Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 1036-1040. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
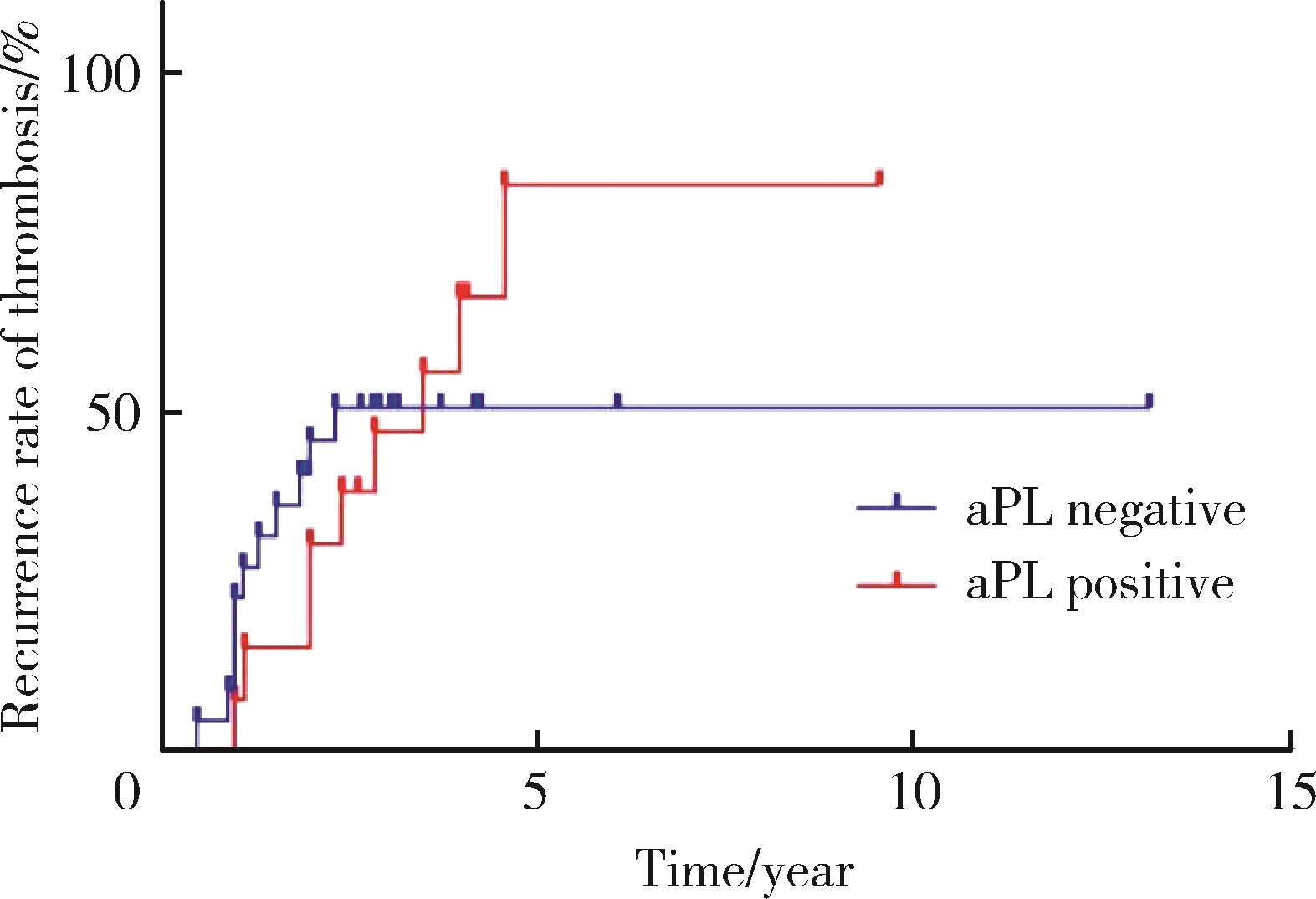
Clinical significance of antiphospholipid antibodies in Behcet disease with thrombosis
Yukai LI1, Hongyan WANG1, Liang LUO1,2, Yun LI1, Chun LI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University People' s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
2. Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, the People' s Hospital of Yubei District of Chongqing, Chongqing 401120, China
CLC Number:
- R593.2
| 1 |
Bulur I , Onder M . Behçet disease: New aspects[J]. Clin Dermatol, 2017, 35 (5): 421- 434.
doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2017.06.004 |
| 2 |
Saadoun D , Wechsler B . Behçet' s disease[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2012, 7, 20.
doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-7-20 |
| 3 |
Shapouri-Moghaddam A , Tavakkol Afshari SJ , Rahimi HR , et al. Para-clinical and immunological evaluation in Buerger' s disease as a suspected autoimmune disease: Case series[J]. Rep Biochem Mol Biol, 2021, 9 (4): 379- 384.
doi: 10.52547/rbmb.9.4.379 |
| 4 |
El-Ageb EM , Al-Maini MH , Al-Shukaily AK , et al. Clinical features of Behçet' s disease in patients in the Sultanate of Oman: The significance of antiphospholipid antibodies?[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2002, 21 (5): 176- 181.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-001-0157-8 |
| 5 |
Espinosa G , Font J , Tàssies D , et al. Vascular involvement in Behçet' s disease: Relation with thrombophilic factors, coagulation activation, and thrombomodulin[J]. Am J Med, 2002, 112 (1): 37- 43.
doi: 10.1016/S0002-9343(01)01048-8 |
| 6 |
Calamia KT , Schirmer M , Melikoglu M . Major vessel involvement in Behçet ' s disease: An update[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2011, 23 (1): 24- 31.
doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283410088 |
| 7 | Lie JT . Vascular involvement in Behçet' s disease: Arterial and venous and vessels of all sizes[J]. J Rheumatol, 1992, 19 (3): 341- 343. |
| 8 |
Islam MA , Alam SS , Kundu S , et al. Prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies in Behçet' s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15 (1): e0227836.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227836 |
| 9 |
Le Joncour A , Martos R , Loyau S , et al. Critical role of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in patients with Behcet' s disease[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2019, 78 (9): 1274- 1282.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214335 |
| 10 |
Li C , Zuo Y , Zhang S , et al. Additional risk factors associated with thrombosis and pregnancy morbidity in a unique cohort of antiphospholipid antibody-positive patients[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2022, 135 (6): 658- 664.
doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001964 |
| 11 |
Zhang X , Gong Z , Shen Y , et al. Alkaline ceramidase 1-mediated platelet ceramide catabolism mitigates vascular inflammation and abdominal aortic aneurysm formation[J]. Nat Cardiovasc Res, 2023, 2 (12): 1173- 1189.
doi: 10.1038/s44161-023-00364-1 |
| 12 |
Güngörer V , Polat MC , Çelikel E , et al. Factors associated with the development of thrombosis in pediatric Behçet disease[J]. J Clin Rheumatol, 2023, 29 (4): e19- e24.
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000001930 |
| 13 | Hatemi G , Christensen R , Bang D , et al. 2018 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of Behçet' s syndrome[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2018, 77 (6): 808- 818. |
| 14 |
Seyahi E . Phenotypes in Behçet' s syndrome[J]. Intern Emerg Med, 2019, 14 (5): 677- 689.
doi: 10.1007/s11739-019-02046-y |
| 15 | Bettiol A , Prisco D , Emmi G . Behçet: The syndrome[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2020, 59 (Suppl 3): iii101- iii107. |
| [1] | Yang TIAN, Yongzheng HAN, Jiao LI, Mingya WANG, Yinyin QU, Jingchao FANG, Hui JIN, Min LI, Jun WANG, Mao XU, Shenglin WANG, Xiangyang GUO. Incidence and risk factors of postoperative epidural hematoma following anterior cervical spine surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1058-1064. |
| [2] | Mingrui WANG, Jinhui LAI, Jiaxiang JI, Xinwei TANG, Haopu HU, Qi WANG, Kexin XU, Tao XU, Hao HU. Risk factors for decreased quality of life in patients with kidney stones predicted by the Chinese version of Wisconsin stone quality of life questionnaire [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1069-1074. |
| [3] | Yinji JIN, Rui LIU. Hereditary protein S deficiency in a patient with prominent mesenteric venous thrombosis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 1106-1109. |
| [4] | Yujing ZHU, Lei WANG, Chengyin LYU, Wenfeng TAN, Miaojia ZHANG. Analysis of clinical features of ruccrent interstitial lung disease in patients with anti-EJ positive antisynthetase syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(6): 980-986. |
| [5] | Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG, Qian ZHANG. Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [6] | Ye YAN,Xiaolong LI,Haizhui XIA,Xuehua ZHU,Yuting ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ke LIU,Cheng LIU,Lulin MA. Analysis of risk factors for long-term overactive bladder after radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [7] | Yuqing LI,Biao WANG,Peng QIAO,Wei WANG,Xing GUAN. Medium to long-term efficacy of tension-free vaginal tape procedure in the treatment of female recurrent stress urinary incontinence [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 600-604. |
| [8] | Yan CHEN,Kuangmeng LI,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG,Jianxing CHENG,Zhongjie ZHENG,Wenhao TANG,Lianming ZHAO,Haitao ZHANG,Hui JIANG,Haocheng LIN. Retrospective study on the impact of penile corpus cavernosum injection test on penile vascular function [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [9] | Bo PANG,Tongjun GUO,Xi CHEN,Huaqi GUO,Jiazhang SHI,Juan CHEN,Xinmei WANG,Yaoyan LI,Anqi SHAN,Hengyi YU,Jing HUANG,Naijun TANG,Yan WANG,Xinbiao GUO,Guoxing LI,Shaowei WU. Personal nitrogen oxides exposure levels and related influencing factors in adults over 35 years old in Tianjin and Shanghai [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 700-707. |
| [10] | Jing HE,Zhongze FANG,Ying YANG,Jing LIU,Wenyao MA,Yong HUO,Wei GAO,Yangfeng WU,Gaoqiang XIE. Relationship between lipid metabolism molecules in plasma and carotid atheroscle-rotic plaques, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and dietary factors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 722-728. |
| [11] | Shan CAI,Yihang ZHANG,Ziyue CHEN,Yunfe LIU,Jiajia DANG,Di SHI,Jiaxin LI,Tianyu HUANG,Jun MA,Yi SONG. Status and pathways of factors influencing physical activity time among elementary and junior high school students in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 403-410. |
| [12] | Zuhong ZHANG,Tianjiao CHEN,Jun MA. Associations between puberty timing and cardiovascular metabolic risk factors among primary and secondary students [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 418-423. |
| [13] | Yuting LIN,Huali WANG,Yu TIAN,Litong GONG,Chun CHANG. Factors influencing cognitive function among the older adults in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [14] | Jinrong ZHU,Yana ZHAO,Wei HUANG,Weiwei ZHAO,Yue WANG,Song WANG,Chunyan SU. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 infection in patients undergoing hemodialysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [15] | Xiaofei TANG,Yonghong LI,Qiuling DING,Zhuo SUN,Yang ZHANG,Yumei WANG,Meiyi TIAN,Jian LIU. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 279-283. |
|
||