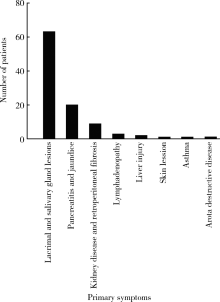
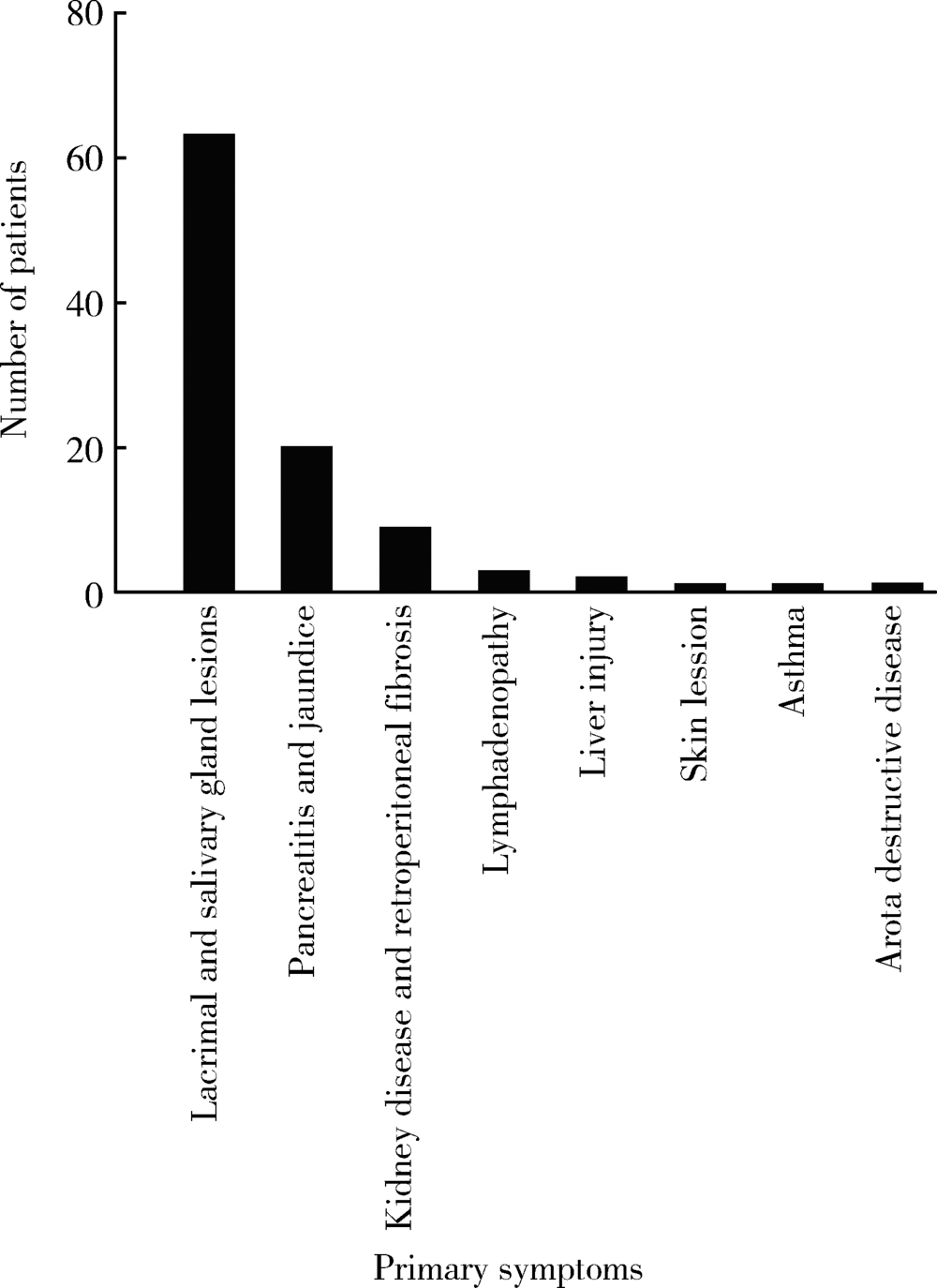
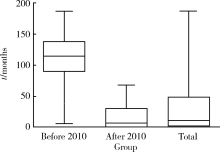
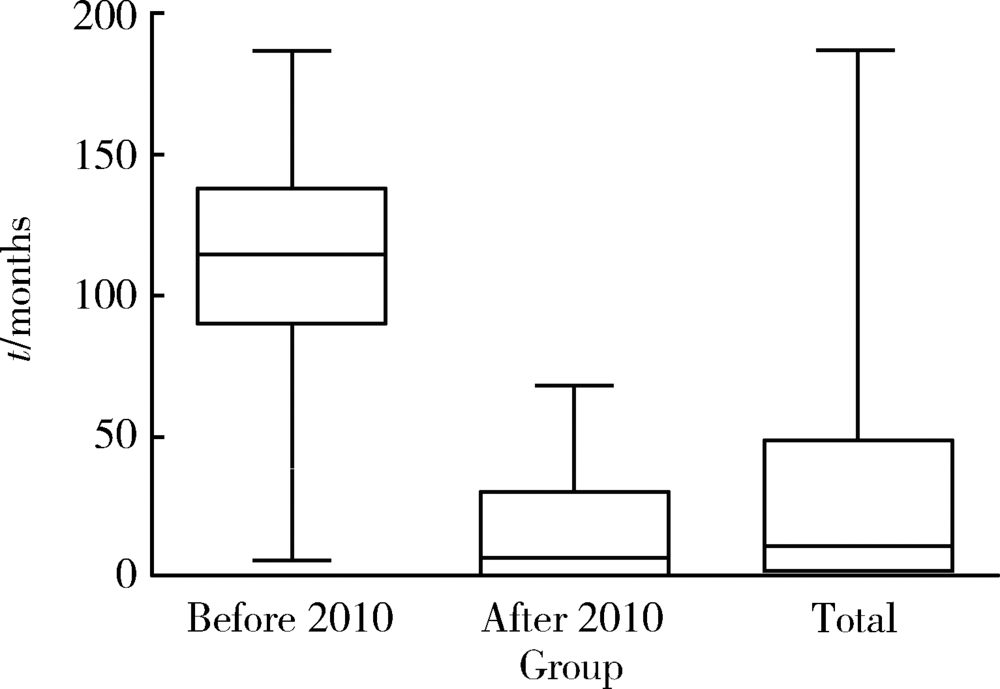
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1039-1043. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.017
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
A cross-sectional study of the clinical features and physician visit patterns at onset of immunoglobulin G4 related disease
Xing-yun ZHU1,Yan-ying LIU1,△( ),Xue-juan SUN2,Ping YU3,Shuang LIU4,Mei-yan FU5,Xu LIU1,Li-min REN1,Zhan-guo LI1
),Xue-juan SUN2,Ping YU3,Shuang LIU4,Mei-yan FU5,Xu LIU1,Li-min REN1,Zhan-guo LI1
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The People’s Hospital of Langfang City, Langfang 065000, Hebei, China
3. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Kailuan General Hospital, Tangshan 063000, Hebei, China
4. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, First Affiliated Hospital of Kuiming Medical University, Kunming 650032, China
5. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Urumuqi Youyi Hospital, Urumuqi 830049, China
CLC Number:
- R593.2
| [1] |
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y , et al. A new clinicopatholo-gical entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2003,38(10):982-984.
doi: 10.1007/s00535-003-1175-y pmid: 14614606 |
| [2] |
Umehara H, Nakajima A, Nakamura T , et al. IgG4-related di-sease and its pathogenesis-cross-talk between innate and acquired immunity[J]. Int Immunol, 2014,26(11):585-595.
doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxu074 pmid: 4201844 |
| [3] |
Su Y, Sun W, Wang C , et al. Detection of serum IgG4 levels in patients with IgG4-related disease and other disorders[J]. PLoS One, 2015,10(4):e0124233.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124233 pmid: 4401680 |
| [4] |
Inoue D, Yoshida K, Yoneda N , et al. IgG4-related disease: dataset of 235 consecutive patients[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2015,94(15):e680.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000680 |
| [5] |
Lin W, Lu S, Chen H , et al. Clinical characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: a prospective study of 118 Chinese patients[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2015,54(11):1982-1990.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev203 pmid: 26106212 |
| [6] |
Zhang J, Chen H, Ma Y , et al. Characterizing IgG4-related di-sease with 18F-FDG PET/CT: a prospective cohort study [J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2014,41(8):1624-1634.
doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2729-3 pmid: 4089015 |
| [7] |
Uchida K, Masamune A, Shimosegawa T , et al. Prevalence of IgG4-related disease in Japan based on nationwide survey in 2009[J]. Int J Rheumatol, 2012,2012:358371.
doi: 10.1155/2012/358371 pmid: 22899936 |
| [8] |
Takahashi H, Yamamoto M, Suzuki C , et al. The birthday of a new syndrome: IgG4-related diseases constitute a clinical entity[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2010,9(9):591-594.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.05.003 pmid: 20457280 |
| [9] |
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y , et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2012,22(1):21-30.
doi: 10.3109/s10165-011-0571-z |
| [10] |
Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S , et al. IgG4-related disease[J]. Lancet, 2015,385(9976):1460-1471.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60720-0 |
| [11] |
Masaki Y, Dong L, Kurose N , et al. Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multiorgan lymphoproliferative syndrome: analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related disorders[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2009,68(8):1310-1315.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.089169 pmid: 18701557 |
| [12] |
Zen Y, Nakanuma Y . IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2010,34(12):1812-1819.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181f7266b |
| [13] |
Fong W, Liew I, Tan D , et al. IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2018,36(Suppl. 112):89-93.
pmid: 29846168 |
| [14] |
Finkelman FD, Boyce JA, Vercelli D , et al. Key advances in mechanisms of asthma, allergy, and immunology in 2009[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2010,125(2):312-318.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.12.968 pmid: 2671063 |
| [15] |
Gao Y, Zheng M, Cui L , et al. IgG4-related disease: association between chronic rhino-sinusitis and systemic symptoms[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2018,275(8):2013-2019.
doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5013-5 |
| [16] |
Hirano K, Tada M, Isayama H , et al. Long-term prognosis of autoimmune pancreatitis with and without corticosteroid treatment[J]. Gut, 2007,56(12):1719-1724.
doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.115246 pmid: 2095691 |
| [17] |
Hong X, Zhang YY, Li W , et al. Treatment of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis: outcomes of glucocorticoid therapy combined with steroid-sparing agents[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2018,20(1):12.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1507-6 pmid: 5791187 |
| [1] | Guang-yan YU,Jia-zeng SU,Deng-gao LIU,Li-ling WU,Xin CONG. Establishment and application of new techniques for submandibular gland preservation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 842-845. |
| [2] | MENG Guang-yan,ZHANG Yun-xiao,ZHANG Yu-xin,LIU Yan-ying. Clinical characteristics of central nervous system involvement in IgG4 related diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1043-1048. |
| [3] | Feng-yun-zhi ZHU,Xiao-yan XING,Xiao-fei TANG,Yi-min LI,Miao SHAO,Xue-Wu ZHANG,Yu-hui LI,Xiao-lin SUN,Jing HE. Clinical and immunological characteristics of myositis complicated with thromboembolism [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 995-1000. |
| [4] | Yi-ming ZHENG,Hong-jun HAO,Yi-lin LIU,Jing GUO,Ya-wen ZHAO,Wei ZHANG,Yun YUAN. Correlation study on anti-Ro52 antibodies frequently co-occur with other myositis-specific and myositis-associated autoantibodies [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(6): 1088-1092. |
| [5] | Jiao-niu DUAN,Wei DU,Rui-hong HOU,Ke XU,Gai-lian ZHANG,Li-yun ZHANG. Progressive necrosis of lipid: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1182-1184. |
| [6] | Xiao-ran NING,Zi-qiao WANG,Shan-shan ZHANG,Xia ZHANG,Su-mei TANG,Yan-ying LIU. Application of ultrasonography scoring system in the assessment of IgG4-related sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1032-1035. |
| [7] | Hong-xia YANG,Xiao-lan TIAN,Wei JIANG,Wen-li LI,Qing-yan LIU,Qing-lin PENG,Guo-chun WANG,Xin LU. Clinical and pathological characteristics of immune mediated necrotizing myopathy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 989-995. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yi-lan, WANG Zhi-feng, CHEN Ning. Expression of serum IgG4 in patients with different diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(6): 961-964. |
| [9] | LIU En-yang, LIU Jing-fang, SHAO Wen-wei, XIAO Lin, LI Guo-hui, CHANG Xiao-hong, QIU Xiao-yan. Tumor derived IgG suppress the proliferation of T cells in cord blood [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 824-828. |
| [10] | WANG Le, YANG Yue, JIA Yuan, MIAO Heng, ZHOU Yun-shan, ZHANG Xiao-ying. Clinical characteristics of 4 cases of scleritis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(6): 1081-1085. |
| [11] | LIU Ai-chun, CHEN Yong, JIA Jin-song, GAO Song-yuan, LIU Yan-ying. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma mimicking Mikulicz disease: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(6): 1074-1076. |
| [12] | FENG Xiang-hui, ZHANG Li, XU Li, MENG Huan-xin, CHEN Zhi-bin, SHI Dong, LU Rui-fang. Analysis of serum IgG titers to Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotype c in aggressive periodontitis patients [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 820-824. |
| [13] | LIU Dan, Li-Ru, LIU Jia-Yu, YAO Hai-Hong, CHEN Qing-Ping, JIA Yuan, SU Yin- . Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of microscopic polyangiitis combined with autoimmune hemolytic anemia [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(4): 657-660. |
| [14] | DUN Yao-Jun,YU Lu-Ping, DU Yi-Qing, SHENG Zheng-Zuo, WANG Gong-Wei, LI Xue, YANG Bing, XU Tao, HUANG Xiao-Bo, WANG Xiao-Feng. Clinical characteristics of IgG4 related retroperitoneal fibrosis: a report of 5 cases and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(4): 622-627. |
| [15] | ZHU Yi-Dan, WEI Jian-Rong, HUANG Lu, WANG Shao-Hua, TIAN Han-Mei, GUO Xin-Biao. Comparison of respiratory diseases and symptoms among school-age children in areas with different levels of air pollution in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(3): 395-399. |
|
||