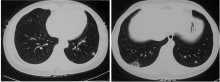
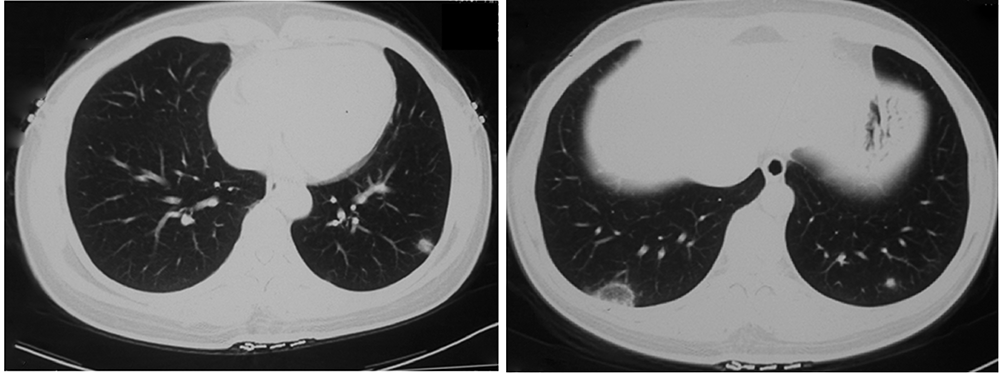
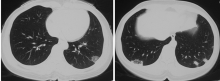
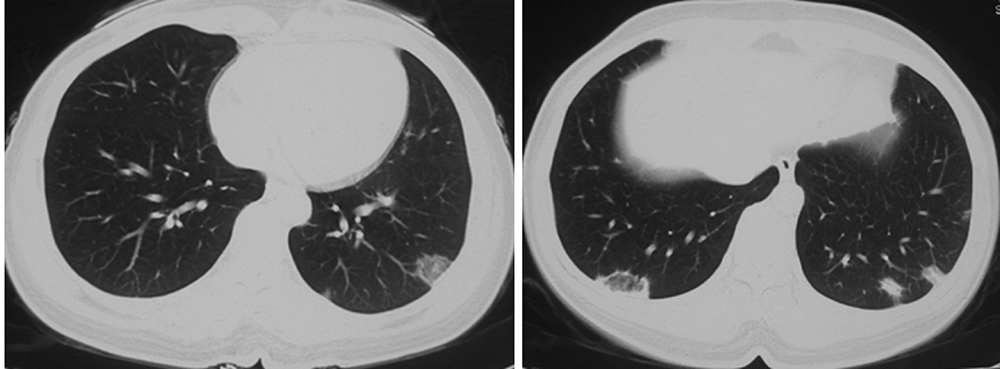
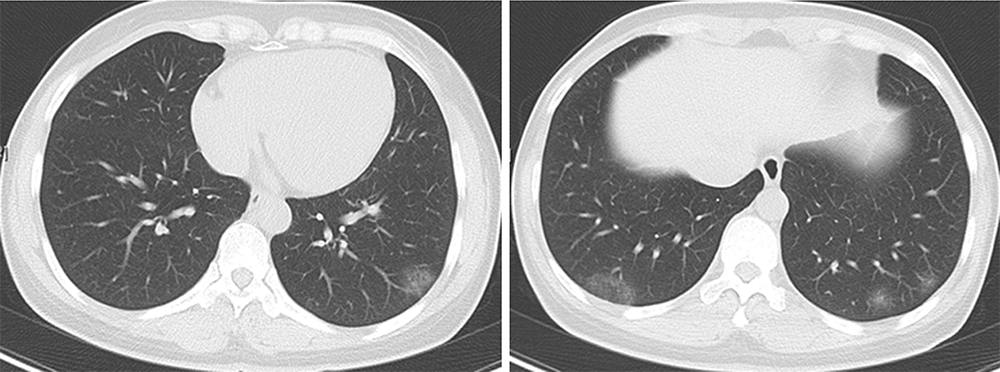
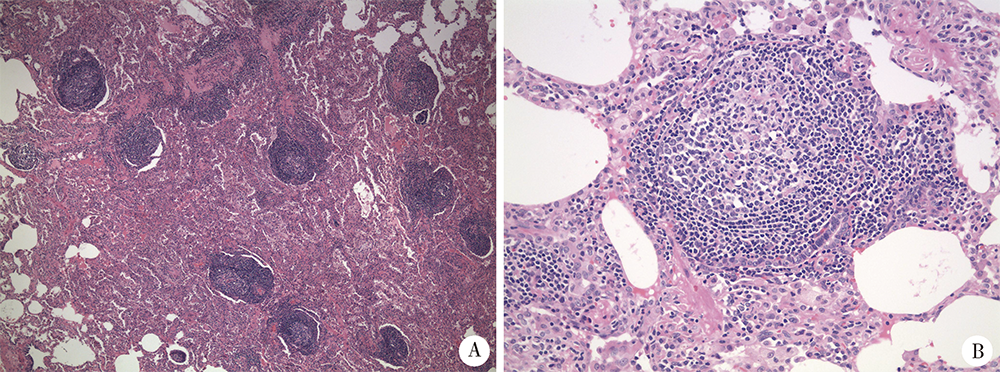
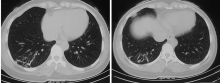
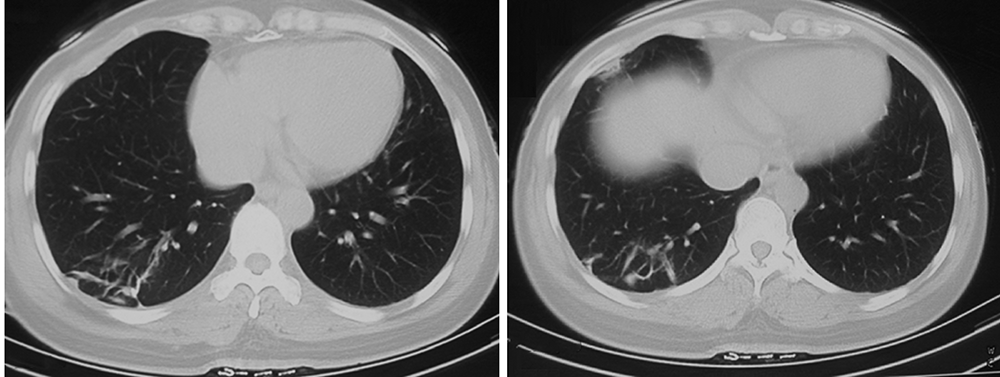
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2021, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1196-1200. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.06.032
Previous Articles Next Articles
Spontaneous remission of follicular bronchiolitis with nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: A case report and literature review
WANG Fei1,ZHU Xiang2,HE Bei1,ZHU Hong1,SHEN Ning1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Pathology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R562.21
| [1] |
Romero S, Barroso E, Gil J, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis: Clinical and pathologic findings in six patients[J]. Lung, 2003, 181(6):309-319.
pmid: 14749935 |
| [2] |
Burgel PR, Bergeron A, de Blic J, et al. Small airways diseases, excluding asthma and COPD: An overview[J]. Eur Respir Rev, 2013, 22(128):131-147.
doi: 10.1183/09059180.00001313 |
| [3] | 方芳, 王芳, 张伟, 等. 肺活检表现为滤泡性细支气管炎的干燥综合征一例[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2013, 36(3):229-230. |
| [4] | 戴建, 蔡后荣, 李燕, 等. 滤泡性细支气管炎三例并文献复习[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2017, 40(6):457-462. |
| [5] |
Lu J, Ma M, Zhao Q, et al. The clinical characteristics and outcomes of follicular bronchiolitis in chinese adult patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1):7300.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25670-8 |
| [6] |
Aerni MR, Vassallo R, Myers JL, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis in surgical lung biopsies: Clinical implications in 12 patients[J]. Respir Med, 2008, 102(2):307-312.
doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2007.07.032 |
| [7] |
Exley CM, Suvarna SK, Matthews S. Follicular bronchiolitis as a presentation of HIV[J]. Clin Radiol, 2006, 61(8):710-713.
pmid: 16843757 |
| [8] | Mateos EA, Lópze FIA, Medel EB, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis. A review of 11 cases[J]. Virchows Arch, 2008, 452(Suppl 1):S56. |
| [9] |
Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 17-2001. A 42-year-old man with multiple pulmonary cysts and recurrent respiratory infections[J]. N Engl J Med, 2001, 344(22):1701-1708.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM200105313442208 |
| [10] |
Vos R, Vanaudenaerde BM, De Vleeschauwer SI, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis. A rare cause of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation: A case report[J]. Am J Transplant, 2009, 9(3):644-650.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02518.x pmid: 19191770 |
| [11] |
Shimizu K, Konno S, Nasuhara Y, et al. A case of follicular bronchiolitis associated with asthma, eosinophilia, and increased immunoglobulin E[J]. J Asthma, 2010, 47(10):1161-1164.
doi: 10.3109/02770903.2010.515326 |
| [12] |
Goksel O, Nart D, Ergonul AG, et al. Successful colchicine the-rapy in a patient with follicular bronchiolitis presumed to be asthma[J]. Respir Care, 2015, 60(7):e122-e124.
doi: 10.4187/respcare.03610 |
| [13] |
Roddy E, Summers G, Chaudry Z, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis, an unusual cause of haemoptysis in giant cell arteritis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2006, 25(3):433-435.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-005-0009-0 |
| [14] | Terada T. Follicular bronchiolitis and lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia in a Japanese man[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2011(6):85. |
| [15] |
Hwangbo Y, Cha SI, Lee YH, et al. A case of multicentric castleman’s disease presenting with follicular bronchiolitis[J]. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul), 2013, 74(1):23-27.
doi: 10.4046/trd.2013.74.1.23 |
| [16] | Wakamatsu K, Nagata N, Taguchi K, et al. A case of follicular bronchiolitis as the histological counterpart to nodular opacities in bronchiectatic mycobacterium avium complex disease[J]. Case Rep Pulmonol, 2012, 2012:214601. |
| [17] | Thalanayar PM, Holguin F. Follicular bronchiolitis in primary ciliary dyskinesia[J]. Australas Med J, 2014, 7(7):294-297. |
| [18] | 牟向东, 廖纪萍, 贺丹眉, 等. 滤泡性细支气管炎一例[J]. 呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2018, 17(1):86-87. |
| [19] |
Hare SS, Souza CA, Bain G, et al. The radiological spectrum of pulmonary lymphoproliferative disease[J]. Br J Radiol, 2012, 85(1015):848-864.
doi: 10.1259/bjr/16420165 pmid: 22745203 |
| [20] | 何慕芝, 蔡闯, 王继业, 等. 反晕征的病因谱及临床意义研究进展[J]. 国际呼吸杂志, 2018, 38(19):1516-1520. |
| [21] |
Tansey D, Wells AU, Colby TV, et al. Variations in histological patterns of interstitial pneumonia between connective tissue disorders and their relationship to prognosis[J]. Histopathology, 2004, 44(6):585-596.
pmid: 15186274 |
| [22] |
Travis WD, Hoffman GS, Leavitt RY, et al. Surgical pathology of the lung in Wegener’s granulomatosis: Review of 87 open lung biopsies from 67 patients[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 1991, 15(4):315-333.
pmid: 2006712 |
| [23] | Tashtoush B, Okafor NC, Ramirez JF, et al. Follicular bronchiolitis: A literature review [J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2015, 9(9): OE01-OE05. |
| [24] |
Bates CA, Ellison MC, Lynch DA, et al. Granulomatous-lymphocytic lung disease shortens survival in common variable immunodeficiency[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2004, 114(2):415-421.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.05.057 |
| [1] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [3] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [4] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [5] | Yangyi FANG,Qiang LI,Zhigao HUANG,Min LU,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [6] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [7] | Wenjing LI,Baozhou ZHANG,Heng LI,Liangpeng LAI,Hui DU,Ning SUN,Xiaofeng GONG,Ying LI,Yan WANG,Yong WU. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis for end-stage ankle and hindfoot arthropathy: Short- and mid-term clinical outcomes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [8] | Qichen FENG,Shuo GAI,Changming WANG,Xuan LI. Application of iliac vein molding and stent implantation through the ipsilateral great saphenous vein approach in daytime treatment mode [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 322-325. |
| [9] | Bochun MAO,Yajing TIAN,Xuedong WANG,Jing LI,Yanheng ZHOU. Soft and hard tissue changes of hyperdivergent class Ⅱ patients before and after orthodontic extraction treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [10] | Xunmin XU,Xiao SHAO,Aiping JI. Analysis of death cases in the oral emergency department [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 185-189. |
| [11] | Xiaomeng REN,Kaiyi LI,Chunlei LI. Detection of molecular affecting sensitivity to local glucocorticoid therapy in oral lichen planus through transcriptome sequencing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 32-38. |
| [12] | Ying ZHOU,Ning ZHAO,Hongyuan HUANG,Qingxiang LI,Chuanbin GUO,Yuxing GUO. Application of double-layer soft tissue suture closure technique in the surgical treatment of patients with mandible medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw of early and medium stages [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 51-56. |
| [13] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [14] | Xue ZOU,Xiao-juan BAI,Li-qing ZHANG. Effectiveness of tofacitinib combined with iguratimod in the treatment of difficult-to-treat moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1013-1021. |
| [15] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
|
||