Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1032-1035. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
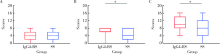
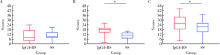
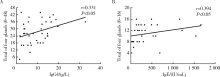
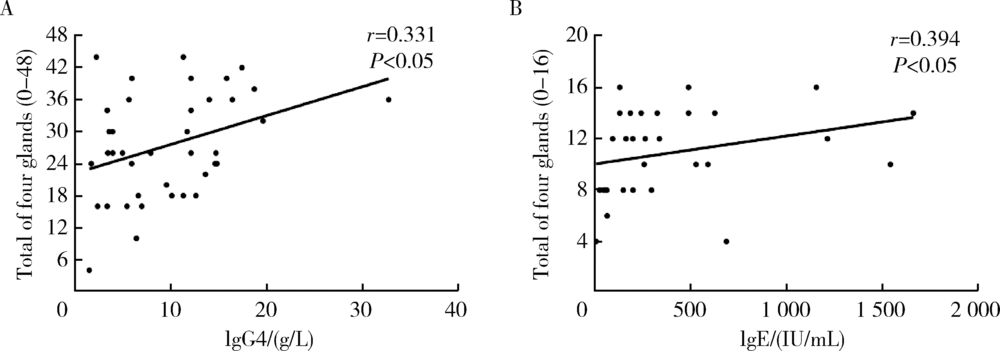
Application of ultrasonography scoring system in the assessment of IgG4-related sialadenitis
Xiao-ran NING1,2,Zi-qiao WANG1,Shan-shan ZHANG3,Xia ZHANG1,Su-mei TANG1,Yan-ying LIU1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology & Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Rheumatology & Immunology, People’s Hospital of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang 050051, China
3. Department of Ultrasound, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R781.72
| [1] | Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Shinomura Y . Mechanisms and assessment of IgG4-related disease: Lessons for the rheumatologist[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2013,10(3):148-159. |
| [2] | Vivino FB . Sjögren’s syndrome: Clinical aspects[J]. Clin Immunol, 2017,9(182):48-54. |
| [3] | Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y , et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2012,22(1):21-30. |
| [4] | Shiboski SC, Shiboski CH, Criswell L , et al. American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a data-driven, expert consensus approach in the Sjogren’s International Collaborative Clinical Alliance cohort[J]. Arthritis Care Res, 2012,64(4):475-487. |
| [5] | Cornec D, Jousse-Joulin S, Pers JO , et al. Contribution of sali-vary gland ultrasonography to the diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome: toward new diagnostic criteria?[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2013,65(1):216-225. |
| [6] | Hocevar A, Ambrozic A, Rozman B , et al. Ultrasonographic changes of major salivary glands in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Diagnostic value of a novel scoring system[J]. Rheumatol, 2005,63(3):379-383. |
| [7] | Satomi A, Kenji O, Naoya N , et al. Sonographic appearance of the submandibular glands in patients with immunoglobulin G4-related disease[J]. J Ultrasound Med, 2012,31(3):489-493. |
| [8] | Narayan AK, Baer A, Fradin J . Sonographic findings of IgG4-related disease of the salivary glands: Case report and review of the literature[J]. J Clin Ultrasound, 2018,46(1):73-77. |
| [9] | Omotehara S, Nishida M, Satoh M , et al. Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing sialadenitis[J]. J Med Ultrason, 2016,43(2):257-262. |
| [10] | Li W, Xie XY, Su JZ , et al. Ultrasonographic features of immunoglobulin G4-related sialadenitis[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2016,42(1):167-175. |
| [11] | Shimizu M, Okamura K, Kise Y , et al. Effectiveness of imaging modalities for screening IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialadenitis (Mikulicz’s disease) and for differentiating it from Sjögren’s syndrome (SS), with an emphasis on sonography[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2015,17(1):223-234. |
| [12] | Zhang X, Zhang S, He J , et al. Ultrasonographic evaluation of major salivary glands in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: comparison of two scoring systems[J]. Rheumatol, 2015,54(9):1680-1687. |
| [13] | Tang J, Cai S, Ye C , et al. Biomarkers in IgG4-related disease: A systematic review [J/OL]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, ( 2019 -06-28). doi: 201910.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.06.018. |
| [1] | Jinfang YUAN, Xinli WANG, Yunpu CUI, Xuemei WANG. Application of urinary luteinizing hormone in the prediction of central precocious puberty in girls [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 788-793. |
| [2] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [3] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [4] | Yan CHEN,Kuangmeng LI,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG,Jianxing CHENG,Zhongjie ZHENG,Wenhao TANG,Lianming ZHAO,Haitao ZHANG,Hui JIANG,Haocheng LIN. Retrospective study on the impact of penile corpus cavernosum injection test on penile vascular function [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [5] | Zhengfang LI,Cainan LUO,Lijun WU,Xue WU,Xinyan MENG,Xiaomei CHEN,Yamei SHI,Yan ZHONG. Application value of anti-carbamylated protein antibody in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [6] | Yue WEI,Lan YAO,Xi LU,Jun WANG,Li LIN,Kun-peng LIU. Evaluation of gastric emptying after drinking carbohydrates before cesarean section by gastric ultrasonography [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1082-1087. |
| [7] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [8] | Yue WEI,Xi LU,Jing ZHANG,Kun-peng LIU,Yong-jun WANG,Lan YAO. Effect of preoperative carbohydrates intake on the gastric volume and the risk of reflux aspiration in patients positioning in trendelenburg undergoing gynecological laparoscopic procedures [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 893-898. |
| [9] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [10] | Ting WANG,Qiao-sheng LI,Hao-ran LIU,Wei-yan JIAN. Urban-rural differentials in the relationship between personality traits and changes in depressive symptoms [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 385-391. |
| [11] | Yan XIONG,Xin LI,Li LIANG,Dong LI,Li-min YAN,Xue-ying LI,Ji-ting DI,Ting LI. Evaluation of accuracy of pathological diagnosis based on thyroid core needle biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [12] | Xue-mei HA,Yong-zheng YAO,Li-hua SUN,Chun-yang XIN,Yan XIONG. Solid placental transmogrification of the lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 357-361. |
| [13] | Bo-han NING,Qing-xia ZHANG,Hui YANG,Ying DONG. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma with proliferated stromal cells, hyalinization and cord-like formations: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 366-369. |
| [14] | Rui-jie CAO,Zhong-qiang YAO,Peng-qing JIAO,Li-gang CUI. Comparison of diagnostic efficacy of different classification criteria for Takayasu arteritis in Chinese patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1128-1133. |
| [15] | Yu WANG,Hui-min ZHANG,Xue-rong DENG,Wei-wei LIU,Lu CHEN,Ning ZHAO,Xiao-hui ZHANG,Zhi-bo SONG,Yan GENG,Lan-lan JI,Yu WANG,Zhuo-li ZHANG. Diagnostic values of urinary citrate for kidney stones in patients with primary gout [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1134-1140. |
|
||