Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1069-1074. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.06.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
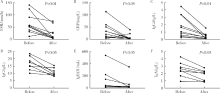
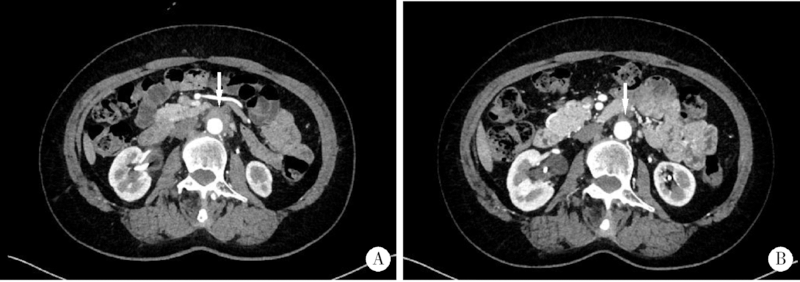
Clinical features of hydronephrosis induced by retroperitoneal fibrosis: 17 cases reports
Shi-bo LIU1,Hui GAO2,Yuan-chun FENG3,Jing LI4,Tong ZHANG5,Li WAN6,Yan-ying LIU7,Sheng-guang LI2,Cheng-hua LUO1,△( ),Xue-wu ZHANG7,△(
),Xue-wu ZHANG7,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Retroperitoneal Tumor Surgery
2.Department of Rheumatology and Immunology
3. Department of Radiology
4. Department of Laboratory Medicine
5. Department of Pathology
6. Department of Nephrology, Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
7. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
- R656.5
| [1] |
Uibu T, Oksa P, Auvinen A, et al. Asbestos exposure as a risk factor for retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. Lancet, 2004,363(9419):1422-1426.
pmid: 15121404 |
| [2] |
Vaglio A, Palmisano A, Alberici F, et al. Prednisone versus tamoxifen in patients with idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: An open-label randomised controlled trial[J]. Lancet, 2011,378(9788):338-346.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60934-3 pmid: 21733570 |
| [3] |
Scheel PJ Jr, Feeley N. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: the clinical, laboratory, and radiographic presentation[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2009,88(4):202-207.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e3181afc439 |
| [4] |
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease[J]. Mod Pathol, 2012,25(9):1181-1192.
doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2012.72 pmid: 22596100 |
| [5] |
Ormond JK. Bilateral ureteral obstruction due to envelopment and compression by an inflammatory retroperitoneal process[J]. J Urol, 1948,59(6):1072-1079.
doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)69482-5 pmid: 18858051 |
| [6] |
Zen Y, Onodera M, Inoue D, et al. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: A clinicopathologic study with respect to immunoglobulin G4[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2009,33(12):1833-1839.
doi: 10.1097/pas.0b013e3181b72882 pmid: 19950407 |
| [7] |
Rossi GM, Rocco R, Accorsi Buttini E, et al. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis and its overlap with IgG4-related disease[J]. Intern Emerg Med, 2017,12(3):287-299.
doi: 10.1007/s11739-016-1599-z pmid: 28070877 |
| [8] | Yamashita K, Haga H, Mikami Y, et al. Degree of IgG4+ plasma cell infiltration in retroperitoneal fibrosis with or without multifocal fibrosclerosis[J]. 2010,52(3):404-409. |
| [9] |
Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Stone JH, et al. Rethinking Ormond's disease: "idiopathic" retroperitoneal fibrosis in the era of IgG4-related disease[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2013,92(2):82-91.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e318289610f |
| [10] |
Caiafa RO, Vinuesa AS, Izquierdo RS, et al. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: Role of imaging in diagnosis and follow-up[J]. Radiographics, 2013,33(2):535-552.
doi: 10.1148/rg.332125085 pmid: 23479712 |
| [11] |
George V, Tammisetti VS, Surabhi VR, et al. Chronic fibrosing conditions in abdominal imaging[J]. Radiographics, 2013,33(4):1053-1080.
doi: 10.1148/rg.334125081 pmid: 23842972 |
| [12] |
Pelkmans LG, Aarnoudse AJ, Hendriksz TR, et al. Value of acute-phase reactants in monitoring disease activity and treatment response in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2012,27(7):2819-2825.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr779 pmid: 22273666 |
| [13] |
van Bommel EF, Siemes C, Hak LE, et al. Long-term renal and patient outcome in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis treated with prednisone[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2007,49(5):615-625.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.02.268 pmid: 17472843 |
| [14] |
Fry AC, Singh S, Gunda SS, et al. Successful use of steroids and ureteric stents in 24 patients with idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: A retrospective study[J]. Nephron Clin Pract, 2008,108(3):c213-220.
doi: 10.1159/000119715 pmid: 18332635 |
| [15] |
Alberici F, Palmisano A, Urban ML, et al. Methotrexate plus prednisone in patients with relapsing idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013,72(9):1584-1586.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203545 pmid: 23696631 |
| [16] |
Scheel PJ Jr, Feeley N, Sozio SM. Combined prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil treatment for retroperitoneal fibrosis: a case series[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2011,154(1):31-36.
doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-154-1-201101040-00005 pmid: 21200036 |
| [17] |
Binder M, Uhl M, Wiech T, et al. Cyclophosphamide is a highly effective and safe induction therapy in chronic periaortitis: a long-term follow-up of 35 patients with chronic periaortitis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2012,71(2):311-312.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200148 pmid: 21859695 |
| [18] |
Li KP, Zhu J, Zhang JL, et al. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis (RPF): Clinical features of 61 cases and literature review[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2011,30(5):601-605.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-010-1580-6 pmid: 20957401 |
| [19] |
Vaglio A, Maritati F. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016,27(7):1880-1889.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015101110 pmid: 26860343 |
| [20] |
Mertens S, Zeegers AG, Wertheimer PA, et al. Efficacy and complications of urinary drainage procedures in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis complicated by extrinsic ureteral obstruction[J]. Int J Urol, 2014,21(3):283-288.
doi: 10.1111/iju.12234 pmid: 24033464 |
| [21] |
Cristian S, Cristian M, Cristian P, et al. Management of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis from the urologist's perspective[J]. Ther Adv Urol, 2015,7(2):85-99.
doi: 10.1177/1756287214565637 pmid: 25829952 |
| [1] | Shuang REN, Huijuan SHI, Zixuan LIANG, Si ZHANG, Xiaoqing HU, Hongshi HUANG, Yingfang AO. Biomechanics during cutting movement in individuals after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 868-873. |
| [2] | Silu CHEN, Haiju WANG, Yucai WU, Zhihua LI, Yanbo HUANG, Yuhui HE, Yangyang XU, Xuesong LI, Hua GUAN. Etiological analysis of hydronephrosis in adults: A single-center cross-sectional study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 913-918. |
| [3] | Mingrui WANG, Qi WANG, Hao HU, Jinhui LAI, Xinwei TANG, Chunyan WAN, Kexin XU, Tao XU. Efficacy of coated metal ureteral stent in the treatment of pelvic lipomatosis induced hydronephrosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 919-922. |
| [4] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [5] | Mingrui WANG,Jun LIU,Liulin XIONG,Luping YU,Hao HU,Kexin XU,Tao XU. Efficacy and safety of mini-track, mini-nephroscopy and mini-ultrasonic probe percutaneous nephrolithotomy for the treatment of 1.5-2.5 cm kidney stones [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 605-609. |
| [6] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [7] | Yicen YING,Yicong DU,Zhihua LI,Yiming ZHANG,Xinfei LI,Bing WANG,Peng ZHANG,Hongjian ZHU,Liqun ZHOU,Kunlin YANG,Xuesong LI. Robot-assisted laparoscopic ureteroplasty with buccal mucosa graft for complex ureteral stricture [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 640-645. |
| [8] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [9] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [10] | Yangyi FANG,Qiang LI,Zhigao HUANG,Min LU,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [11] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [12] | Kewei CHEN,Shaohui DENG,Zhuo LIU,Hongxian ZHANG,Lulin MA,Shudong ZHANG. Discussion on the surgical timing of rupture and hemorrhage of renal angiomyolipoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 326-331. |
| [13] | Xinyu XU,Ling WU,Fengqi SONG,Zili LI,Yi ZHANG,Xiaojing LIU. Mandibular condyle localization in orthognathic surgery based on mandibular movement trajectory and its preliminary accuracy verification [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 57-65. |
| [14] | Andong CAI,Xiaoxia WANG,Wenjuan ZHOU,Zhonghao LIU. Comparison of the virtual surgical planning position of maxilla and condyle with the postoperative real position in patients with mandibular protrusion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 74-80. |
| [15] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
|
||