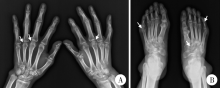
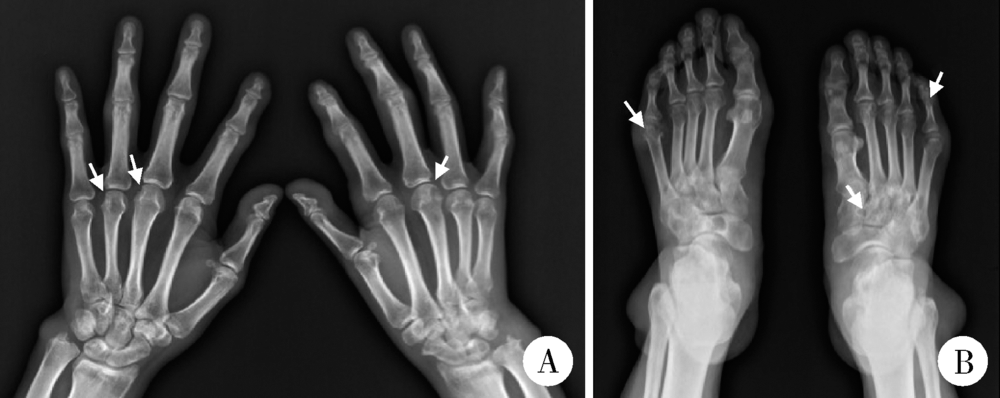
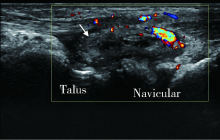
Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1117-1119. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.032
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
A case of gout secondary to primary myelofibrosis
Lan-lan JI,Yan-jie HAO,Zhuo-li ZHANG( )
)
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology,Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R593
| [1] | 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 2016中国痛风诊疗指南[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2016,55(11):892-899. |
| [2] |
Neogi T, Jansen TLTA, Dalbeth N , et al. 2015 Gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015,74(10):1789-1798.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208237 pmid: 4602275 |
| [3] |
Yü TF . Secondary gout associated with myeloproliferative diseases[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1965,8(5):765-771.
doi: 10.1002/art.1780080439 pmid: 5216775 |
| [4] |
Gutman AB . The past four decades of progress in the knowledge of gout, with an assessment of the present status[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1973,16(4):431-445.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1529-0131 |
| [5] |
Takahashi H, Hattori A, Shibata A . Profile of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis in chronic myeloproliferative disorders[J]. Tohoku J Exp Med, 1982,138(1):71-80.
doi: 10.1620/tjem.138.71 pmid: 6959382 |
| [6] |
Barbui T, Carobbio A, Cervantes F , et al. Thrombosis in primary myelofibrosis: incidence and risk factors[J]. Blood, 2010,115(4):778-782.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-08-238956 pmid: 19965680 |
| [7] |
Liu TT, Chen JB, Chen WJ , et al. Idiopathic myelofibrosis associated with renal extramedullary hematopoiesis and nephrotic syndrome: case report[J]. Chang Gung Med J, 2000,23(3):169-174.
pmid: 15641221 |
| [1] | Jiayi TIAN, Yixue GUO, Xia ZHANG, Xiaolin SUN, Jing HE. Flow cytometry analysis of normal range of natural killer cells and their subsets in peripheral blood of healthy Chinese adults [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 839-844. |
| [2] | Yushu YANG, Xuan QI, Meng DING, Wei WANG, Huifang GUO, Lixia GAO. Diagnostic values of anti-salivary gland protein-1 antibody combined with anti-parotid secretory protein antibody for Sjögren's syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 845-852. |
| [3] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [4] | Zhihui WU, Mingzhi HU, Qiaoying ZHAO, Fengfeng LV, Jingying ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Yongfu WANG, Xiaolin SUN, Hui WANG. Immunomodulatory mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-125b-5p in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 860-867. |
| [5] | Dongwu LIU, Jie CHEN, Mingli GAO, Jing YU. Rheumatoid arthritis with Castleman-like histopathology in lymph nodes: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [6] | Zhengfang LI,Cainan LUO,Lijun WU,Xue WU,Xinyan MENG,Xiaomei CHEN,Yamei SHI,Yan ZHONG. Application value of anti-carbamylated protein antibody in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [7] | 佳佳 乔,聪 田,晓波 黄,军 刘. [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 745-749. |
| [8] | Huina HUANG,Jing ZHAO,Xiangge ZHAO,Ziran BAI,Xia LI,Guan WANG. Regulatory effect of lactate on peripheral blood CD4+ T cell subsets in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [9] | Limin REN,Chuchu ZHAO,Yi ZHAO,Huiqiong ZHOU,Liyun ZHANG,Youlian WANG,Lingxun SHEN,Wenqiang FAN,Yang LI,Xiaomei LI,Jibo WANG,Yongjing CHENG,Jiajing PENG,Xiaozhen ZHAO,Miao SHAO,Ru Li. Low disease activity and remission status of systemic lupus erythematosus in a real-world study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 273-278. |
| [10] | Xiaofei TANG,Yonghong LI,Qiuling DING,Zhuo SUN,Yang ZHANG,Yumei WANG,Meiyi TIAN,Jian LIU. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [11] | Zhanhong LAI,Jiachen LI,Zelin YUN,Yonggang ZHANG,Hao ZHANG,Xiaoyan XING,Miao SHAO,Yuebo JIN,Naidi WANG,Yimin LI,Yuhui LI,Zhanguo LI. A unicenter real-world study of the correlation factors for complete clinical response in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 284-292. |
| [12] | Yi-jun HAN,Chang-hong LI,Xiu-ying CHEN,Jin-xia ZHAO. Comparison of clinical and immunological characteristics between primary Sjögren's syndrome patients with positive and negative anti-SSB antibody [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1000-1006. |
| [13] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [14] | Xue ZOU,Xiao-juan BAI,Li-qing ZHANG. Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [15] | Wen-gen LI,Xiao-dong GU,Rui-qiang WENG,Su-dong LIU,Chao CHEN. Expression and clinical significance of plasma exosomal miR-34-5p and miR-142-3p in systemic sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1022-1027. |
|
||