北京大学学报(医学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 678-683. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.014
肾癌伴下腔静脉瘤栓合并血栓的多种影像学比较
李丽伟1,刘茁2,王国良2,张华3,陈文1,马静1,张丽1,何为4,马潞林2,△( ),王淑敏1,△(
),王淑敏1,△( )
)
- 1. 北京大学第三医院 超声科, 北京 100191
2. 北京大学第三医院 泌尿外科, 北京 100191
3. 北京大学第三医院 临床流行病研究中心, 北京 100191
4. 北京大学第三医院 放射科, 北京 100191
Comparison of various imaging in the diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus combined with bland thrombus
Li-wei LI1,Zhuo LIU2,Guo-liang WANG2,Hua ZHANG3,Wen CHEN1,Jing MA1,Li ZHANG1,Wei HE4,Lu-lin MA2,△( ),Shu-min WANG1,△(
),Shu-min WANG1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Ultrasound, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
3. Research Center of Clinical Epidemiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
4. Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
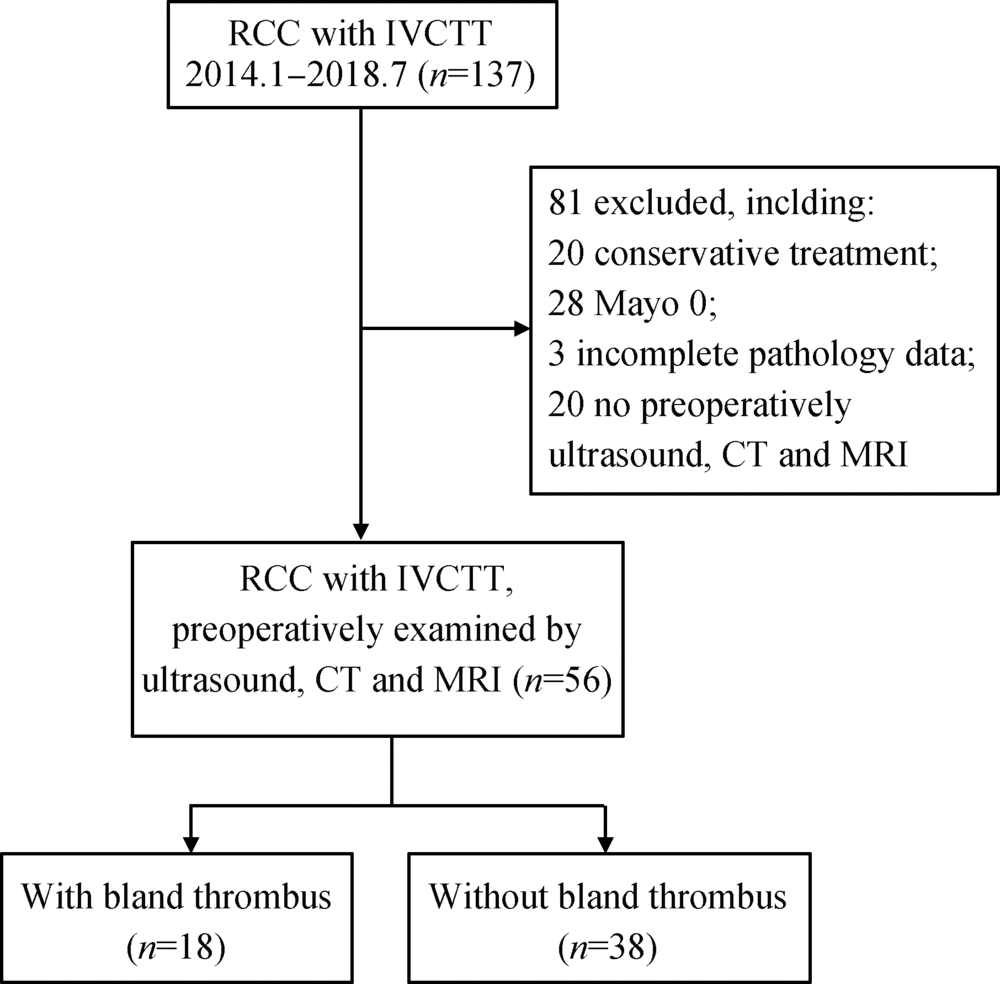
目的:研究肾癌伴下腔静脉瘤栓合并血栓患者的临床及影像资料,分析下腔静脉超声、泌尿系增强CT及增强磁共振3种影像学检查方法对下腔静脉瘤栓伴血栓的诊断效能。方法:选择北京大学第三医院泌尿外科2014年1月至2018年7月的肾癌伴瘤栓病例56例进行回顾性分析,所有患者术前均同时行下腔静脉超声、泌尿系增强CT及增强磁共振检查并完成手术治疗,且术后病理诊断证实为肾癌伴下腔静脉瘤栓。结果:根据术中观察及术后病理诊断证实下腔静脉瘤栓是否合并血栓为标准,将56例患者分为合并血栓组(n=18)及不合并血栓组(n=38)。比较发现,瘤栓合并血栓的患者,瘤栓长度更长[(10.50 ± 5.55) cm vs.(6.66 ± 3.73) cm,P = 0.014];瘤栓直径/下腔静脉(inferior vena cava, IVC)冠状最大径比值更接近1[1.0(0.7,1.0) vs. 0.9 (0.2,1.0), P= 0.004];出现下肢水肿的比例更高[66.7%(12/18) vs.5.3%(2/36),P = 0.005];行下腔静脉节段性切除或下腔静脉横断术的比例更高[66.7%(12/18) vs.15.8%(6/38), P<0.001]。对比下腔静脉超声、泌尿系增强CT及增强磁共振3种影像检查方法,鉴别瘤栓合并血栓,灵敏度最高的是增强磁共振(77.8%),特异性最高的是下腔静脉超声和增强CT(97.4%), 准确性最高的是增强CT及增强磁共振(83.9%),阳性预测值最高的是增强CT(90.9%),阴性预测值最高的是增强磁共振(89.2%)。结论:肾癌伴下腔静脉瘤栓合并血栓的患者,下腔静脉瘤栓长度更长,瘤栓直径/IVC冠状最大径比值更接近1,更易出现下肢水肿。术前需综合多种影像方法,提高诊断的准确率。
中图分类号:
- R737.1
| [1] | 刘茁, 马潞林, 田晓军 , 等. 根治性肾切除术+下腔静脉癌栓取出术治疗Mayo 0~Ⅳ 级下腔静脉癌栓的临床经验[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2017,38(11):842-847. |
| [2] | 刘茁, 马潞林, 田晓军 , 等. 肾癌根治性切除加癌栓取出术治疗Mayo Ⅲ 级下腔静脉癌栓的手术技术及临床经验[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017,49(4):597-602. |
| [3] | 刘茁, 田晓军, 马潞林 . 根治性肾切除术联合Mayo 0-Ⅱ 级静脉癌栓取出术的临床麻醉管理[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2017,25(16):2672-2677. |
| [4] | 刘茁, 马潞林, 田晓军 , 等. 腹腔镜和开放肾癌根治性切除+Mayo Ⅱ 级下腔静脉癌栓取出术11例临床分析[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2017,22(8):603-607. |
| [5] | 马潞林, 刘茁 . 肾癌并肝段和肝以上下腔静脉癌栓的诊治体会[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2017,38(7):481-484. |
| [6] | Blute ML, Leibovich BC, Lohse CM , et al. The mayo clinic experience with surgical management, complications and outcome for patients with renal cell carcinoma and venous tumour thrombus[J] . BJU Int, 2004,94(1):33-41. |
| [7] | Wang M, Ping H, Niu Y , et al. Pure conventional laparoscopic radical nephrectomy with level II vena cava tumor thrombectomy[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2014,40(2):266-273. |
| [8] | 程艳, 蔡欣, 刘基巍 . 恶性肿瘤与血栓形成[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2010,15(4):376-379. |
| [9] | Ayyathurai R, Garciaroig M, Gorin MA , et al. Bland thrombus association with tumour thrombus in renal cell carcinoma: Analysis of surgical significance and role of inferior vena caval interruption[J]. BJU Int, 2013,110(11b):E449-E455. |
| [10] | Hutchinson R, Rew C, Chen G , et al. The adverse survival implications of bland thrombus in renal cell carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus[J]. Urology, 2018,115:119-124. |
| [11] | Blute ML, Boorjian SA, Leibovich BC , et al. Results of inferior vena caval interruption by greenfield filter, ligation or resection during radical nephrectomy and tumor thrombectomy[J]. J Urol, 2007,178(2):440-445. |
| [12] | 马鑫 . 机器人腹腔镜腔静脉瘤栓取出术:新的思考新的策略[J]. 中华腔镜外科杂志: 电子版, 2017,10(5):272-273. |
| [13] | Quencer KB, Friedman T, Sheth R , et al. Tumor thrombus: Incidence, imaging, prognosis and treatment[J]. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther, 2017,7(Suppl 3):S165-S177. |
| [14] | Mukai M, Oka T . Mechanism and management of cancer-associated thrombosis[J]. J Cardiol, 2018,72(2):89-93. |
| [15] | 肾癌伴静脉瘤栓北京专家共识[J]. 微创泌尿外科杂志, 2017: 6(6):321-327. |
| [16] | 宋奕宁, 赵艺超, 李建国 . 下腔静脉肿瘤的超声影像诊断与鉴别[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2018,34(1):37-39. |
| [17] | Tarantino L . Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in differentiating malignant from benign portal vein thrombosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015,21(32):9457-9460. |
| [18] | Sonavane SN, Malhotra G, Asopa R , et al. Role of fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in a case of renal cell carcinoma to differentiate tumor thrombus from bland thrombus[J]. Indian J Nucl Med, 2015,30(4):355-357. |
| [19] | Sharma P, Kumar R, Jeph S , et al. 18F-FDG PET-CT in the diagnosis of tumor thrombus[J]. Nucl Med Commun, 2011,32(9):782-788. |
| [1] | 原晋芳, 王新利, 崔蕴璞, 王雪梅. 尿促黄体生成素在女童中枢性性早熟预测中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(5): 788-793. |
| [2] | 张树栋,谢睿扬. 机器人手术时代的肾癌合并腔静脉瘤栓治疗策略[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 562-564. |
| [3] | 王明瑞,刘军,熊六林,于路平,胡浩,许克新,徐涛. 经皮微通道-微电子肾镜-微超声探针碎石术治疗1.5~2.5 cm肾结石的疗效和安全性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [4] | 杨捷,冯杰莉,张树栋,马潞林,郑清. 经食管超声心动图在肾切除术联合Mayo Ⅲ~Ⅳ级静脉瘤栓取栓术不同手术方式中的临床作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [5] | 舒帆,郝一昌,张展奕,邓绍晖,张洪宪,刘磊,王国良,田晓军,赵磊,马潞林,张树栋. 肾部分切除术治疗囊性肾癌的功能学和肿瘤学结果:单中心回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [6] | 陈延,李况蒙,洪锴,张树栋,程建星,郑仲杰,唐文豪,赵连明,张海涛,姜辉,林浩成. 阴茎海绵体注射试验对阴茎血管功能影响的回顾性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [7] | 汤晓菲,李永红,丁秋玲,孙卓,张阳,王育梅,田美伊,刘坚. 类风湿关节炎患者下肢深静脉血栓发病率及危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [8] | 魏越,姚兰,陆希,王军,蔺莉,刘鲲鹏. 胃超声检查评估剖宫产产妇术前饮用碳水化合物后胃排空的效果[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(6): 1082-1087. |
| [9] | 兰东,刘茁,李宇轩,王国良,田晓军,马潞林,张树栋,张洪宪. 根治性肾切除和静脉癌栓取出术大出血的危险因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 825-832. |
| [10] | 魏越,陆希,张静,刘鲲鹏,王永军,姚兰. 术前2 h口服碳水化合物对妇科腹腔镜特殊体位手术患者胃容量及反流误吸风险的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(5): 893-898. |
| [11] | 彭清,刘佳君,刘焱,尚华,唐果,韩雅欣,龙丽. Padua预测评分和血清白蛋白水平在评估风湿病住院患者静脉血栓栓塞中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 625-630. |
| [12] | 傅强,高冠英,徐雁,林卓华,孙由静,崔立刚. 无症状髋关节前上盂唇撕裂超声与磁共振检查的对比研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [13] | 庄金满,李天润,李选,栾景源,王昌明,冯琦琛,韩金涛. Rotarex旋切导管在股腘动脉狭窄合并血栓形成中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2023, 55(2): 328-332. |
| [14] | 刘蕊,赵金霞,闫良. 类风湿关节炎合并下肢静脉血栓患者的临床特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
| [15] | 侯玉珂,蔡青猛,刘香君,贠泽霖,李春,张学武. 氧化型低密度脂蛋白抗体在抗磷脂综合征中的临床意义[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2022, 54(6): 1117-1122. |
|
||