Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 598-601. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.03.027
Previous Articles Next Articles
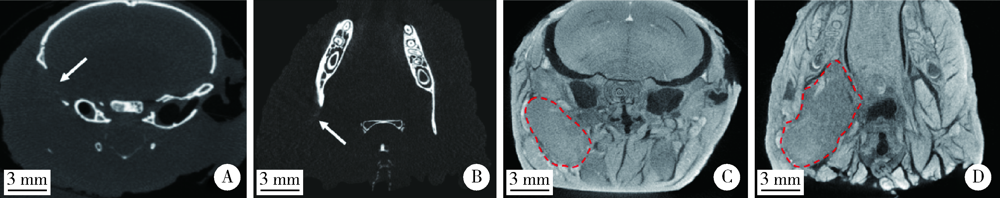
Application of iodine staining technique for tumor identification in Micro-CT of mouse model with skull base-infratemporal fossa tumor
YANG Rong1,LI Qing-xiang1,WANG Yi-fei1,ZHOU Wen2,WANG Wen3,GUO Chuan-bin1,LIU Hao2,Δ( ),GUO Yu-xing1,Δ(
),GUO Yu-xing1,Δ( )
)
- 1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
2. Central Laboratory,Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China
3. Department of Orthodontics, Hospital of Stomotology, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, China
CLC Number:
- R329.4
| [1] | 阮彩莲, 杨延庆, 薛涛, 等. 经耳前颞叶底入路显露中颅底和岩斜区的便携式视频显微解剖[J]. 解剖学报, 2016,47(4):507-509. |
| [2] |
Guo Y, Guo C. Maxillary-fronto-temporal approach for removal of recurrent malignant infratemporal fossa tumors: Anatomical and clinical study[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2014,42(3):206-212.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.05.001 |
| [3] | 杨榕, 李庆祥, 毛驰, 等. 多模态影像融合技术与颅底-颞下区肿瘤的诊断和治疗[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2019,51(1):53-58. |
| [4] | 郭玉兴, 彭歆, 刘筱菁, 等. 导航技术在颅底-颞下区肿瘤手术中的应用[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2013,48(11):645-647. |
| [5] | 郭玉兴, 郭传瑸. 增强CT三维重建在颞下咽旁间隙肿瘤中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2011,43(1):148-150. |
| [6] | 郭玉兴, 郭传瑸, 俞光岩, 等. 影响颞下咽旁间隙恶性肿瘤预后的因素分析[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2012,28(8):775-779. |
| [7] | 毛以华, 朱昭炜, 丁茂超, 等. 应用高分辨率显微CT进行大鼠周围神经微血管三维可视化研究[J]. 解剖学报, 2013,44(3):353-356. |
| [8] |
Faraj KA, Cuijpers VM, Wismans RG, et al. Micro-computed tomographical imaging of soft biological materials using contrast techniques[J]. Tissue Eng Part C Methods, 2009,15(3):493-499.
doi: 10.1089/ten.tec.2008.0436 |
| [9] |
Degenhardt K, Wright AC, Horng D, et al. Rapid 3D phenotyping of cardiovascular development in mouse embryos by micro-CT with iodine staining[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, 2010,3(3):314-322.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.109.918482 pmid: 20190279 |
| [10] |
Jeffery NS, Stephenson RS, Gallagher JA, et al. Micro-computed tomography with iodine staining resolves the arrangement of muscle fibres[J]. J Biomech, 2011,44(1):189-192.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.08.027 pmid: 20846653 |
| [11] |
Metscher BD. MicroCT for developmental biology: a versatile tool for high-contrast 3D imaging at histological resolutions[J]. Dev Dyn, 2009,238(3):632-640.
doi: 10.1002/dvdy.v238:3 |
| [12] |
Wu J, Yin N. Anatomy research of nasolabial muscle structure in fetus with cleft lip: an iodine staining technique based on microcomputed tomography[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2014,25(3):1056-1061.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000651 |
| [13] |
Wu J, Yin N. Detailed anatomy of the nasolabial muscle in human fetuses as determined by Micro-CT combined with iodine staining[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2016,76(1):111-116.
doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000219 |
| [14] | 崔国峰, 魏戎, 武军龙, 等. 骨关节炎动物模型的综合评估[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2019,12(1):68-74. |
| [1] | Jiajun LIU, Guokang LIU, Yuhu ZHU. Immune-related severe pneumonia: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 932-937. |
| [2] | Kewei CHEN,Zhuo LIU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Jianfei YE,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of renal angiomyolipoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 617-623. |
| [3] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [4] | Jie YANG,Jieli FENG,Shudong ZHANG,Lulin MA,Qing ZHENG. Clinical effects of transesophageal echocardiography in different surgical methods for nephrectomy combined with Mayo Ⅲ-Ⅳ vena tumor thrombectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 631-635. |
| [5] | Binshuai WANG,Min QIU,Qianjin ZHANG,Maofeng TIAN,Lei LIU,Guoliang WANG,Min LU,Xiaojun TIAN,Shudong ZHANG. Experience in diagnosis and treatment of 6 cases of renal Ewing's sarcoma with venous thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 636-639. |
| [6] | Xiaodong CHAI,Ziwen SUN,Haishuang LI,Liangyi ZHU,Xiaodan LIU,Yantao LIU,Fei PEI,Qing CHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics of the CD8+ T lymphocytes infiltration and its mechanism in distinct molecular subtype of medulloblastoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 512-518. |
| [7] | Guozhong LIN,Changcheng MA,Chao WU,Yu SI,Jun YANG. Application of microchannel technique in minimally invasive resection of cervical intraspinal tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 318-321. |
| [8] | Xiaotong LING,Liuyang QU,Danni ZHENG,Jing YANG,Xuebing YAN,Denggao LIU,Yan GAO. Three-dimensional radiographic features of calcifying odontogenic cyst and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 131-137. |
| [9] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [10] | Dong LAN,Zhuo LIU,Yu-xuan LI,Guo-liang WANG,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG,Hong-xian ZHANG. Risk factors for massive hemorrhage after radical nephrectomy and removal of venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 825-832. |
| [11] | Zhong CAO,Hong-bing CEN,Jian-hong ZHAO,Jun MEI,Ling-zhi QIN,Wei LIAO,Qi-lin AO. Expression and significance of INSM1 and SOX11 in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and solid pseudopapillary neoplasm [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 575-581. |
| [12] | Li LIANG,Xin LI,Lin NONG,Ying DONG,Ji-xin ZHANG,Dong LI,Ting LI. Analysis of microsatellite instability in endometrial cancer: The significance of minimal microsatellite shift [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 254-261. |
| [13] | Yu-mei LAI,Zhong-wu LI,Huan LI,Yan WU,Yun-fei SHI,Li-xin ZHOU,Yu-tong LOU,Chuan-liang CUI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of anorectal melanoma: A report of 68 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 262-269. |
| [14] | Yan XIONG,Bo ZHANG,Li-gong NIE,Shi-kai WU,Hu ZHAO,Dong LI,Ji-ting DI. Thoracic SMARCA4-deficient undifferentiated tumor-pathological diagnosis and combined immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 351-356. |
| [15] | Fang CAO,Ming ZHONG,Cong-rong LIU. Uterine POLE mutant endometrioid carcinoma combined with human papilloma virus-associated cervical adenocarcinoma: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 370-374. |
|
||