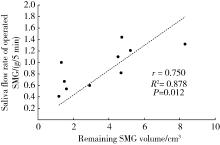
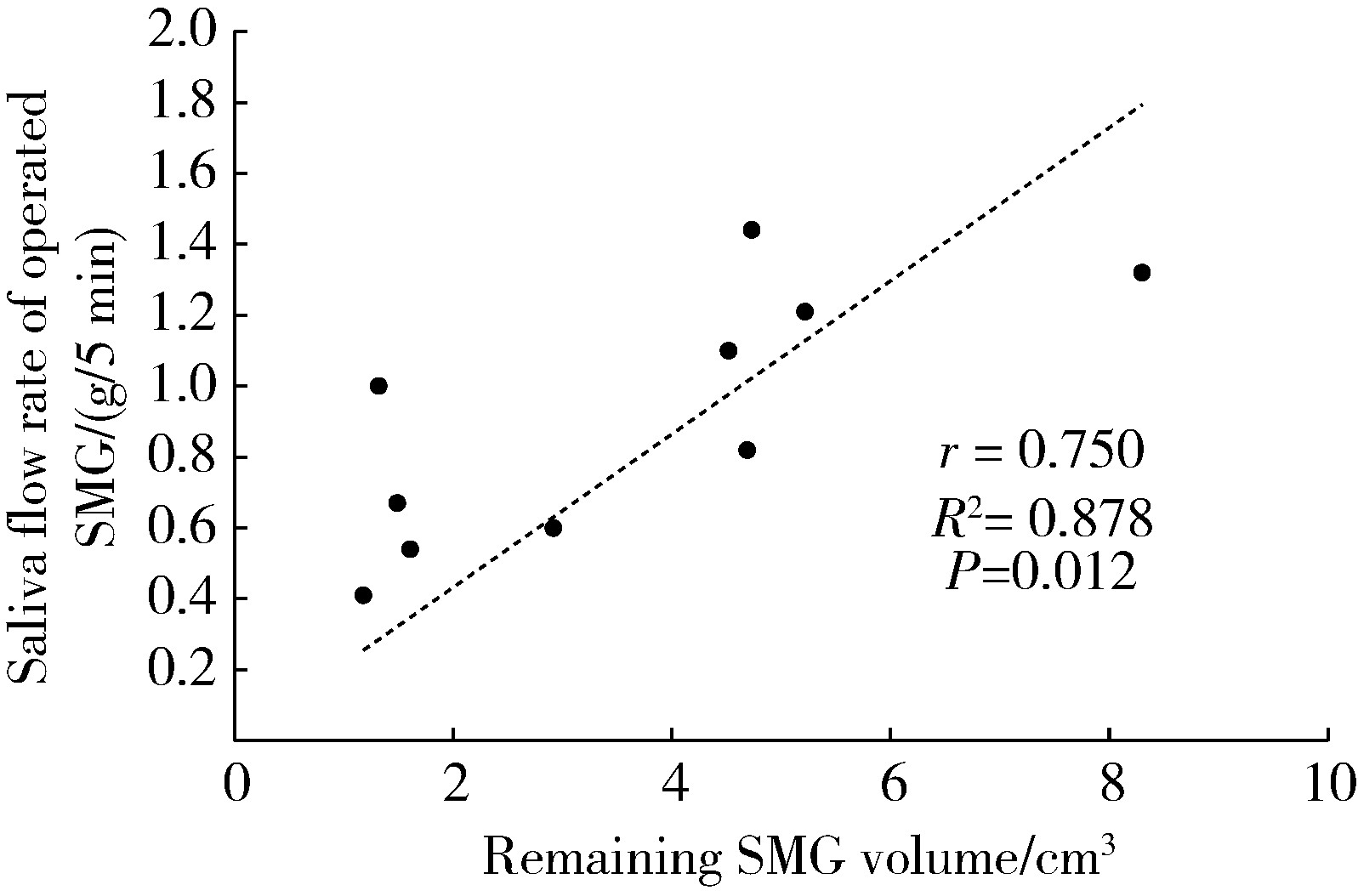
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 334-339. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
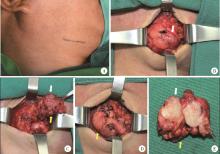
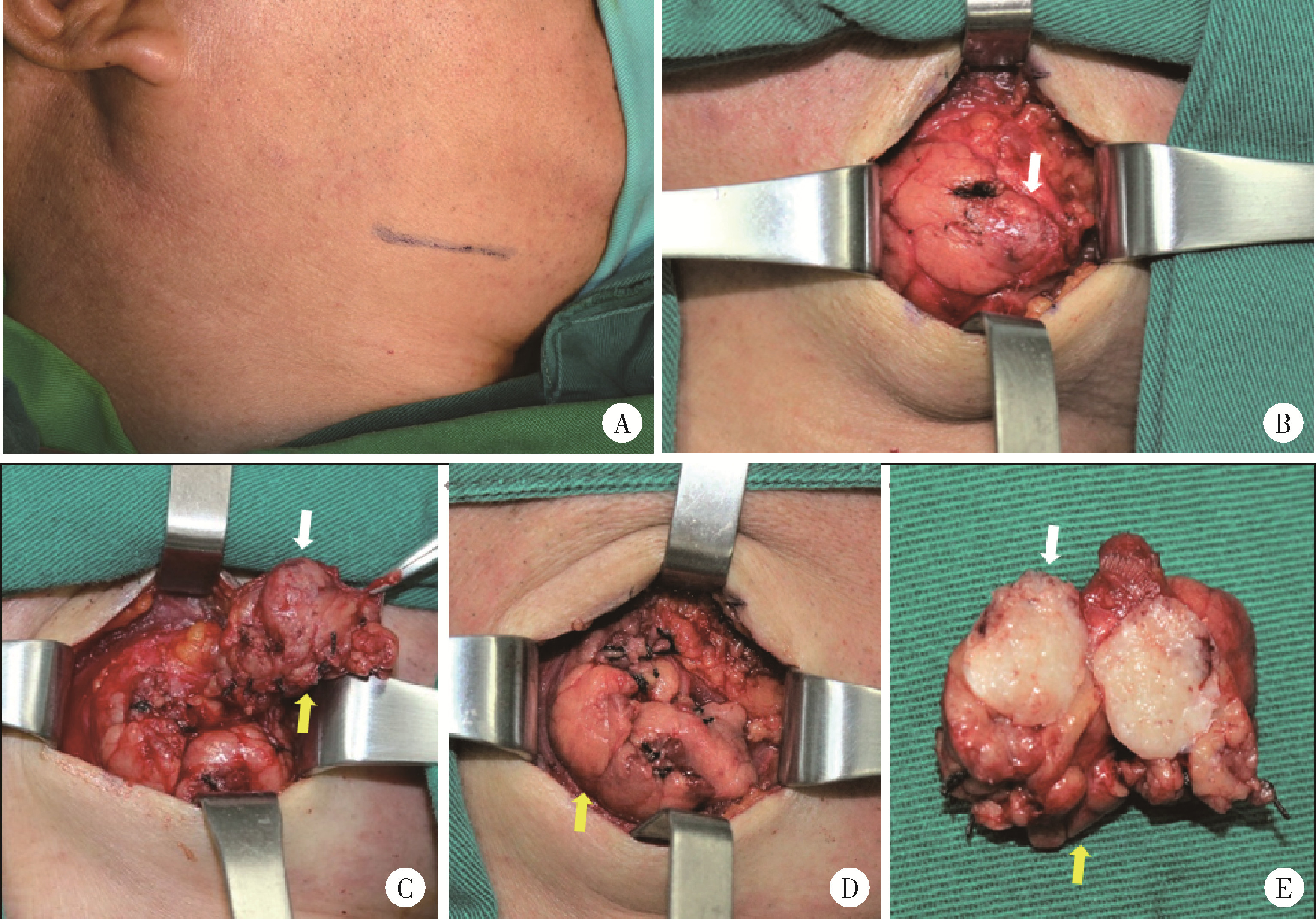
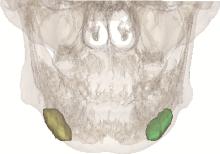
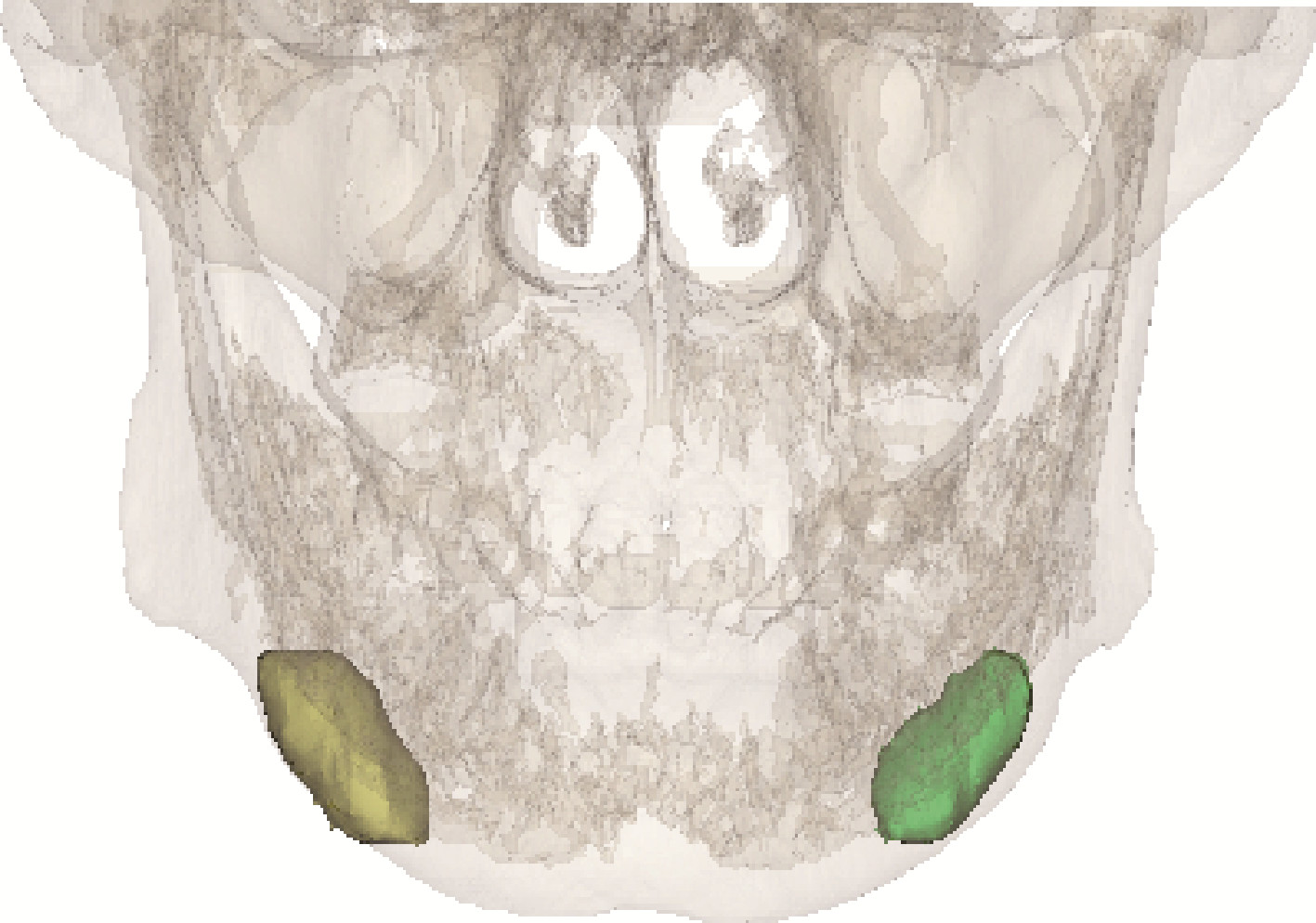
Clinical outcomes of partial sialoadenectomy for the treatment of benign tumors in the submandibular gland
Yuanyuan YANG1,2, Shanshan ZHANG2, Guangyan YU3, Huijun YANG2,*( ), Hongyu YANG2,*(
), Hongyu YANG2,*( )
)
- 1. Department of General Dentistry Ⅱ, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Research Center of Oral Biomaterials and Digital Medical Devices & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Stomatological Center, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital & Guangdong Province High-level Clinical Key Specialty & Guangdong Province Engineering Research Center of Oral Disease Diagnosis and Treatment, Shenzhen 518036, Guangdong, China
3. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
- R782.7
| 1 |
Roblegg E , Coughran A , Sirjani D . Saliva: An all-rounder of our body[J]. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 2019, 142, 133- 141.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.06.016 |
| 2 |
Carpenter GH . The secretion, components, and properties of saliva[J]. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol, 2013, 4, 267- 276.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-030212-182700 |
| 3 |
de Brito Neves CP , Lira RB , Chulam TC , et al. Retroauricular endoscope-assisted versus conventional submandibular gland excision for benign and malignant tumors[J]. Surg Endosc, 2020, 34 (1): 39- 46.
doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-07173-3 |
| 4 |
Cammaroto G , Vicini C , Montevecchi F , et al. Submandibular gland excision: From external surgery to robotic intraoral and extraoral approaches[J]. Oral Dis, 2020, 26 (5): 853- 857.
doi: 10.1111/odi.13340 |
| 5 |
Dhiwakar M , Ronen O , Malone J , et al. Feasibility of submandi-bular gland preservation in neck dissection: A prospective anatomic-pathologic study[J]. Head Neck, 2011, 33 (5): 603- 609.
doi: 10.1002/hed.21499 |
| 6 |
Proctor GB , Shaalan AM . Disease-induced changes in salivary gland function and the composition of saliva[J]. J Dent Res, 2021, 100 (11): 1201- 1209.
doi: 10.1177/00220345211004842 |
| 7 |
Yu GY , Ma DQ , Liu XB , et al. Local excision of the parotid gland in the treatment of Warthin' s tumour[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1998, 36 (3): 186- 189.
doi: 10.1016/S0266-4356(98)90495-8 |
| 8 |
Roh JL , Park CI . Gland-preserving surgery for pleomorphic adenoma in the submandibular gland[J]. Br J Surg, 2008, 95 (10): 1252- 1256.
doi: 10.1002/bjs.6306 |
| 9 |
Xu H , Mao C , Liu JM , et al. Microanatomic study of the vascular and duct system of the submandibular gland[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2011, 69 (4): 1103- 1107.
doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2010.03.006 |
| 10 |
Min R , Zun Z , Siyi L , et al. Gland-preserving surgery can effectively preserve gland function without increased recurrence in treatment of benign submandibular gland tumour[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2013, 51 (7): 615- 619.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2013.01.009 |
| 11 |
Yang TL , Ko JY , Lou PJ , et al. Gland-preserving robotic surgery for benign submandibular gland tumours: A comparison between robotic and open techniques[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014, 52 (5): 420- 424.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.02.015 |
| 12 |
Ge N , Peng X , Zhang L , et al. Partial sialoadenectomy for the treatment of benign tumours in the submandibular gland[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016, 45 (6): 750- 755.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2015.12.013 |
| 13 |
李巍, 孙志鹏, 刘筱菁, 等. 腮腺和颌下腺体积的测量[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014, 46 (2): 288- 293.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2014.02.022 |
| 14 |
Huang L , Wang Z , Shan Z , et al. Nasal asymmetry changes during growth and development in 6- to 12-year-old children with repaired unilateral cleft lip and palate: A 3D computed tomography analysis[J]. J Anat, 2022, 240 (1): 155- 165.
doi: 10.1111/joa.13538 |
| 15 |
俞光岩. 要重视下颌下腺功能器官的保护[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2017, 52 (4): 204- 205.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2017.04.002 |
| 16 |
Ethunandan M , Davies B , Pratt CA , et al. Primary epithelial submandibular salivary gland tumours: Review of management in a district general hospital setting[J]. Oral Oncol, 2009, 45 (2): 173- 176.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2008.04.011 |
| 17 |
Li LJ , Li Y , Wen YM , et al. Clinical analysis of salivary gland tumor cases in West China in past 50 years[J]. Oral Oncol, 2008, 44 (2): 187- 192.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2007.01.016 |
| 18 |
Tian Z , Li L , Wang L , et al. Salivary gland neoplasms in oral and maxillofacial regions: A 23-year retrospective study of 6 982 cases in an eastern Chinese population[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2010, 39 (3): 235- 242.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2009.10.016 |
| 19 |
Gao M , Hao Y , Huang MX , et al. Salivary gland tumours in a northern Chinese population: A 50-year retrospective study of 7 190 cases[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 46 (3): 343- 349.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2016.09.021 |
| 20 |
Hu Y , Zheng C , Cao R , et al. Resection of benign tumours of the submandibular gland with harmonic scalpel-assisted minimally extracapsular dissection[J]. J Int Med Res, 2020, 48 (1): 300060519892783.
doi: 10.1177/0300060519892783 |
| 21 |
Li L , Gao XL , Song YZ , et al. Anatomy of arteries and veins of submandibular glands[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2007, 120 (13): 1179- 1182.
doi: 10.1097/00029330-200707010-00013 |
| 22 |
Garcia-Serrano G , Moñux A , Maranillo E , et al. Vascular clinical anatomy of the submandibular gland[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2020, 48 (6): 582- 589.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2020.04.004 |
| 23 | 王张嵩, 谢舒乐, 张汉卿, 等. 2 456例唾液腺肿瘤临床病理分析[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2020, 28 (5): 298- 302. |
| 24 | Andreasen S , Therkildsen MH , Bjørndal K , et al. Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland 1985-2010: A Danish nationwide study of incidence, recurrence rate, and malignant transformation[J]. Head Neck, 2016, 38 (Suppl 1): E1364- E1369. |
| 25 | Dai L , Lou W , Fang Q , et al. Recurrent pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland: Experience of 128 patients with first recurrence[J]. J Oncol, 2020, 2020, 6645340. |
| 26 |
Valstar MH , de Ridder M , van den Broek EC , et al. Salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma in the Netherlands: A nationwide observational study of primary tumor incidence, malignant transformation, recurrence, and risk factors for recurrence[J]. Oral Oncol, 2017, 66, 93- 99.
doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.01.004 |
| 27 |
Roldan-Valadez E , Garcia-Ulloa AC , Gonzalez-Gutierrez O , et al. 3D volumetry comparison using 3T magnetic resonance imaging between normal and adenoma-containing pituitary glands[J]. Neurol India, 2011, 59 (5): 696- 699.
doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.86543 |
| 28 |
王怡平, 蔡志刚, 彭歆, 等. 下颌下腺质量和体积的实体体外检测[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2021, 53 (1): 126- 132.
doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.01.019 |
| 29 |
Hong X , Zhang YY , Li W , et al. Treatment of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis: Outcomes of glucocorticoid therapy combined with steroid-sparing agents[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2018, 20 (1): 12.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1507-6 |
| [1] | Yifan KANG, Yanjun GE, Xiaoming LV, Shang XIE, Xiaofeng SHAN, Zhigang CAI. One-stage mandibular reconstruction combining iliac flap with immediate implant-based denture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(1): 78-84. |
| [2] | Wenjing LI,Baozhou ZHANG,Heng LI,Liangpeng LAI,Hui DU,Ning SUN,Xiaofeng GONG,Ying LI,Yan WANG,Yong WU. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis for end-stage ankle and hindfoot arthropathy: Short- and mid-term clinical outcomes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [3] | Xue ZOU,Xiao-juan BAI,Li-qing ZHANG. Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [4] | Min QIU,You-long ZONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Bin YANG,Chu-xiao XU,Zheng-hui SUN,Min LU,Lei ZHAO,Jian LU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA. Treatment outcome of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in patients with renal tumors of moderate to high complexity [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [5] | Lei WANG,Tian-dong HAN,Wei-xing JIANG,Jun LI,Dao-xin ZHANG,Ye TIAN. Comparison of safety and effectiveness of active migration technique and in situ lithotripsy technique in the treatment of 1-2 cm upper ureteral calculi by flexible ure-teroscopy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 553-557. |
| [6] | LI Wei-hao,LI Wei,ZHANG Xue-min,LI Qing-le,JIAO Yang,ZHANG Tao,JIANG Jing-jun,ZHANG Xiao-ming. Comparison of the outcomes between open and hybrid approaches in the treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms repair [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 177-181. |
| [7] | Yan-fang JIANG,Jian WANG,Yong-jian WANG,Jia LIU,Yin PEI,Xiao-peng LIU,Ying-fang AO,Yong MA. Mid-to-long term clinical outcomes and predictors after anterior cruciate ligament revision [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 857-863. |
| [8] | Zheng-da ZHU,Yan GAO,Wen-xiu HE,Xin FANG,Yang LIU,Pan WEI,Zhi-min YAN,Hong HUA. Efficacy and safety of Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for the treatment of erosive oral lichen planus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 964-969. |
| [9] | Xiao LI,Jia-zeng SU,Yan-yan ZHANG,Li-qi ZHANG,Ya-qiong ZHANG,Deng-gao LIU,Guang-yan YU. Inflammation grading and sialoendoscopic treatment of131I radioiodine-induced sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(3): 586-590. |
| [10] | Ying ZHAN,Yi-tian DU,Zhen-zhen YANG,Chun-li ZHANG,Xian-rong QI. Preparation and characterization of paclitaxel microspheres in situ gel and its antitumor efficacy by local injection [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 477-486. |
| [11] | Ze-chuan YANG,Chao-xu LIU,Yang LIN,Wei-hua HU,Wen-jian CHEN,Feng LI,Heng ZENG. All levels miniplate fixation and a modified hybrid fixation method in expansive open-door cervical laminoplasty: a retrospective comparative study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 187-193. |
| [12] | Wen-zhe YOU,Gui-li DOU,Bin XIA. Two-year outcomes and the influence factors of indirect pulp treatment in primary teeth: a retrospective study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 65-69. |
| [13] | Xin yi LI,Jin xia ZHAO,Xiang yuan LIU. Diagnosis and treatment of antiphospholipid antibody:related recurrent spontaneous abortion and analysis of therapeutic drugs and pregnancy outcome in 75 patients with antiphospholipid syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(6): 956-961. |
| [14] | ZHANG Ming-ming, ZHENG Ying-dong, LIANG Yu-hong. A prognostic model for assessment of outcome of root canal treatment in teeth with pulpitis or apical periodontitis#br# [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 123-130. |
| [15] | LI Xu, LI Feng-long, LU Yi, ZHU Yi-ming, GUO Si-yi, LI Yi-jun, JIANG Chun-yan. Clinical study on locking plate for the treatment of non-osteoporotic complex proximal humeral fractures [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 855-860. |
|
||