Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1067-1070. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
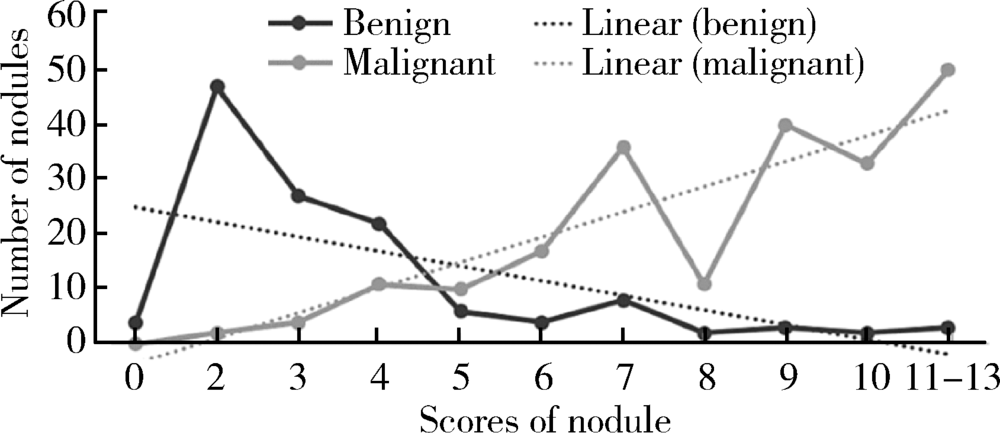
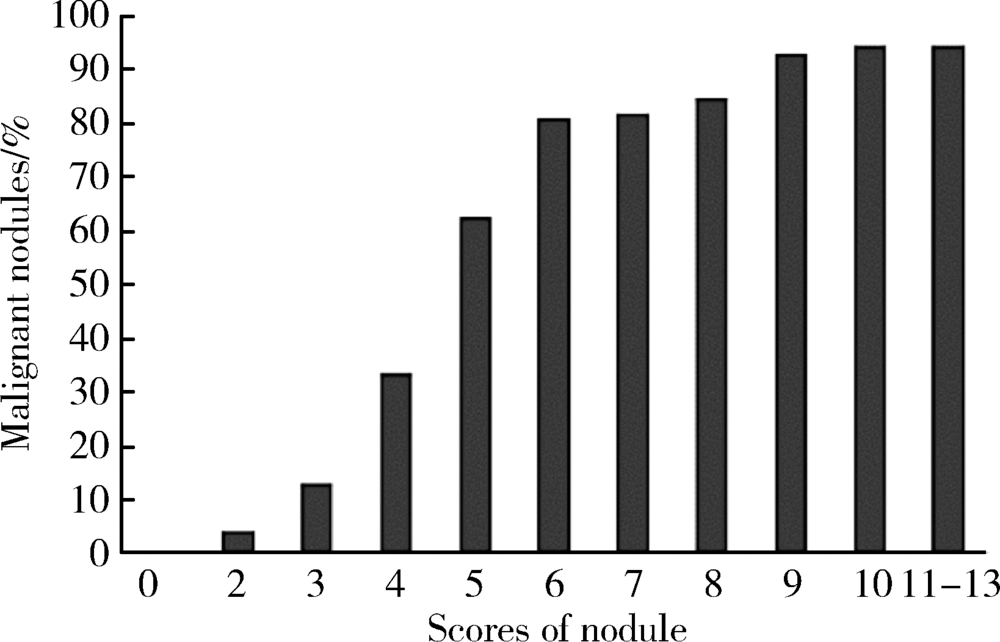
Applicational value of 2017 ACR TI-RADS stratification in diagnosing thyroid nodules
Peng FU,Wen CHEN( ),Li-gang CUI,Hui-yu GE,Shu-min WANG
),Li-gang CUI,Hui-yu GE,Shu-min WANG
- Department of Ultrasound, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R736.1
| [1] | Tessler FN, Middleton WD, Grant EG , et al. ACR thyroid imaging, reporting and data system (TI-RADS): White paper of the ACR TI-RADS Committee[J]. J Am Coll Radiol, 2017,14(5):587-595. |
| [2] | Grant EG, Tessler FN, Hoang JK , et al. Thyroid ultrasound reporting lexicon: white paper of the ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TIRADS) Committee[J]. J Am Coll Ra-diol, 2015,12(12):1272-1279. |
| [3] | Gharib H, Papini E, Garber JR , et al. AACE/AME Guidelines American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and Associazione Medici Endocrinologi medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules: 2016 update[J]. Endocr Pract, 2016,22(5):622-639. |
| [4] | Middleton WD, Teefey SA, Reading CC , et al. Multiinstitutional analysis of thyroid nodule risk stratification using the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2017,208(6):1331-1341. |
| [5] | Kumbhar SS, O’Malley RB, Robinson TJ, et al. Why thyroid surgeons are frustrated with radiologists: Lessons learned from pre-and postoperative US[J]. Radiographics, 2016,36(7):150-250. |
| [6] | Gunderman RB, Mcneive LR . Is structured reporting the answer?[J]. Radiology, 2014,273(1):7-9. |
| [7] | Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC , et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid, 2016,26(1):1-133. |
| [8] | Haddad RI, Lydiatt WM, Ball DW , et al. Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma, Version 2.2015[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2015,13(9):1140-1150. |
| [9] | Wémeau JL, Sadoul JL, d’Herbomez M, et al. Guidelines of the French Society of Endocrinology for the management of thyroid nodules[J]. Ann Endocrinol (Paris), 2011,72(4):251-281. |
| [10] | Shin JH, Baek JH, Chung J , et al. Ultrasonography diagnosis and imaging-based management of thyroid nodules: Revised Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology consensus statement and recommendations[J]. Korean J Radiol, 2016,17(3):370-395. |
| [11] | 刘红, 胡正明, 罗海愉 , 等. ACR TI-RADS分类在诊断甲状腺结节中的应用价值探究[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2018,34(8):673-675. |
| [12] | 钟敏莹, 石小红, 杨丽丽 , 等. TI-RADS分类系统对不同直径甲状腺结节的诊断价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2016,32(4):289-291. |
| [1] | Jinfang YUAN, Xinli WANG, Yunpu CUI, Xuemei WANG. Application of urinary luteinizing hormone in the prediction of central precocious puberty in girls [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 788-793. |
| [2] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [3] | Hua ZHONG, Yuan LI, Liling XU, Mingxin BAI, Yin SU. Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in rheumatic diseases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 853-859. |
| [4] | Dongwu LIU, Jie CHEN, Mingli GAO, Jing YU. Rheumatoid arthritis with Castleman-like histopathology in lymph nodes: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 928-931. |
| [5] | Yan CHEN,Kuangmeng LI,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG,Jianxing CHENG,Zhongjie ZHENG,Wenhao TANG,Lianming ZHAO,Haitao ZHANG,Hui JIANG,Haocheng LIN. Retrospective study on the impact of penile corpus cavernosum injection test on penile vascular function [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [6] | Zhengfang LI,Cainan LUO,Lijun WU,Xue WU,Xinyan MENG,Xiaomei CHEN,Yamei SHI,Yan ZHONG. Application value of anti-carbamylated protein antibody in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 729-734. |
| [7] | Yue WEI,Lan YAO,Xi LU,Jun WANG,Li LIN,Kun-peng LIU. Evaluation of gastric emptying after drinking carbohydrates before cesarean section by gastric ultrasonography [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1082-1087. |
| [8] | Hai-hong YAO,Fan YANG,Su-mei TANG,Xia ZHANG,Jing HE,Yuan JIA. Clinical characteristics and diagnostic indicators of macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and adult-onset Still's disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 966-974. |
| [9] | Yue WEI,Xi LU,Jing ZHANG,Kun-peng LIU,Yong-jun WANG,Lan YAO. Effect of preoperative carbohydrates intake on the gastric volume and the risk of reflux aspiration in patients positioning in trendelenburg undergoing gynecological laparoscopic procedures [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 893-898. |
| [10] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [11] | Ting WANG,Qiao-sheng LI,Hao-ran LIU,Wei-yan JIAN. Urban-rural differentials in the relationship between personality traits and changes in depressive symptoms [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 385-391. |
| [12] | Yun-fei SHI,Hao-jie WANG,Wei-ping LIU,Lan MI,Meng-ping LONG,Yan-fei LIU,Yu-mei LAI,Li-xin ZHOU,Xin-ting DIAO,Xiang-hong LI. Analysis of clinicopathological and molecular abnormalities of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [13] | Yan XIONG,Xin LI,Li LIANG,Dong LI,Li-min YAN,Xue-ying LI,Ji-ting DI,Ting LI. Evaluation of accuracy of pathological diagnosis based on thyroid core needle biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 234-242. |
| [14] | Qi SHEN,Yi-xiao LIU,Qun HE. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of kidney: Clinicopathology and prognosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 276-282. |
| [15] | Wei-hua HOU,Shu-jie SONG,Zhong-yue SHI,Mu-lan JIN. Clinicopathological features of Helicobacter pylori-negative early gastric cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 292-298. |
|
||