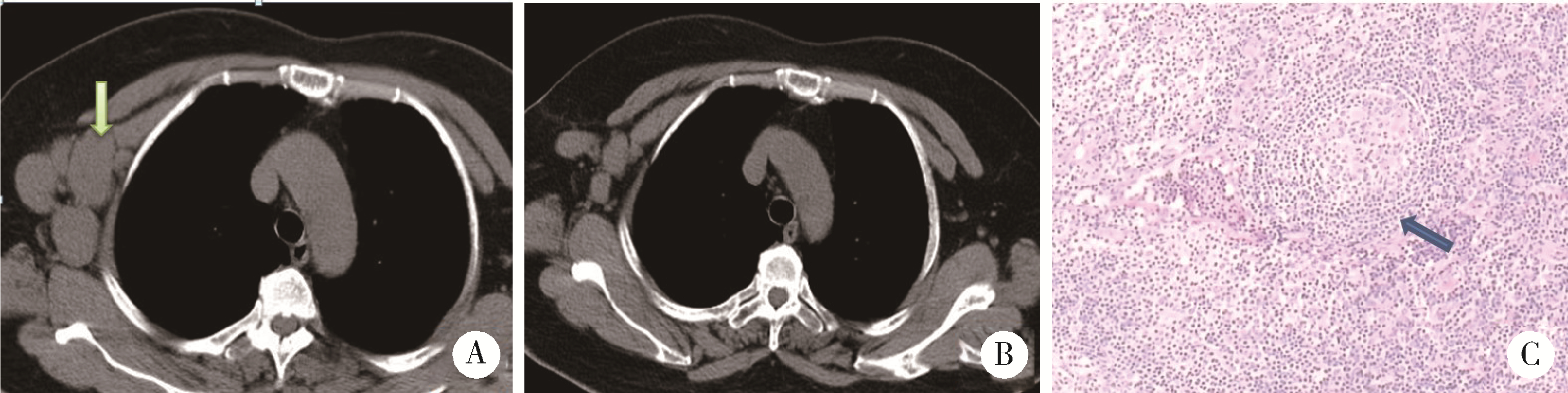
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (5): 928-931. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.028
Previous Articles Next Articles
Rheumatoid arthritis with Castleman-like histopathology in lymph nodes: A case report
Dongwu LIU1, Jie CHEN2, Mingli GAO1, Jing YU1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, China
2. College of Integrative Medicine, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, China
CLC Number:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Demirkan FG , Doǧan S , Kalyoncu Uçar A , et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus complicated with Castleman disease: A case-based review[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2021, 41 (2): 475- 479.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-020-04684-4 |
| 2 |
Minemura H , Tanino Y , Ikeda K . Possible association of multicentric Castleman' s disease with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome[J]. Biores Open Access, 2018, 7 (1): 47- 51.
doi: 10.1089/biores.2017.0025 |
| 3 |
Tabata S , Higuchi T , Tatsukawa S , et al. Idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease with autoimmune hemolytic anemia and production of anti-drug antibody against tocilizumab[J]. Intern Med, 2019, 58 (22): 3313- 3318.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2989-19 |
| 4 | 中华医学会血液学分会淋巴细胞疾病学组, 中国抗癌协会血液肿瘤专业委员会, 中国Castleman病协作组. 中国Castleman病诊断与治疗专家共识(2021年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2021, 42 (7): 529- 534. |
| 5 | 郑东辉, 莫颖倩, 戴冽, 等. 类风湿关节炎不同滑膜淋巴细胞分布类型的临床病理特点[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2009, 30 (5): 571- 576. |
| 6 | 张玲玲, 魏伟. BAFF/BAFF-R通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号转导通路调节B淋巴细胞功能在类风湿关节炎发病机制中的意义[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2010, 26 (7): 847- 850. |
| 7 | Picemo V , Ferro F , Adinolfi A , et al. One year in riview: The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2015, 33 (4): 551- 558. |
| 8 | 唐果, 龙丽, 韩雅欣, 等. 类风湿关节炎合并结核感染的临床特点及相关因素[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52 (6): 1029- 1033. |
| 9 | 刘娣, 郭万珍, 蔡华聪, 等. 类风湿关节炎并发淋巴瘤的临床特征[J]. 中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志, 2015, 9 (4): 292- 296. |
| 10 |
Castleman B , Towne V . Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital weekly clinicopathological exercises: Case 40011[J]. N Engl J Med, 1954, 250 (1): 26- 30.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM195401072500107 |
| 11 |
Wang HW , Pittaluga S , Jaffe ES . Multicentric Castleman disease: Where are we now?[J]. Semin Diagn Pathol, 2016, 33 (5): 294- 306.
doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2016.05.006 |
| 12 |
Nguyen D , Diamond L , Hansmann N , et al. Castleman' s disease. Differences in follicular dendritic network in the hyaline vascular and plasma cell variants[J]. Histopathology, 1994, 24 (5): 437- 443.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1994.tb00552.x |
| 13 |
Herrada J , Cabanillas F , Rice L , et al. The clinical behavior of localized and multicentric Castleman disease[J]. Ann Intern Med, 1998, 128 (8): 657- 662.
doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-128-8-199804150-00010 |
| 14 | Peterson B , Frizzera G . Multicentric Castleman' s disease[J]. Semin Oncol, 1993, 20 (6): 636- 647. |
| 15 |
Frizzera G , Peterson BA , Bayrd ED , et al. A systemic lymphoproliferative disorder with morphologic features of Castleman' s disease: Clinical findings and clinicopathologic correlations in 15 patients[J]. J Clin Oncol, 1985, 3 (9): 1202- 1216.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.1985.3.9.1202 |
| 16 |
Bowne WB , Lewis JJ , Filippa DA , et al. The management of unicentric and multicentric Castleman' s disease: A report of 16 cases and a review of the literature[J]. Cancer, 1999, 85 (3): 706- 717.
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19990201)85:3<706::AID-CNCR21>3.0.CO;2-7 |
| 17 |
Nishimoto N , Kanakura Y , Aozasa K , et al. Humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody treatment of multicentric Castleman disease[J]. Blood, 2005, 106 (8): 2627- 2632.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-12-4602 |
| 18 |
Casper C , Voorhees PM , Fayad LE , et al. An open-label, phase 2, multicenter study of the safety of long-term treatment with siltuximab (an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody) in patients with multicentric Castleman' s disease[J]. Blood, 2013, 122 (21): 1806.
doi: 10.1182/blood.V122.21.1806.1806 |
| 19 | de Marchi G , de Vita S , Fabris M , et al. Systemic connective tissue disease complicated by Castleman' s disease: Report of a case and review of the literature[J]. Haematologica, 2004, 89 (4): 7- 10. |
| 20 |
Jacobs SA , Vidnovic N , Patel H , et al. Durable remission of HIV-negative, Kaposi' s sarcoma herpes virus-associated multicentric Castleman disease in patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2007, 26 (7): 1148- 1150.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-006-0272-8 |
| 21 | Sun Y , Wang D , Salvadore G , et al. The effects of interleukin-6 neutralizing antibodies on symptoms of depressed mood and anhedonia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and multicentric Castle-man' s disease[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2017, 66 (11): 156- 164. |
| [1] | Huina HUANG,Jing ZHAO,Xiangge ZHAO,Ziran BAI,Xia LI,Guan WANG. Regulatory effect of lactate on peripheral blood CD4+ T cell subsets in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 519-525. |
| [2] | Xiaofei TANG,Yonghong LI,Qiuling DING,Zhuo SUN,Yang ZHANG,Yumei WANG,Meiyi TIAN,Jian LIU. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
| [3] | Xue ZOU,Xiao-juan BAI,Li-qing ZHANG. Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [4] | Qi WU,Yue-ming CAI,Juan HE,Wen-di HUANG,Qing-wen WANG. Correlation between dyslipidemia and rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 982-992. |
| [5] | Jing-feng ZHANG,Yin-ji JIN,Hui WEI,Zhong-qiang YAO,Jin-xia ZHAO. Correlation analysis between body mass index and clinical characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 993-999. |
| [6] | Yin-ji JIN,Lin SUN,Jin-xia ZHAO,Xiang-yuan LIU. Significance of IgA isotype of anti-v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homologue B1 antibody in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 631-635. |
| [7] | Wen-xin CAI,Shi-cheng LI,Yi-ming LIU,Ru-yu LIANG,Jing LI,Jian-ping GUO,Fan-lei HU,Xiao-lin SUN,Chun LI,Xu LIU,Hua YE,Li-zong DENG,Ru LI,Zhan-guo LI. A cross-sectional study on the clinical phenotypes of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1068-1073. |
| [8] | Fang CHENG,Shao-ying YANG,Xing-xing FANG,Xuan WANG,Fu-tao ZHAO. Role of the CCL28-CCR10 pathway in monocyte migration in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1074-1078. |
| [9] | Rui LIU,Jin-xia ZHAO,Liang YAN. Clinical characteristics of patients with rheumatoid arthritis complicated with venous thrombosis of lower extremities [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1079-1085. |
| [10] | Jing-feng ZHANG,Yin-ji JIN,Hui WEI,Zhong-qiang YAO,Jin-xia ZHAO. Cross-sectional study on quality of life and disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1086-1093. |
| [11] | GAO Chao,CHEN Li-hong,WANG Li,YAO Hong,HUANG Xiao-wei,JIA Yu-bo,LIU Tian. Validation of the Pollard’s classification criteria (2010) for rheumatoid arthritis patients with fibromyalgia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 278-282. |
| [12] | ZHONG Hua,XU Li-ling,BAI Ming-xin,SU Yin. Effect of chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 on bone erosion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | LOU Xue,LIAO Li,LI Xing-jun,WANG Nan,LIU Shuang,CUI Ruo-mei,XU Jian. Methylation status and expression of TWEAK gene promoter region in peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1020-1025. |
| [14] | LUO Liang,HUO Wen-gang,ZHANG Qin,LI Chun. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of rheumatoid arthritis with ulcerative keratitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1032-1036. |
| [15] | ZHANG Lu,HU Xiao-hong,CHEN Cheng,CAI Yue-ming,WANG Qing-wen,ZHAO Jin-xia. Analysis of cervical instability and clinical characteristics in treatment-naive rheumatoid arthritis patients [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1049-1054. |
|
||