Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 284-290. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation between streptococcal infection and renal damage in children with Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis
Ziwei WANG1, Min LI1, Hui GAO1,2, Fang DENG1,2,3,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Pediatrics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, China
2. Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for Birth Population Health, Hefei 230032, China
3. Department of Nephrology, Anhui Provincial Children's Hospital, Hefei 230051, China
CLC Number:
- R726.9
| 1 |
Hetland LE , Susrud KS , Lindahl KH , et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura: A literature review[J]. Acta Derm Venereol, 2017, 97 (10): 1160- 1166.
doi: 10.2340/00015555-2733 |
| 2 |
Aalberse J , Dolman K , Ramnath G , et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura in children: An epidemiological study among Dutch paediatricians on incidence and diagnostic criteria[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2007, 66 (12): 1648- 1650.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.069187 |
| 3 |
Arslansoyu Çamlar S , Soylu A , Akil I· , et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis and acute rheumatic carditis after group A β-haemolytic streptococcal infection[J]. Paediatr Int Child Health, 2018, 38 (1): 73- 75.
doi: 10.1080/20469047.2017.1284394 |
| 4 |
al-Sheyyab M , Batieha A , el-Shanti H , et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura and streptococcal infection: A prospective case-control study[J]. Ann Trop Paediatr, 1999, 19 (3): 253- 255.
doi: 10.1080/02724939992329 |
| 5 | Chan H , Tang YL , Lv XH , et al. Risk factors associated with renal involvement in childhood Henoch-Schönlein purpura: A meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11 (11): 1- 21. |
| 6 | 曹芳, 邓芳, 董扬, 等. 血清胱抑素C水平在儿童过敏性紫癜肾损害评价中的意义[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2014, 49 (10): 1517- 1520. |
| 7 | 寻劢, 李志辉, 段翠蓉, 等. 五种常见病原体感染与紫癜性肾炎患儿肾小管-间质损伤的相关性研究[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2014, 15 (3): 216- 218. |
| 8 |
Szeto CC , Choi PC , To KF , et al. Grading of acute and chronic renal lesions in Henoch-Schönlein purpura[J]. Mod Pathol, 2001, 14 (7): 635- 640.
doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3880364 |
| 9 | Kawasaki Y , Suzuki J , Sakai N , et al. Clinical and pathological features of children with Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis: Risk factors associated with poor prognosis[J]. Clin Nephrol, 2003, 60 (3): 153- 160. |
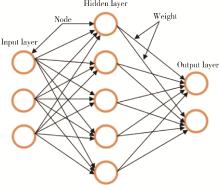
| 10 | Renganathan V . Overview of artificial neural network models in the biomedical domain[J]. Bratisl Lek Listy, 2019, 120 (7): 536- 540. |
| 11 |
Koskela M , Ylinen E , Autio-Harmainen H , et al. Prediction of renal outcome in Henoch-Schönlein nephritis based on biopsy findings[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2020, 35 (4): 659- 668.
doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04415-3 |
| 12 | 彭启迪, 袁丽萍, 邓芳, 等. 酸敏感离子通道在过敏性紫癜肾炎和IgA肾病肾组织中的表达及意义[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2016, 51 (4): 578- 582. |
| 13 | 李文安, 刘凯, 江帆, 等. 急性失代偿性心力衰竭患者血清碱性磷酸酶与肾功能恶化的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21 (7): 818- 821. |
| 14 | Bérubé MD , Blais N , Lanthier S . Neurologic manifestations of Henoch-Schönlein purpura[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2014, 120, 1101- 1111. |
| 15 | 钦云峰, 闵芳梅. 紫癜性肾炎儿童凝血和纤溶系统的变化特点及其临床意义[J]. 中国基层医药, 2019, 26 (23): 2903- 2906. |
| 16 | Shao WX , Ye Q , Wang XJ . Application value of laboratory indexes in the differential diagnosis of Henoch-Schönlein purpura[J]. Z Rheumatol, 2017, 76 (4): 351- 356. |
| 17 | Delbet JD , Hogan J , Aoun B , et al. Clinical outcomes in children with Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis without crescents[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2017, 32 (7): 1193- 1199. |
| [1] | Minting DENG, Nan WANG, Bin XIA, Yuming ZHAO, Junxia ZHU. Factors associated with spontaneous re-eruption of traumatically intruded permanent anterior teeth in children and adolescents [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(1): 148-153. |
| [2] | Yingting YANG, Ruozhu LI, Guili DOU, Yue LEI, Bin XIA. A randomized controlled trial of iRoot BP Plus used as pulp capping agent in the complex fracture of young permanent tooth [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1083-1088. |
| [3] | Shuangyun ZHAO, Siyu ZOU, Xueying LI, Lijuan SHEN, Hong ZHOU. Evaluation of reliability and validity of Chinese version of a short-form of Health Literacy Dental scale (HeLD-14) in the application among parents of preschool children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [4] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [5] | Zhihan YUE,Na HAN,Zheng BAO,Jinlang LYU,Tianyi ZHOU,Yuelong JI,Hui WANG,Jue LIU,Haijun WANG. A prospective cohort study of association between early childhood body mass index trajectories and the risk of overweight [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [6] | Xiuwen FEI,Si LIU,Bo WANG,Aimei DONG. Clinical characteristics and treatment in adults and children with histiocytic necroti-zing lymphadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 533-540. |
| [7] | Xiao-jin YAN,Yun-fei LIU,Ning MA,Jia-jia DANG,Jing-shu ZHANG,Pan-liang ZHONG,Pei-jin HU,Yi SONG,Jun MA. Assessment of prevalence of malnutrition among Chinese primary and secondary school students and analysis of policy effect during the period of the Program for the Development of Chinese Children 2011-2020 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [8] | Xiao-yi MI,Shan-shan HOU,Zi-yuan FU,Mo ZHOU,Xin-xuan LI,Zhao-xue MENG,Hua-fang JIANG,Hong Zhou. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of adverse childhood experiences international questionnaire in parents of preschool children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 408-414. |
| [9] | Meng-jie CUI,Qi MA,Man-man CHEN,Tao MA,Xin-xin WANG,Jie-yu LIU,Yi ZHANG,Li CHEN,Jia-nuo JIANG,Wen YUAN,Tong-jun GUO,Yan-hui DONG,Jun MA,Yi XING. Association between different growth patterns and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents aged 7 to 17 years [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [10] | Jia-jia DANG,Shan CAI,Pan-liang ZHONG,Ya-qi WANG,Yun-fei LIU,Di SHI,Zi-yue CHEN,Yi-hang ZHANG,Pei-jin HU,Jing LI,Jun MA,Yi SONG. Association of outdoor artificial light at night exposure with overweight and obesity among children and adolescents aged 9 to 18 years in China [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [11] | Hui LI,Yang-xu GAO,Shu-lei WANG,Hong-xin YAO. Surgical complications of totally implantable venous access port in children with malignant tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [12] | Jing LIU,Ai-dong LU,Ying-xi ZUO,Jun WU,Zhi-zhuo HUANG,Yue-ping JIA,Ming-ming DING,Le-ping ZHANG,Jiong QIN. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of seizures in 75 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [13] | Ya-xi CUI,Jun-bao DU,Qing-you ZHANG,Ying LIAO,Ping LIU,Yu-li WANG,Jian-guang QI,Hui YAN,Wen-rui XU,Xue-qin LIU,Yan SUN,Chu-fan SUN,Chun-yu ZHANG,Yong-hong CHEN,Hong-fang JIN. A 10-year retrospective analysis of spectrums and treatment options of orthostatic intolerance and sitting intolerance in children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 954-960. |
| [14] | Tao MA,Yan-hui LI,Man-man CHEN,Ying MA,Di GAO,Li CHEN,Qi MA,Yi ZHANG,Jie-yu LIU,Xin-xin WANG,Yan-hui DONG,Jun MA. Associations between early onset of puberty and obesity types in children: Based on both the cross-sectional study and cohort study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 961-970. |
| [15] | Yan-yan DU,Jian WANG,Lan HE,Li-na JI,Xi-wei XU. Kawasaki disease complicated with mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 756-761. |
|
||