Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1068-1073. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.06.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
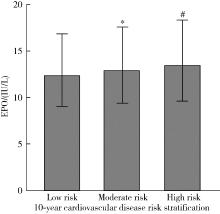
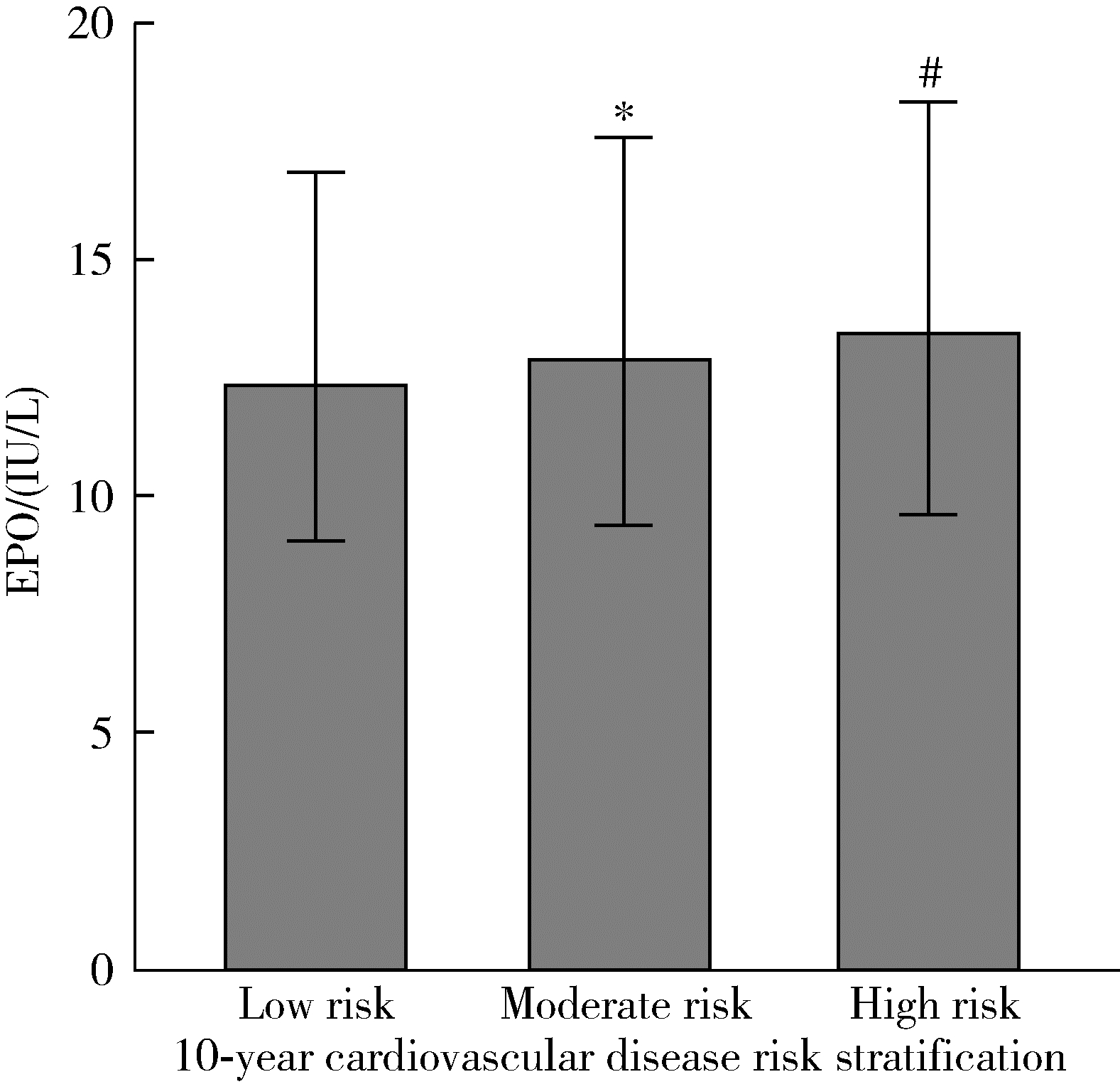
Related factors of endogenous erythropoietin and its association with 10-year risks of cardiovascular disease in a community-based Chinese study
Chu-yun CHEN,Peng-fei SUN,Jing ZHAO,Jia JIA,Fang-fang FAN,Chun-yan WANG,Jian-ping LI,Yi-meng JIANG,Yong HUO,Yan ZHANG*( )
)
- Department of Cardiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R754
| 1 | 吴超群, 李希, 路甲鹏, 等. 中国居民心血管疾病危险因素分布报告[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2021, 36 (1): 4- 13. |
| 2 | 赵林林, 吴乃石. EPO在心肌缺血再灌注损伤的相关作用及保护机制的研究进展[J]. 现代诊断与治疗, 2022, 33 (9): 1289- 1291. |
| 3 |
Suresh S , Rajvanshi PK , Noguchi CT . The many facets of erythropoietin physiologic and metabolic response[J]. Front Physiol, 2019, 10, 1534.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01534 |
| 4 | 常晋瑞, 赵妍, 曹健, 等. 促红细胞生成素在心肌缺血和缺血再灌注损伤中应用及其保护作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2019, 35 (15): 1695- 1698. |
| 5 |
Minamino T , Higo S , Araki R , et al. Low-dose erythropoietin in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction(EPO-AMI-Ⅱ): A randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. Circ J, 2018, 82 (4): 1083- 1091.
doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-17-0889 |
| 6 | 秦永根, 蔡立刚, 董佳丽, 等. 小剂量促红细胞生成素联合基础疗法对AMI患者心肌损伤、氧化应激机制的影响[J]. 中国现代医生, 2023, 61 (12): 94- 98. |
| 7 |
Nagai T , Nishimura K , Honma T , et al. Prognostic significance of endogenous erythropoietin in long-term outcome of patients with acute decompensated heart failure[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2016, 18 (7): 803- 813.
doi: 10.1002/ejhf.537 |
| 8 | Onoda H, Imamura T, Ueno H, et al. Prognostic impact of elevated erythropoietin levels in patients with severe aortic stenosis receiving trans-catheter aortic valve implantation[J/OL]. J Cardiol, 2023[2023-10-10]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0914508723001648?via%3Dihub. |
| 9 |
Mas-Peiro S , Seppelt PC , De Rosa R , et al. Potential role and prognostic value of erythropoietin levels in patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2020, 7, 605257.
doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.605257 |
| 10 | 李锴印, 范芳芳, 贾佳, 等. 中心动脉收缩压与中国动脉粥样硬化性心血管病风险预测研究模型评估的心血管病10年风险的关系[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2023, 31 (1): 45- 51. |
| 11 |
Levey AS , Stevens LA , Schmid CH , et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2009, 150 (9): 604- 612.
doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006 |
| 12 |
Sun P , Jia J , Fan F , et al. Hemoglobin and erythrocyte count are independently and positively associated with arterial stiffness in a community-based study[J]. J Hum Hypertens, 2021, 35 (3): 265- 273.
doi: 10.1038/s41371-020-0332-6 |
| 13 | 唐迅, 张杜丹, 何柳, 等. China-PAR模型在北方农村人群中预测动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病发病风险的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49 (3): 439- 445. |
| 14 | 艾合买提·阿布都卡地尔, 黄莺. 心血管疾病高危人群的早期筛查模型[J]. 中国心血管杂志, 2019, 24 (5): 474- 476. |
| 15 | 何靖楠, 宁尚勇, 韩晓燕, 等. 北京社区老年人群促红细胞生成素水平及贫血相关因素研究[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2012, 4 (2): 158- 160. |
| 16 | Kristjansdottir HL , Lewerin C , Lerner UH , et al. High Plasma erythropoietin predicts incident fractures in elderly men with normal renal function: The MrOS Sweden Cohort[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2020, 35 (2): 298- 305. |
| 17 | Nahm CH , Lee MH , Fujii T , et al. Lipocalin-2, soluble transferrin receptor, and erythropoietin in anemia during mild renal dysfunction[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2023, 16, 3603- 3612. |
| 18 | Panjeta M , Tahirović I , Sofić E , et al. Interpretation of erythropoietin and haemoglobin levels in patients with various stages of chronic kidney disease[J]. J Med Biochem, 2017, 36 (2): 145- 152. |
| 19 | Schmieder RE , Langenfeld MR , Hilgers KF . Endogenous rythropoietin correlates with blood pressure in essential[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 1997, 29 (3): 376- 382. |
| 20 | Grote BN , Verweij N , Klip IT , et al. Erythropoietin in the general population: reference ranges and clinical, biochemical and genetic correlates[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10 (4): e125215. |
| 21 | Muhammad TG , Haroon ZH , Younas M , et al. Correlation of serum erythropoietin levels with different stages of diabetic reti-nopathy[J]. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak, 2023, 33 (4): 380- 384. |
| 22 | Hämäläinen P , Saltevo J , Kautiainen H , et al. Erythropoietin, ferritin, haptoglobin, hemoglobin and transferrin receptor in metabolic syndrome: A case control study[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2012, 11, 116. |
| 23 | Reinhardt M , Dey S , Tom Noguchi C , et al. Non-hematopoietic effects of endogenous erythropoietin on lean mass and body weight regulation[J]. Obesity, 2016, 24 (7): 1530- 1536. |
| 24 | Chiang WF , Hsiao PJ , Wu KL , et al. Investigation of the relationship between lean muscle mass and erythropoietin resistance in maintenance haemodialysis patients: A cross-sectional study[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19 (9): 5704. |
| 25 | Yanamandra U , Senee H , Yanamadra S , et al. Erythropoietin and ferritin response in native highlanders aged 4-19 years from the Leh-Ladakh region of India[J]. Br J Haematol, 2019, 184 (2): 263- 268. |
| 26 | Cai G , Qiu J , Chen S , et al. Hematological, hormonal and fitness indices in youth swimmers: Gender-related comparisons[J]. J Hum Kinet, 2019, 70, 69- 80. |
| 27 | Ershler WB , Sheng S , Mckelvey J , et al. Serum erythropoietin and aging: A longitudinal analysis[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2005, 53 (8): 1360- 1365. |
| 28 | Sinkeler SJ , Zelle DM , Homan van der Heide JJ , et al. Endogenous plasma erythropoietin, cardiovascular mortality and all-cause mortality in renal transplant recipients[J]. Am J Transplant, 2012, 12 (2): 485- 491. |
| 29 | Szummer K , Lindahl B , Sylven C , et al. Relationship of plasma erythropoietin to long-term outcome in acute coronary syndrome[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2010, 143 (2): 165- 170. |
| 30 | Grote BN , van der Wal HH , Klip IT , et al. High serum erythropoietin levels are related to heart failure development in subjects from the general population with albuminuria: Data from PREVEND[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2016, 18 (7): 814- 821. |
| [1] | Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG, Qian ZHANG. Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | Ye YAN,Xiaolong LI,Haizhui XIA,Xuehua ZHU,Yuting ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ke LIU,Cheng LIU,Lulin MA. Analysis of risk factors for long-term overactive bladder after radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [3] | Yan CHEN,Kuangmeng LI,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG,Jianxing CHENG,Zhongjie ZHENG,Wenhao TANG,Lianming ZHAO,Haitao ZHANG,Hui JIANG,Haocheng LIN. Retrospective study on the impact of penile corpus cavernosum injection test on penile vascular function [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [4] | Bo PANG,Tongjun GUO,Xi CHEN,Huaqi GUO,Jiazhang SHI,Juan CHEN,Xinmei WANG,Yaoyan LI,Anqi SHAN,Hengyi YU,Jing HUANG,Naijun TANG,Yan WANG,Xinbiao GUO,Guoxing LI,Shaowei WU. Personal nitrogen oxides exposure levels and related influencing factors in adults over 35 years old in Tianjin and Shanghai [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 700-707. |
| [5] | Jing HE,Zhongze FANG,Ying YANG,Jing LIU,Wenyao MA,Yong HUO,Wei GAO,Yangfeng WU,Gaoqiang XIE. Relationship between lipid metabolism molecules in plasma and carotid atheroscle-rotic plaques, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and dietary factors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 722-728. |
| [6] | Jing CHEN,Rui SHAN,Wucai XIAO,Xiaorui ZHANG,Zheng LIU. Association between self-control and co-occurrence of depressive symptoms and overweight or obesity during adolescence and early adulthood: A ten-year prospective cohort study based on national surveys [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 397-402. |
| [7] | Shan CAI,Yihang ZHANG,Ziyue CHEN,Yunfe LIU,Jiajia DANG,Di SHI,Jiaxin LI,Tianyu HUANG,Jun MA,Yi SONG. Status and pathways of factors influencing physical activity time among elementary and junior high school students in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 403-410. |
| [8] | Zuhong ZHANG,Tianjiao CHEN,Jun MA. Associations between puberty timing and cardiovascular metabolic risk factors among primary and secondary students [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 418-423. |
| [9] | Zuoxiang LIU,Xiaowei CHEN,Houyu ZHAO,Siyan ZHAN,Feng SUN. Cardiovascular safety of sitagliptin added to metformin in real world patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 424-430. |
| [10] | Tianjing ZHOU,Qiuping LIU,Minglu ZHANG,Xiaofei LIU,Jiali KANG,Peng SHEN,Hongbo LIN,Xun TANG,Pei GAO. Comparison of initiation of antihypertensive therapy strategies for primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases in Chinese population: A decision-analytic Markov modelling study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 441-447. |
| [11] | Yuting LIN,Huali WANG,Yu TIAN,Litong GONG,Chun CHANG. Factors influencing cognitive function among the older adults in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [12] | Jinrong ZHU,Yana ZHAO,Wei HUANG,Weiwei ZHAO,Yue WANG,Song WANG,Chunyan SU. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 infection in patients undergoing hemodialysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [13] | Zhanhong LAI,Jiachen LI,Zelin YUN,Yonggang ZHANG,Hao ZHANG,Xiaoyan XING,Miao SHAO,Yuebo JIN,Naidi WANG,Yimin LI,Yuhui LI,Zhanguo LI. A unicenter real-world study of the correlation factors for complete clinical response in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 284-292. |
| [14] | Xiaoqian SI,Xiujuan ZHAO,Fengxue ZHU,Tianbing WANG. Risk factors for acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with traumatic hemorrhagic shock [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 307-312. |
| [15] | Yangyang LI,Lin HOU,Zijun MA,Shanyamei HUANG,Jie LIU,Chaomei ZENG,Jiong QIN. Association of pregnancy factors with cow's milk protein allergy in infants [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 144-149. |
|
||