assessing micro-circulation changes of fingertips in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 636-640. |
| [11] | Ying LIU,Ran HUO,Hui-min XU,Zheng WANG,Tao WANG,Hui-shu YUAN. Correlations between plaque characteristics and cerebral blood flow in patients with moderate to severe carotid stenosis using magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [12] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [13] | Xiang LIU,Hui-hui XIE,Yu-feng XU,Xiao-dong ZHANG,Xiao-feng TAO,Lin LIU,Xiao-ying WANG. Value of artificial intelligence in the improvement of diagnostic consistency of radiology residents [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 670-675. |
| [14] | Wen ZHANG,Xiao-jing LIU,Zi-li LI,Yi ZHANG. Effect of alar base cinch suture based on anatomic landmarks on the morphology of nasolabial region in patients after orthognathic surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 736-742. |
| [15] | Meng-en OU,Yun DING,Wei-feng TANG,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cement flow in abutment margin-crown platform switching [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
|
||