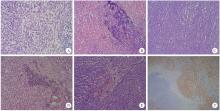
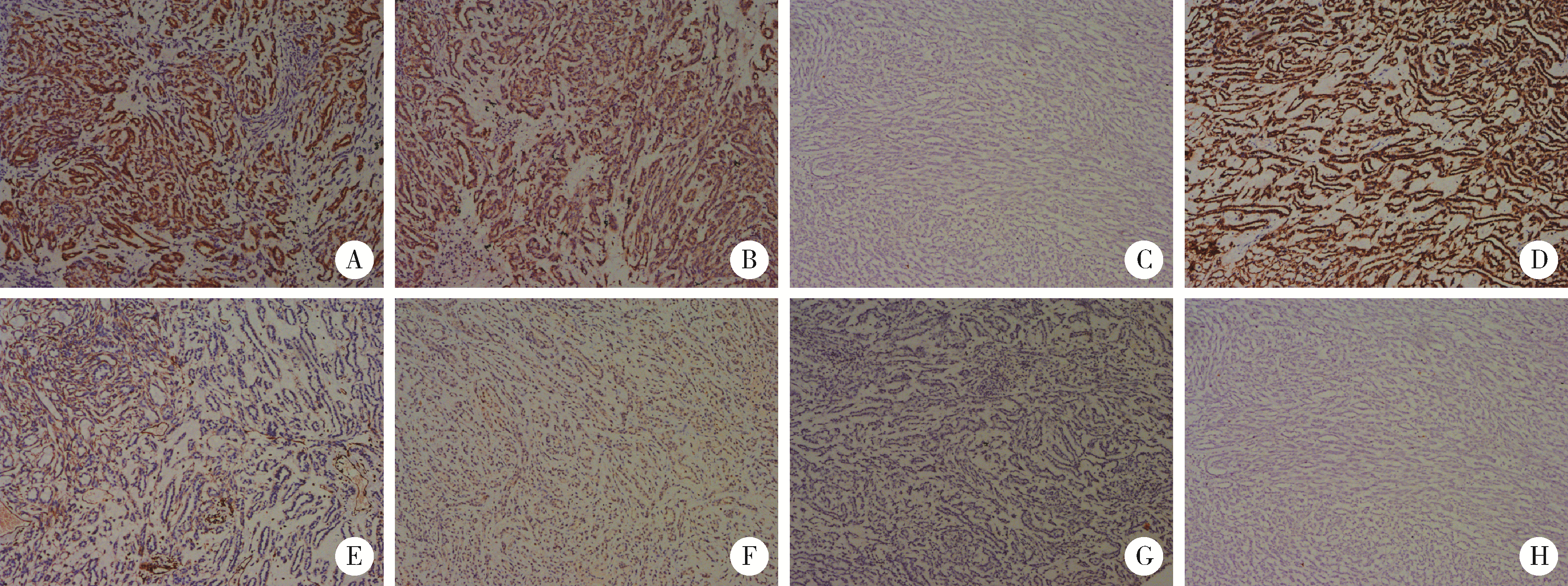
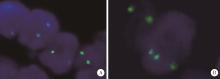
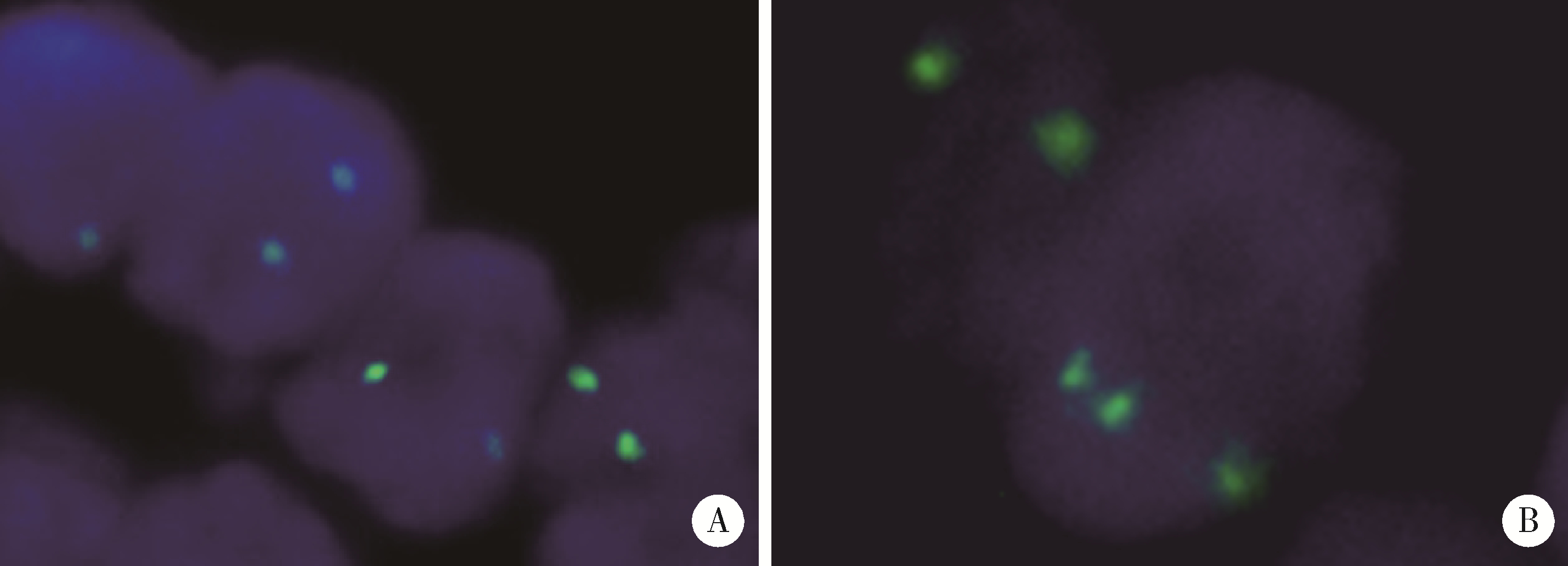
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 276-282. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.02.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of kidney: Clinicopathology and prognosis
- Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital; Institute of Urology, Peking University; National Urological Cancer Center, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R737.11
| 1 | Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, et al. World Health Organization classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs[R]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2004. |
| 2 | Moch H, Humphrey P, Ulbright T, et al. World Health Organization classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs[R]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2016. |
| 3 |
MacLennan GT , Farrow GM , Bostwick DG . Low-grade collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney: Report of 13 cases of low-grade mucinous tubulocystic renal carcinoma of possible collecting duct origin[J]. Urology, 1997, 50 (5): 679- 684.
doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(97)00335-X |
| 4 |
Ged Y , Chen YB , Knezevic A , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle-cell carcinoma of the kidney: Clinical features, genomic profiles, and treatment outcomes[J]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2019, 17 (4): 268- 274.
doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2019.04.006 |
| 5 |
Xu X , Zhong J , Zhou X , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney: A study of clinical, imaging features and treatment outcomes[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12, 865263.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.865263 |
| 6 |
Ferlicot S , Allory Y , Comperat E , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma: A report of 15 cases and a review of the literature[J]. Virchows Arch, 2005, 447 (6): 978- 983.
doi: 10.1007/s00428-005-0036-x |
| 7 |
Rakozy C , Schmahl GE , Bogner S , et al. Low-grade tubular-mucinous renal neoplasms: Morphologic, immunohistochemical, and genetic features[J]. Mod Pathol, 2002, 15 (11): 1162- 1171.
doi: 10.1097/01.MP.0000031709.40712.46 |
| 8 |
Nathany S , Monappa V . Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma: A review of histopathology and clinical and prognostic implications[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2020, 144 (1): 115- 118.
doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0506-RS |
| 9 | Xiao L , Xiao W , Guo Y , et al. Huge mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney: A case report[J]. Urol Case Rep, 2021, 40, 101914. |
| 10 |
Bajpai M , Pooja S , Tyagi M , et al. Mucinous spindle and tubular renal cell cancer: A rare variant of renal cell cancer[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2022, 18 (4): 1168- 1170.
doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_99_21 |
| 11 | Kuroda N , Hes O , Michal M , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma with Fuhrman nuclear grade 3: A histological, immunohistochemical, ultrastructural and FISH study[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2008, 23 (12): 1517- 1523. |
| 12 |
Fuchizawa H , Kijima T , Takada-Owada A , et al. Metastatic mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney responding to nivolumab plus ipilimumab[J]. IJU Case Rep, 2021, 4 (5): 333- 337.
doi: 10.1002/iju5.12342 |
| 13 |
Arafah M , Zaidi SN . Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney with sarcomatoid transformation[J]. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant, 2013, 24 (3): 557- 560.
doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.111066 |
| 14 |
Bulimbasic S , Ljubanovic D , Sima R , et al. Aggressive high-grade mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma[J]. Hum Pathol, 2009, 40 (6): 906- 907.
doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.03.004 |
| 15 |
Pillay N , Ramdial PK , Cooper K , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma with aggressive histomorphology: A sarco-matoid variant[J]. Hum Pathol, 2008, 39 (6): 966- 969.
doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2007.10.006 |
| 16 | Simon RA , di Sant'agnese PA , Palapattu GS , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney with sarcomatoid differentiation[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2008, 1 (2): 180- 184. |
| 17 |
Dhillon J , Amin MB , Selbs E , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney with sarcomatoid change[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2009, 33 (1): 44- 49.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181829ed5 |
| 18 |
Fine SW , Argani P , DeMarzo AM , et al. Expanding the histologic spectrum of mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2006, 30, 1554- 1560.
doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000213271.15221.e3 |
| 19 |
Reuter VE , Argani P , Zhou M , et al. Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in the kidney tumors: Report from the International Society of Urologic Pathology[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2014, 38 (8): e35- e49.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000258 |
| 20 |
Paner GP , Srigley JR , Radhakrishnan A , et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma and papillary renal cell carcinoma of the kidney: Significant immunophenotypic overlap warrants diagnostic caution[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2006, 30 (1): 13- 19.
doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000180443.94645.50 |
| 21 |
Uchida S , Suzuki K , Uno M , et al. Mucin-poor and aggressive mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney: Two case reports[J]. Mol Clin Oncol, 2017, 7 (5): 777- 782.
doi: 10.3892/mco.2017.1400 |
| 22 |
Kuroda N , Nakamura S , Miyazaki E , et al. Low-grade tubular-mucinous renal neoplasm with neuroendocrine differentiation: A histological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study[J]. Pathol Int, 2004, 54 (3): 201- 207.
doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2004.01608.x |
| 23 |
Peckova K , Martinek P , Sperga M , et al. Mucinous spindle and tubular renal cell carcinoma: Analysis of chromosomal aberration pattern of low-grade, high grade, and an overlapping morphologic variant with papillary renal[J]. Ann Diagn Pathol, 2015, 19 (4): 226- 231.
doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.04.004 |
| 24 |
Kuroda N , Naroda T , Tamura M , et al. High-grade mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma: Comparative genomic hybridization study[J]. Ann Diagn Pathol, 2011, 15 (6): 472- 475.
doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2010.08.003 |
| 25 |
Sadimin ET , Chen YB , Wang L , et al. Chromosomal abnormalities of high-grade mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney[J]. Histopathology, 2017, 71 (5): 719- 724.
doi: 10.1111/his.13298 |
| 26 |
Mehra R , Vats P , Cieslik M , et al. Bi-allelic alteration and dysregulation of the Hippo pathway in mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney[J]. Cancer Discov, 2016, 6 (11): 1258- 1266.
doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0267 |
| 27 |
Ren Q , Wang L , Al-Ahmadie HA , et al. Distinct genomic copy number alterations distinguish mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney from papillary renal cell carcinoma with overlapping histologic features[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2018, 42 (6): 767- 777.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001038 |
| 28 |
邹子归, 王玉红, 周晋星, 等. 肾黏液样小管状和梭形细胞癌临床病理分析及全外显子组测序分析[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2021, 50 (7): 762- 767.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20200922-00731 |
| 29 |
Xu H , Li W , Zhu C , et al. Proteomic profiling identifies novel diagnostic biomarkers and molecular subtypes for mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of the kidney[J]. J Pathol, 2022, 257 (1): 53- 67.
doi: 10.1002/path.5869 |
| 30 |
Bharti JN , Choudhary GR , Madduri VKS , et al. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma: A difficult diagnosis[J]. Urol Ann, 2021, 13 (2): 180- 182.
doi: 10.4103/UA.UA_44_20 |
| 31 |
Thway K , du Parcq J , Larkin JM , et al. Metastatic renal muci-nous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma. Atypical behavior of a rare, morphologically bland tumor[J]. Ann Diagn Pathol, 2012, 16 (5): 407- 410.
doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2011.04.001 |
| 32 |
Cossu-Rocca P , Eble JN , Delahunt B , et al. Renal mucinous tubular and spindle carcinoma lacks the gains of chromosomes 7 and 17 and losses of chromosome Y that are prevalent in papillary renal cell carcinoma[J]. Mod Pathol, 2006, 19 (4): 488- 493.
doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800565 |
| [1] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [3] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [4] | Fan SHU,Yichang HAO,Zhanyi ZHANG,Shaohui DENG,Hongxian ZHANG,Lei LIU,Guoliang WANG,Xiaojun TIAN,Lei ZHAO,Lulin MA,Shudong ZHANG. Functional and oncologic outcomes of partial nephrectomy for cystic renal cell carcinoma: A single-center retrospective study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [5] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [6] | Yangyi FANG,Qiang LI,Zhigao HUANG,Min LU,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [7] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [8] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [9] | Yun-chong LIU,Zong-long WU,Li-yuan GE,Tan DU,Ya-qian WU,Yi-meng SONG,Cheng LIU,Lu-lin MA. Mechanism of nuclear protein 1 in the resistance to axitinib in clear cell renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 781-792. |
| [10] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [11] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [12] | Dong LAN,Zhuo LIU,Yu-xuan LI,Guo-liang WANG,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG,Hong-xian ZHANG. Risk factors for massive hemorrhage after radical nephrectomy and removal of venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 825-832. |
| [13] | Han LU,Jian-yun ZHANG,Rong YANG,Le XU,Qing-xiang LI,Yu-xing GUO,Chuan-bin GUO. Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [14] | Yun-fei SHI,Hao-jie WANG,Wei-ping LIU,Lan MI,Meng-ping LONG,Yan-fei LIU,Yu-mei LAI,Li-xin ZHOU,Xin-ting DIAO,Xiang-hong LI. Analysis of clinicopathological and molecular abnormalities of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [15] | Yun-yi XU,Zheng-zheng SU,Lin-mao ZHENG,Meng-ni ZHANG,Jun-ya TAN,Ya-lan YANG,Meng-xin ZHANG,Miao XU,Ni CHEN,Xue-qin CHEN,Qiao ZHOU. Read-through circular RNA rt-circ-HS promotes hypoxia inducible factor 1α expression and renal carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasiveness [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 217-227. |
|
||