Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 903-910. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.05.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
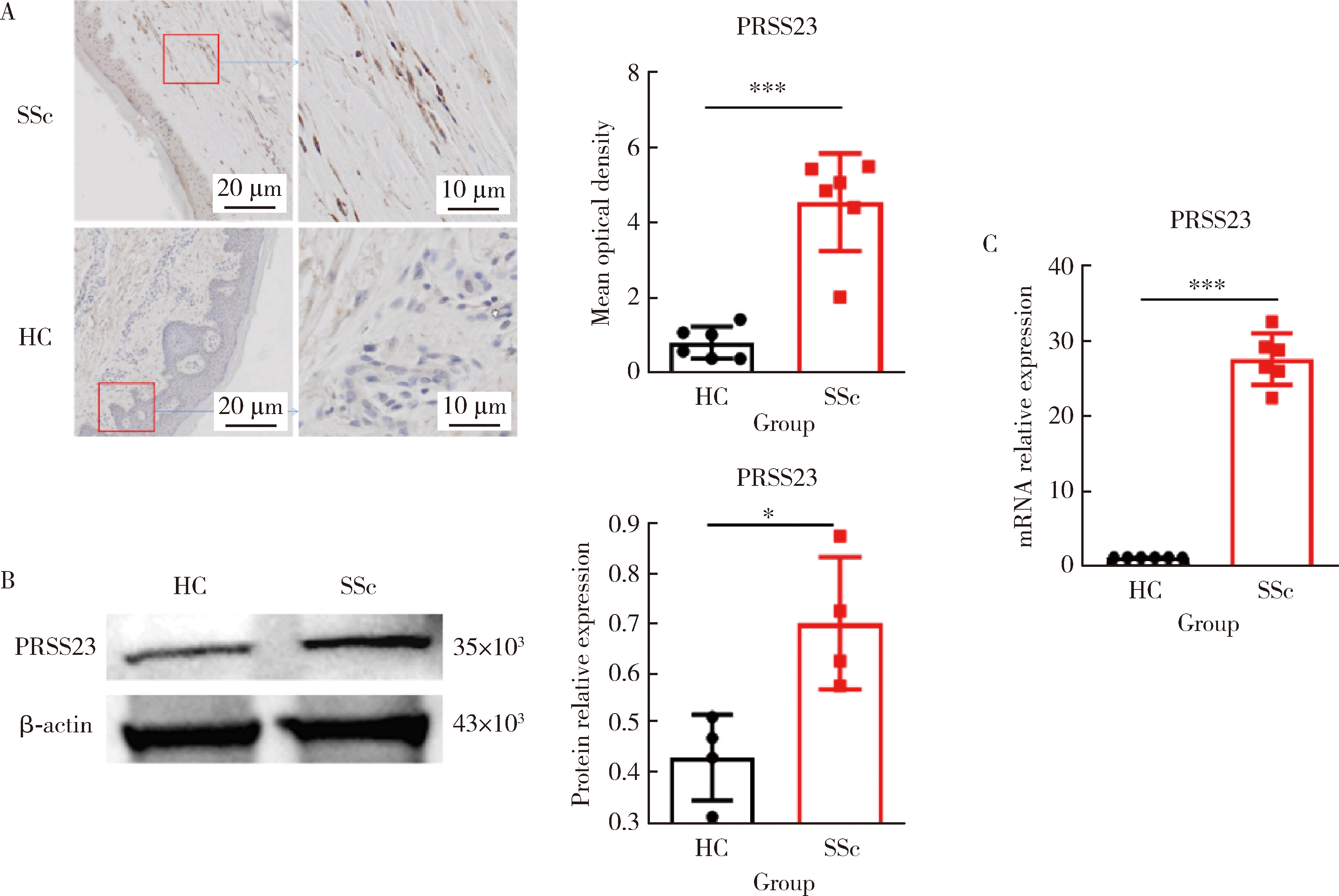
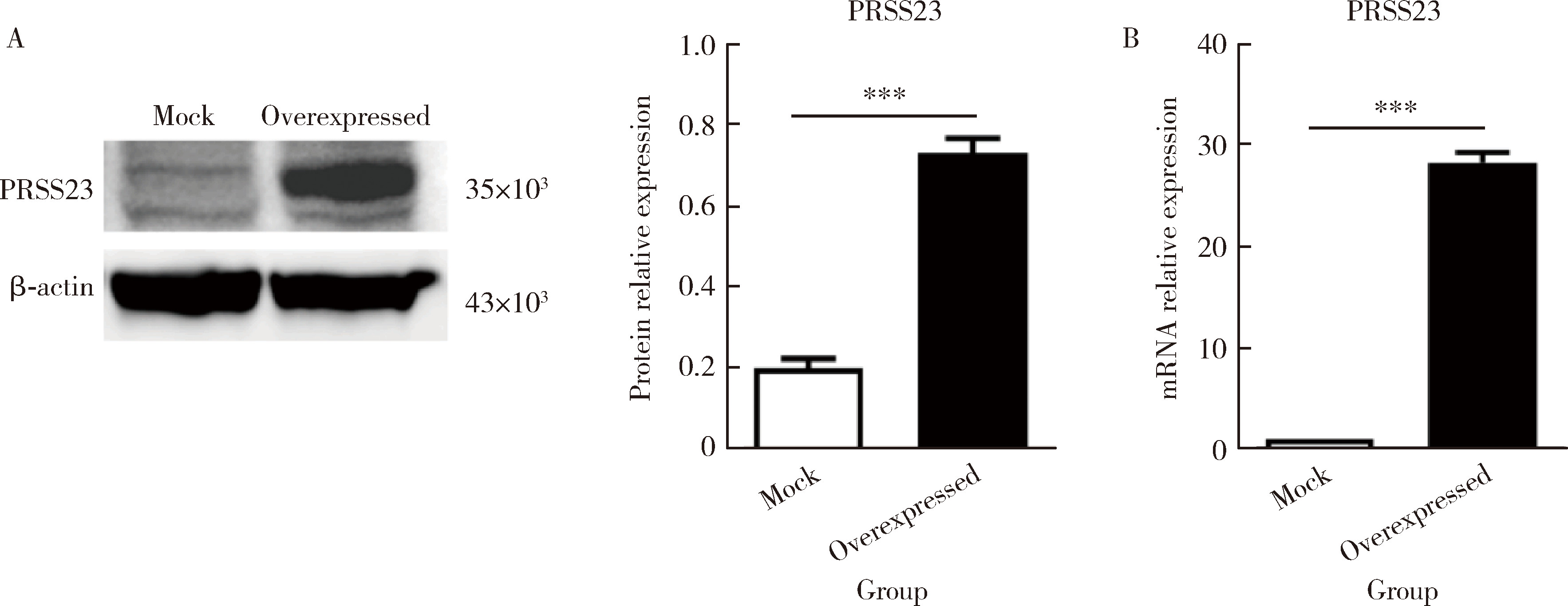
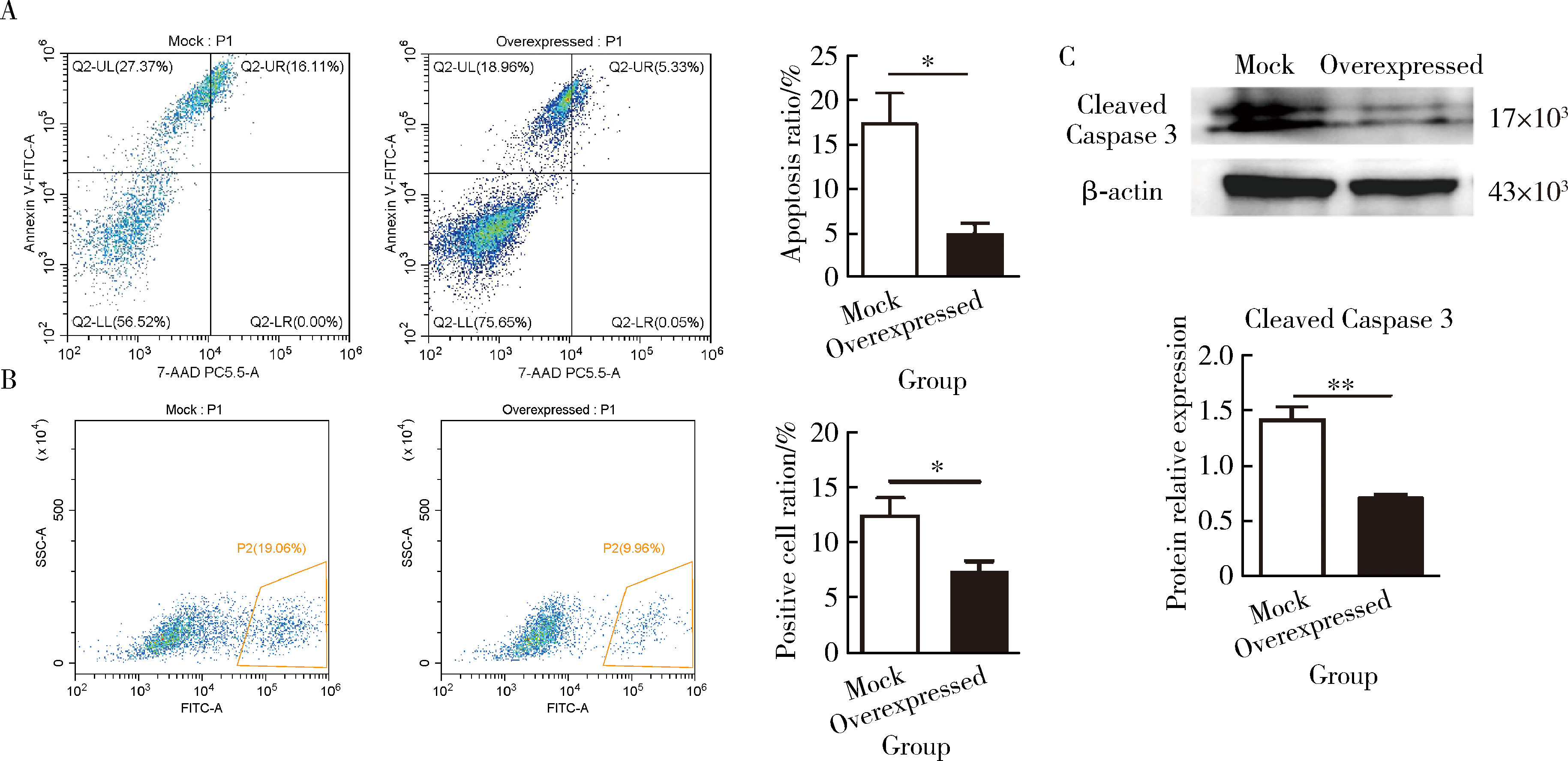
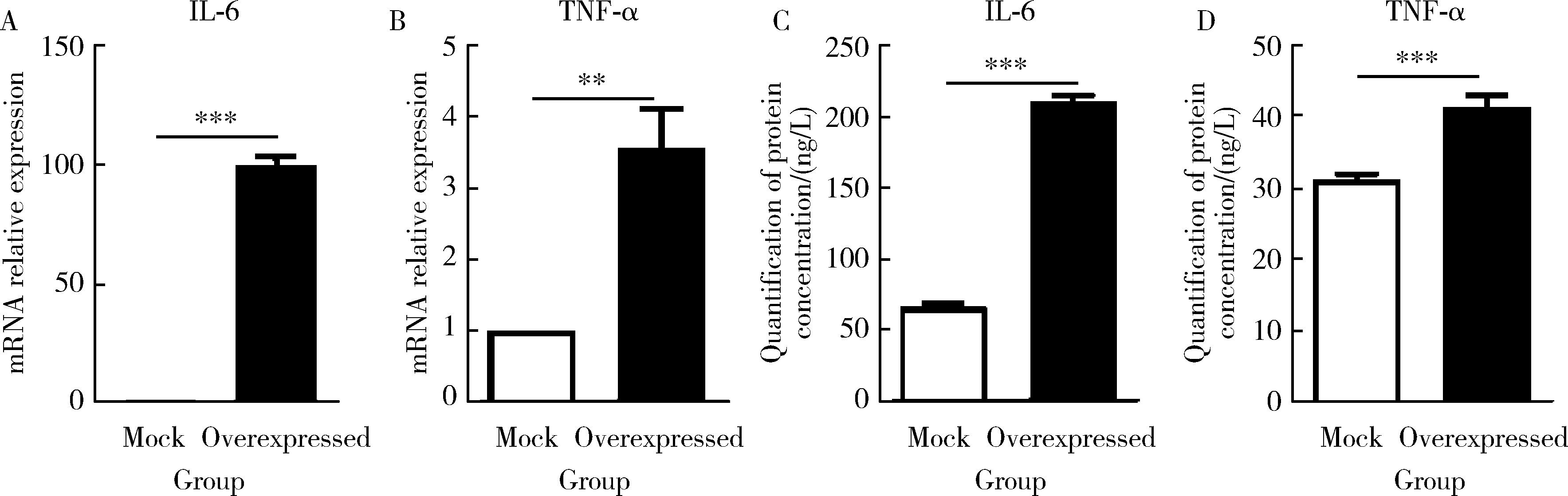
Pathogenesis and mechanism of serine protease 23 in skin fibrosis of systemic sclerosis
Xiandun YUAN, Zhaohua LI, Dan XU, Ting LI, Dan FANG, Rong MU*( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R593.2
| 1 |
doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.127621 |
| 2 |
doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0324-5 |
| 3 |
doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0801-4 |
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24607-6 |
| 6 |
doi: 10.3390/ijms20030619 |
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.02.008 |
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24110-y |
| 12 |
doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01165-9 |
| 13 |
doi: 10.1186/ar4112 |
| 14 |
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00584.x |
| 15 |
doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8050101 |
| 16 |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.09.014 |
| 17 |
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.75876 |
| 18 |
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200955 |
| 19 |
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00232-4 |
| 20 |
doi: 10.1007/s10753-008-9067-1 |
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
doi: 10.7150/thno.60540 |
| 24 |
doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-0922-4 |
| 25 |
doi: 10.1242/dmm.044164 |
| 26 |
doi: 10.1186/s41232-017-0048-3 |
| [1] | Wei PAN, Yun LI, Junjia LUO, Chun LI, Hua YE, Xue LI, Yuan JIA. COVID-19 vaccines efficacy and infection features in patients with systemic sclerosis: A single-center cohort study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1041-1046. |
| [2] | Kelin ZHAO, Xue XIA, Naixu SHI, Han ZHOU, Jingwen GAI, Ping LI. Expression and significance of ferroptosis marker 4-HNE in in vitro model of systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 950-955. |
| [3] | Shan HE,Xin CHEN,Qi CHENG,Lingjiang ZHU,Peiyu ZHANG,Shuting TONG,Jing XUE,Yan DU. Tofacitinib inhibits the transformation of lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts through JAK/STAT3 pathway [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 505-511. |
| [4] | Wen-gen LI,Xiao-dong GU,Rui-qiang WENG,Su-dong LIU,Chao CHEN. Expression and clinical significance of plasma exosomal miR-34-5p and miR-142-3p in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1022-1027. |
| [5] | Yun-chong LIU,Zong-long WU,Li-yuan GE,Tan DU,Ya-qian WU,Yi-meng SONG,Cheng LIU,Lu-lin MA. Mechanism of nuclear protein 1 in the resistance to axitinib in clear cell renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 781-792. |
| [6] | Zhuo-hua LIN,Ru-yi CAI,Yang SUN,Rong MU,Li-gang CUI. Methodology and clinical use of superb microvascular imaging in assessing micro-circulation changes of fingertips in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 636-640. |
| [7] | LOU Xue,LIAO Li,LI Xing-jun,WANG Nan,LIU Shuang,CUI Ruo-mei,XU Jian. Methylation status and expression of TWEAK gene promoter region in peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [8] | GAO Ya-dong,ZHU An,LI Lu-di,ZHANG Tao,WANG Shuo,SHAN Dan-ping,LI Ying-zi,WANG Qi. Cytotoxicity and underlying mechanism of evodiamine in HepG2 cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1107-1114. |
| [9] | MA Xiang-bo,ZHANG Xue-wu,JIA Ru-lin,GAO Ying,LIU Hong-jiang,LIU Yu-fang,LI Ying-ni. Application of lymphocytes test in peripheral blood of patients with systemic sclerosis during the treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 721-727. |
| [10] | GAO Hong-yu,MENG Huan-xin,HOU Jian-xia,HUANG Bao-xin,LI Wei. Expression and distribution of calprotectin in healthy and inflamed periodontal tissues [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 744-749. |
| [11] | Jing ZHAO,Feng SUN,Yun LI,Xiao-zhen ZHAO,Dan XU,Ying-ni LI,Yu-hui LI,Xiao-lin SUN. Significance of anti-tubulin-α-1C autoantibody in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1009-1013. |
| [12] | Lei-zhen SU,Jie CHEN,Xian LI,Ping JI. Effects of salinomycin on proliferation and apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 902-906. |
| [13] | Liang GENG,Jing LV,Jing FAN. Effect of Fei-Liu-Ping ointment combined with cyclophosphamide on lung cancer cell proliferation and acidic microenvironment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 247-253. |
| [14] | Bing-qing SHI,Xiao-jing YUAN,Yu-ming ZHAO. Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate and ethanolic extracts of Shandong propolis on the biological properties of human dental pulp fibroblasts [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1108-1114. |
| [15] | Hong-lin ZHU,Qian DU,Wei-lin CHEN,Xiao-xia ZUO,Quan-zhen LI,Si-jia LIU. Altered serum cytokine expression profile in systemic sclerosis and its regulatory mechanisms [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 716-722. |
|
||