Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1071-1077. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
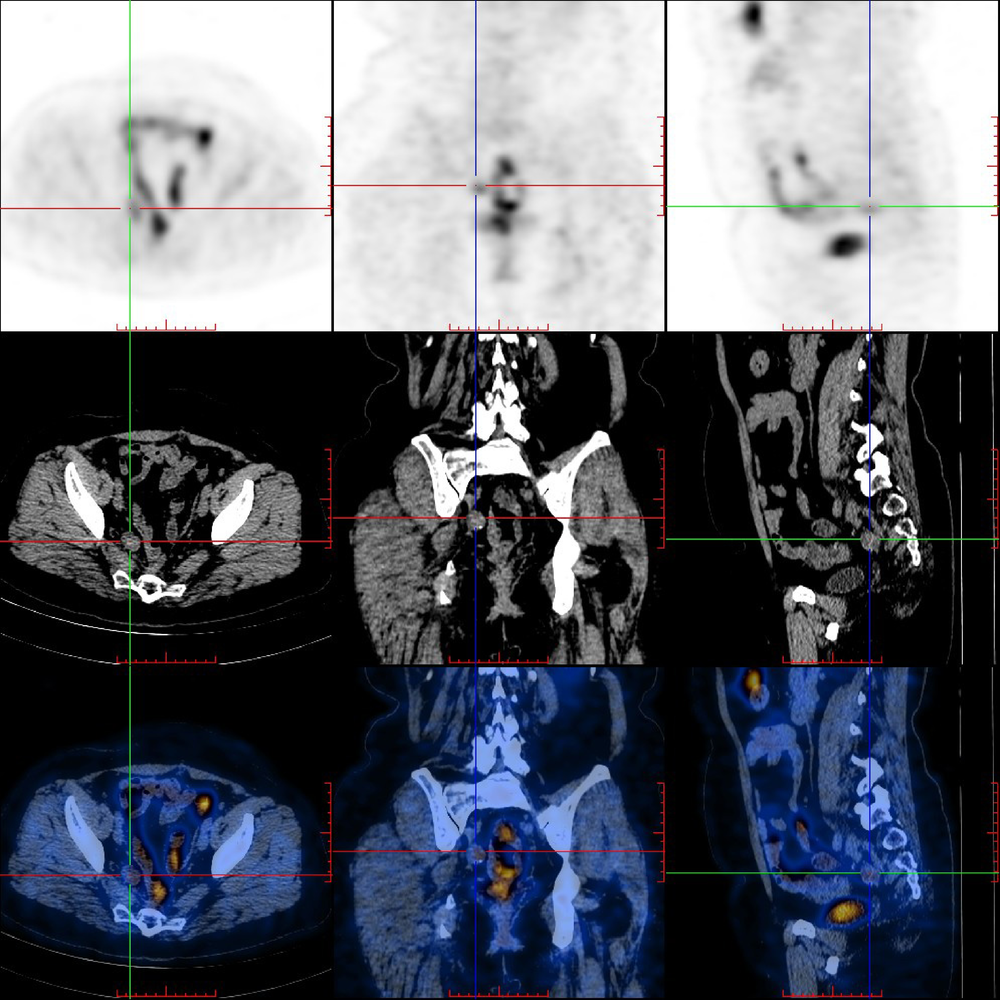
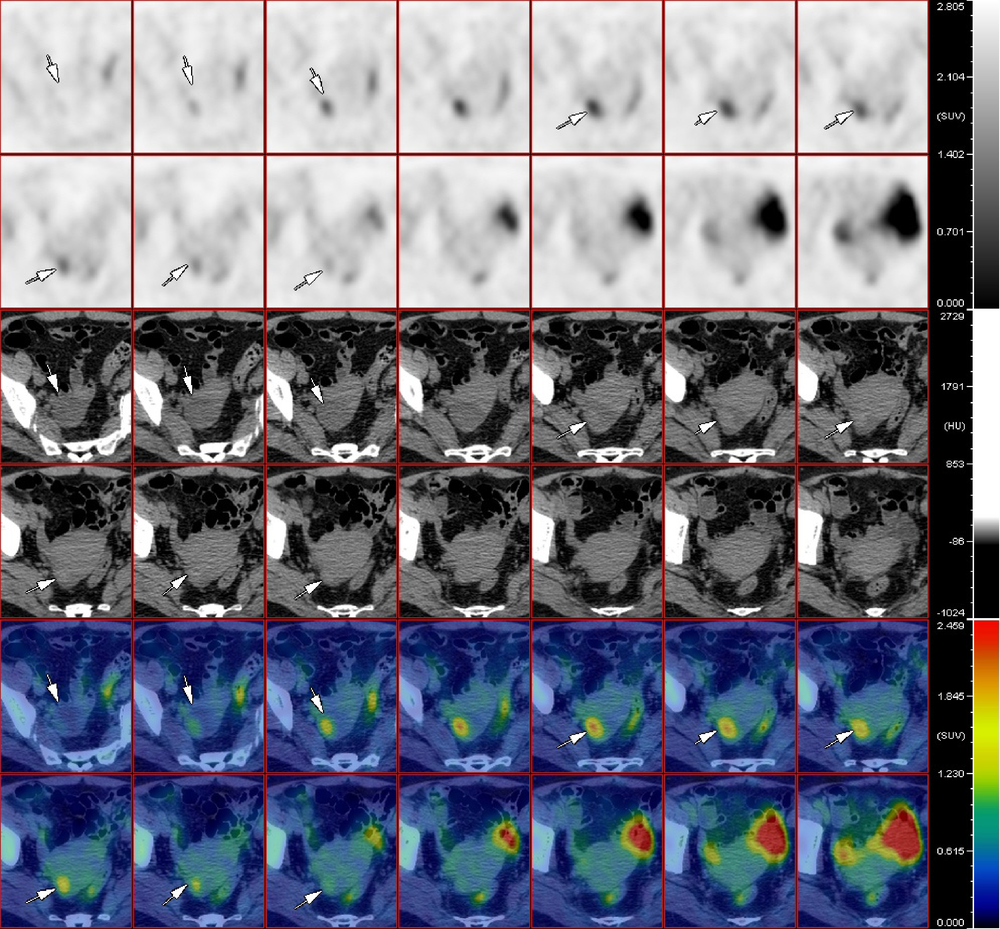
Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT and tumor markers (CEA, CA19-9, CA24-2) in recurrence and metastasis of postoperative colorectal moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma
Xu-chu ZHANG,Jian-hua ZHANG,Rong-fu WANG( ),Yan FAN,Zhan-li FU,Ping YAN,Guang-yu ZHAO,Yan-xia BAI
),Yan FAN,Zhan-li FU,Ping YAN,Guang-yu ZHAO,Yan-xia BAI
- Department of Nuclear Medicine, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R735.5
| [1] | 吴菲, 林国桢, 张晋昕 . 我国恶性肿瘤发病现状及趋势[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2012,21(2):81-85. |
| [2] | 阮丽琴, 李太原, 周凤凤 . 不同年龄组的结直肠癌临床流行病学分析[J]. 实用临床医学, 2016,17(4):86-87. |
| [3] | 张小龙, 高枫, 陈利生 , 等. 结直肠癌病理组织学类型分析[J]. 广西医学, 2008,30(11):1671-1672. |
| [4] | 陈美玲 . 291例结直肠癌患者的临床病理分析[J]. 大家健康(学术版), 2015,9(8):66-67. |
| [5] | 邱大胜, 胡晓燕, 彭辽河 , 等. 18F-FDG-PET/CT对结直肠癌术后血清CEA升高患者的诊断价值 [J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2013,32(12):1739-1742. |
| [6] | 路晓雯, 刘林祥, 崔新建 , 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT对结直肠癌术后血清CEA升高病例的临床诊断价值 [J]. 泰山医学院学报, 2010,31(2):83-85. |
| [7] | 潘睿. 中国慢性病前瞻性研究队列恶性肿瘤发病与死亡分析[C], 2017. |
| [8] |
黄利娟, 陈继贵, 刘丽 , 等. 结直肠癌患者血清肿瘤标志物水平与预后关系[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2011,27(5):563-566.
doi: 10.11847/zgggws-2011-27-05-16 |
| [9] | Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R , et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. Ann Oncol, 2016,27(8):1386-1422. |
| [10] | 王贵玉 . 结直肠癌NCCN、NICE及ESMO指南的对比分析和解读[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2015,25(11):849-853. |
| [11] | Schmoll HJ, Van Cutsem E, Stein A , et al. ESMO Consensus Guidelines for management of patients with colon and rectal can-cer. A personalized approach to clinical decision making[J]. Ann Oncol, 2012,23(10):2479-2516. |
| [12] | Chan K, Welch S, Walker-Dilks C , et al. Evidence-based guideline recommendations on the use of positron emission tomography imaging in colorectal cancer[J]. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol), 2012,24(4):232-249. |
| [13] | 王晶晶, 陈康, 徐万菊 . 直肠癌患者手术前后血清CA199和CA242水平测定及预后评价[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2009,14(21):1667-1668. |
| [14] | 刘传, 清水汪, 王宁 , 等. 结直肠癌术前血清CEA、CA199表达水平与临床病理关系的研究[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2012,41(3):27-30. |
| [15] | 周华胜, 梁光林 . 癌胚抗原测定在直肠癌手术前后及药物化疗过程中的追踪研究[J]. 河北医学, 2010,16(4):455-456. |
| [16] | Lim YK, Kam MH, Eu KW . Carcinoembryonic antigen screening: how far should we go?[J]. Singapore Med J, 2009,50(9):862-865. |
| [17] | 陈恺杰 . 3种血清肿瘤标志物在诊断大肠癌中的价值[J]. 广东医学院学报, 2005,23(4):384-385. |
| [18] | 高志海, 田志军, 安燚 . 五种肿瘤标志物联合检测在胃和结直肠癌诊断及随访中的临床意义[J]. 医学综述, 2012,18(10):1595-1597. |
| [1] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [2] | Jiajun LIU, Guokang LIU, Yuhu ZHU. Immune-related severe pneumonia: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [3] | Kewei CHEN,Zhuo LIU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Jianfei YE,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of renal angiomyolipoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 617-623. |
| [4] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [5] | Jie YANG,Jieli FENG,Shudong ZHANG,Lulin MA,Qing ZHENG. Clinical effects of transesophageal echocardiography in different surgical methods for nephrectomy combined with Mayo Ⅲ-Ⅳ vena tumor thrombectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [6] | Binshuai WANG,Min QIU,Qianjin ZHANG,Maofeng TIAN,Lei LIU,Guoliang WANG,Min LU,Xiaojun TIAN,Shudong ZHANG. Experience in diagnosis and treatment of 6 cases of renal Ewing's sarcoma with venous thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [7] | Xiaodong CHAI,Ziwen SUN,Haishuang LI,Liangyi ZHU,Xiaodan LIU,Yantao LIU,Fei PEI,Qing CHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics of the CD8+ T lymphocytes infiltration and its mechanism in distinct molecular subtype of medulloblastoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 512-518. |
| [8] | Wenjing LI,Baozhou ZHANG,Heng LI,Liangpeng LAI,Hui DU,Ning SUN,Xiaofeng GONG,Ying LI,Yan WANG,Yong WU. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis for end-stage ankle and hindfoot arthropathy: Short- and mid-term clinical outcomes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [9] | Guozhong LIN,Changcheng MA,Chao WU,Yu SI,Jun YANG. Application of microchannel technique in minimally invasive resection of cervical intraspinal tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 318-321. |
| [10] | Xiaotong LING,Liuyang QU,Danni ZHENG,Jing YANG,Xuebing YAN,Denggao LIU,Yan GAO. Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [11] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [12] | Dong LAN,Zhuo LIU,Yu-xuan LI,Guo-liang WANG,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG,Hong-xian ZHANG. Risk factors for massive hemorrhage after radical nephrectomy and removal of venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 825-832. |
| [13] | Zhong CAO,Hong-bing CEN,Jian-hong ZHAO,Jun MEI,Ling-zhi QIN,Wei LIAO,Qi-lin AO. Expression and significance of INSM1 and SOX11 in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and solid pseudopapillary neoplasm [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 575-581. |
| [14] | Li LIANG,Xin LI,Lin NONG,Ying DONG,Ji-xin ZHANG,Dong LI,Ting LI. Analysis of microsatellite instability in endometrial cancer: The significance of minimal microsatellite shift [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 254-261. |
| [15] | Yu-mei LAI,Zhong-wu LI,Huan LI,Yan WU,Yun-fei SHI,Li-xin ZHOU,Yu-tong LOU,Chuan-liang CUI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of anorectal melanoma: A report of 68 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 262-269. |
|
||