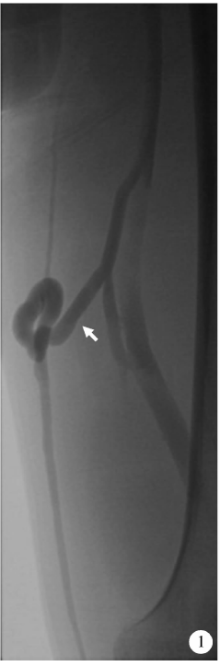
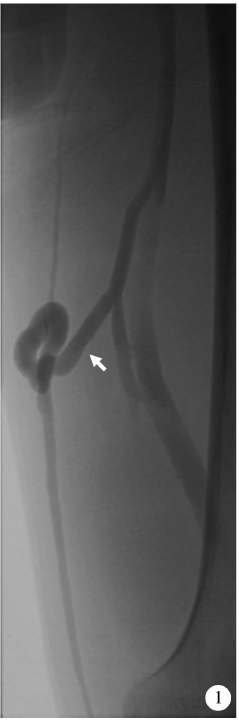
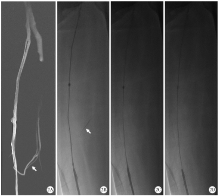
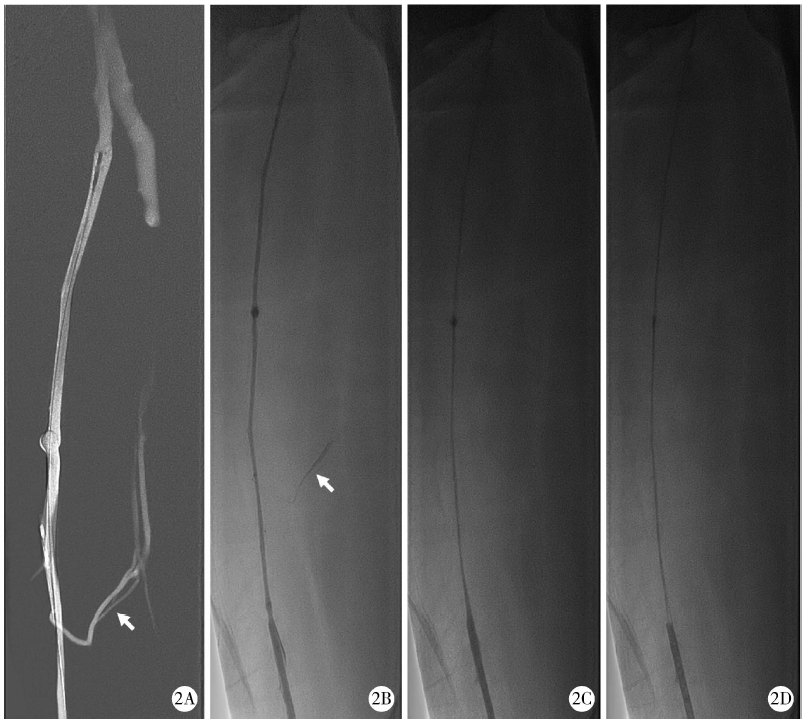
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 332-336. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Radiofrequency obliteration of varicose veins of lower extremity guided by combined venography and ultrasonography
YANG Guang-xin,LUAN Jing-yuan( ),JIA Zi-chang
),JIA Zi-chang
- Department of Interventional Radiology and Vascular Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R543.6
| [1] |
Mallick R, Lal BK, Daugherty C. Relationship between patient-reported symptoms, limitati ons in daily activities, and psychological impact in varicose veins[J]. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord, 2017,5(2):224-237.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2016.11.004 pmid: 28214491 |
| [2] |
Wittens C, Davies AH, Baekgaard N, et al. Editor’s choice: management of chronic venous disease: clinical practice guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS)[J]. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg, 2015,49(6):678-737.
pmid: 25920631 |
| [3] | 刘阳, 黎一呜, 杨文彬, 等. 腔内激光与传统手术治疗大隐静脉曲张的荟萃分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2013,93(23):1822-1826. |
| [4] |
Proebstle TM, Alm BJ, Gockeritz O, et al. Five-year results from the prospective European multicentre cohort study on radiofrequency segmental thermal ablation for incompetent great saphenous veins[J]. Br J Surg, 2015,102(3):212-218.
doi: 10.1002/bjs.9679 pmid: 25627262 |
| [5] | Whiteley MS, Shiangoli I, Dos Santos SJ, et al. Fifteen year results of radiofrequency ablation, using VNUS Closure, for the abolition of truncal venous reflux in patients with varicose veins[J]. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg, 2017,54(3):357-362. |
| [6] |
Lawson JA, Gauw SA, van Vlijmen CJ, et al. Prospective comparative cohort study evaluating incompetent great saphenous vein closure using radiofrequency-powered segmental ablation or 1470-nm endovenous laser ablation with radial-tip fibers (Varico 2 study)[J]. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord, 2018,6(1):31-40.
pmid: 29248107 |
| [7] | 金冲, 冯一浮, 肖春莹, 等. 超声实时监测射频腔内闭合联合点式剥脱治疗大隐静脉曲张[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2018,18(6):528-530. |
| [8] | 冯琦琛, 王昌明, 李选, 等. 超声引导下腔内射频闭合术联合局部点剥治疗下肢静脉曲张[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2018,18(7):577-580. |
| [9] | 牛帅, 张欢, 牛鹿原, 等. 门诊和住院手术模式下静脉曲张微创手术效果比较[J]. 中国血管外科杂志:电子版, 2018,10(4):260-254. |
| [10] |
Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ, Dalsing MC, et al. The care of patients with varicose veins and associated chronic venous diseases: clinical practice guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2011,53(5 Suppl):2S-48S.
pmid: 21536172 |
| [11] |
Nicolaides A, Kakkos S, Eklof B, et al. Management of chronic venous disorders of the lower limbs: guidelines according to scientific evidence[J]. Int Angiol, 2014,33(2):87-208.
pmid: 24780922 |
| [12] |
Pavlovic MD, Schuller-Petrovic S, Pichot O, et al. Guidelines of the first international consensus conference on endovenous thermal ablation for varicose vein disease-ETAV consensus meeting 2012[J]. Phlebology, 2015,30(4):257-273.
pmid: 24534341 |
| [13] | American College of Phlebology. Practice guidelines: Superficial venous disease [EB/OL]. [2019-02-19]. http://www.phlebo-logy.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/SuperficialVenousDisease-GuidelinesPMS313-02.03.16.pdf. |
| [14] |
Siribumrungwong B, Noorit P, Wilasrusmee C, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials comparing endovenous ablation and surgical intervention in patients with varicose vein[J]. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg, 2012,44(2):214-223.
pmid: 22705163 |
| [15] |
Rasmussen L, Lawaetz M, Serup J, et al. Randomized clinical trial comparing endovenous laser ablation, radiofrequency ablation, foam sclerotherapy, and surgical stripping for great saphenous varicose veins with 3-year follow-up[J]. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord, 2013,1(4):349-356.
pmid: 26992754 |
| [16] | He Z, Zheng C, Zhang H, et al. Comparison of ultrasound guided endovenous laser ablation and radiofrequency for the varicose veins treatment: an updated meta-analysis[J]. Int J Surg, 2017,39(5):267-275. |
| [17] |
Reich-Schupke S, Mumme A, Stücker M. Histopathological findings in varicose veins following bipolar radiofrequencyinduced thermotherapy: results of an ex vivo experiment[J]. Phlebology, 2011,26(2):69-74.
doi: 10.1258/phleb.2010.010004 pmid: 21148465 |
| [18] |
Badham GE, Dos Santos SJ, Whiteley MS. Radiofrequency-induced thermotherapy (RFiTT) in a porcine liver model and ex vivo great saphenous vein[J]. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol, 2017,26(4):200-206.
pmid: 28151029 |
| [19] | Quehe P, Alavi Z, Kurylo-Touz T, et al. Endovenous Celon radiofrequency-induced thermal therapy of great saphenous vein: A retrospective study with a 3-year follow-up[J]. SAGE Open Med, 2018,6:2050312118794591. |
| [20] | 刘玉江, 钱林学, 刘冬, 等. 超声引导双极射频感应温热疗法治疗下肢静脉曲张[J]. 中华医学超声杂志:电子版, 2018,15(10):747-750. |
| [21] | 张煜程, 张益明, 吴显光, 等. 射频消融联合泡沫硬化剂闭合、点状剥脱术治疗大隐静脉曲张的效果观察[J]. 浙江医学, 2018,40(19):2155-2157. |
| [22] |
Goodyear SJ, Nyamekye IK. Radiofrequency ablation of varicose veins: best practice techniques and evidence[J]. Phlebology, 2015,30(2 Suppl):9-17.
pmid: 26556697 |
| [23] | Kemaloglu C. Saphenous vein diameter is a single risk factor for early recanalization after endothermal ablation of incompetent great saphenous vein[J]. Vascular, 2019,27(5):537-541. |
| [24] | Patel SJ, Reede DL, Katz DS, et al. Imaging the pregnant patient for nonobstetric conditions: Algorithms and radiation dose conside-rations[J]. Radiographics, 2007,27(6):1705-1722. |
| [1] | Jinfang YUAN, Xinli WANG, Yunpu CUI, Xuemei WANG. Application of urinary luteinizing hormone in the prediction of central precocious puberty in girls [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 788-793. |
| [2] | Yan CHEN,Kuangmeng LI,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG,Jianxing CHENG,Zhongjie ZHENG,Wenhao TANG,Lianming ZHAO,Haitao ZHANG,Hui JIANG,Haocheng LIN. Retrospective study on the impact of penile corpus cavernosum injection test on penile vascular function [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [3] | Yue WEI,Lan YAO,Xi LU,Jun WANG,Li LIN,Kun-peng LIU. Evaluation of gastric emptying after drinking carbohydrates before cesarean section by gastric ultrasonography [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1082-1087. |
| [4] | Yue WEI,Xi LU,Jing ZHANG,Kun-peng LIU,Yong-jun WANG,Lan YAO. Effect of preoperative carbohydrates intake on the gastric volume and the risk of reflux aspiration in patients positioning in trendelenburg undergoing gynecological laparoscopic procedures [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 893-898. |
| [5] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [6] | Yu WANG,Hui-min ZHANG,Xue-rong DENG,Wei-wei LIU,Lu CHEN,Ning ZHAO,Xiao-hui ZHANG,Zhi-bo SONG,Yan GENG,Lan-lan JI,Yu WANG,Zhuo-li ZHANG. Diagnostic values of urinary citrate for kidney stones in patients with primary gout [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1134-1140. |
| [7] | Hai-ying XING,Yu-hui CHEN,Ke XU,Dian-dian HUANG,Qing PENG,Ran LIU,Wei SUN,Yi-ning HUANG. Evaluation of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by vascular plaque quantification (VPQ) technology of three-dimensional ultrasonography [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 991-999. |
| [8] | ZHUANG Jin-man,LI Tian-run,LI Xuan,LUAN Jing-yuan,WANG Chang-ming,FENG Qi-chen,HAN Jin-tao. Application of Rotarex mechanical thrombectomy system in acute lower limb ische-mia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1159-1162. |
| [9] | WANG Yu,DENG Xue-rong,JI Lan-lan,ZHANG Xiao-hui,GENG Yan,ZHANG Zhuo-li. Risk factors and diagnostic value for ultrasound-detected tendon monosodium urate crystal deposition in patients with gout [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 143-149. |
| [10] | Ning-ning LI,Li-na JI,Shuang CHAO,Ke YUAN,Hong MENG,Zhen-yu HUANG,Hua-bin ZHANG. Ultrasound screening and follow-up study of congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract in neonates [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1062-1066. |
| [11] | Xiao-ran NING,Zi-qiao WANG,Shan-shan ZHANG,Xia ZHANG,Su-mei TANG,Yan-ying LIU. Application of ultrasonography scoring system in the assessment of IgG4-related sialadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1032-1035. |
| [12] | Peng FU,Wen CHEN,Li-gang CUI,Hui-yu GE,Shu-min WANG. Applicational value of 2017 ACR TI-RADS stratification in diagnosing thyroid nodules [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1067-1070. |
| [13] | CUI Chen, JIANG Jie, CHEN Wen, CUI Li-gang, WANG Jin-rui. Xanthogranulonatous pyelonephritis: report of 5 cases#br# [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 743-746. |
| [14] | LIU Chang, CUI Li-gang, WANG Hong-lei. Renal Ewing’s sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor: a case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(5): 919-923. |
| [15] | XU Ting, LI Min, TIAN Yang, SONG Jin-tao, NI Cheng, GUO Xiang-yang. Clinical evaluation of in-plane ultrasound-guided thoracic paravertebral block using laterally intercostal approach [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(1): 148-152. |
|
||