Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 740-747. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
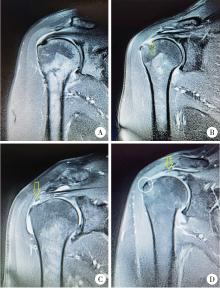
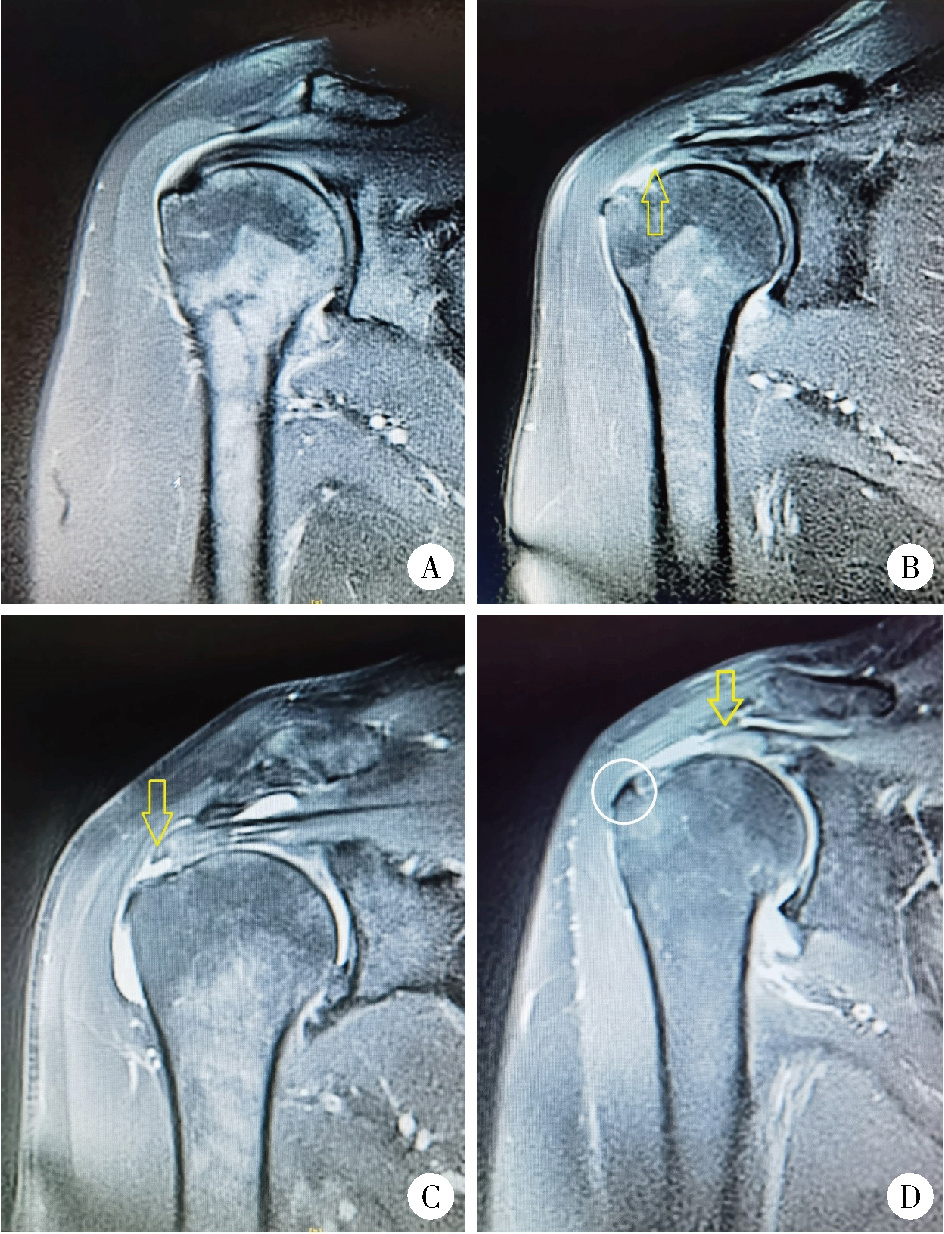
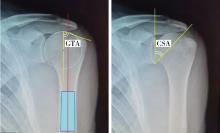
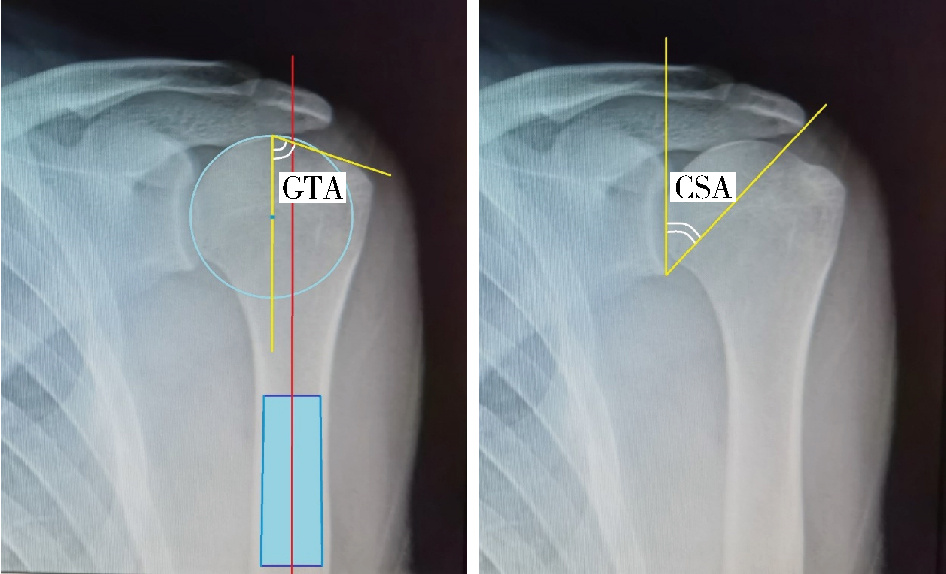
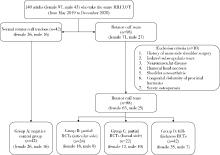
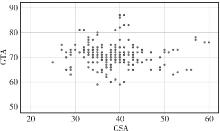
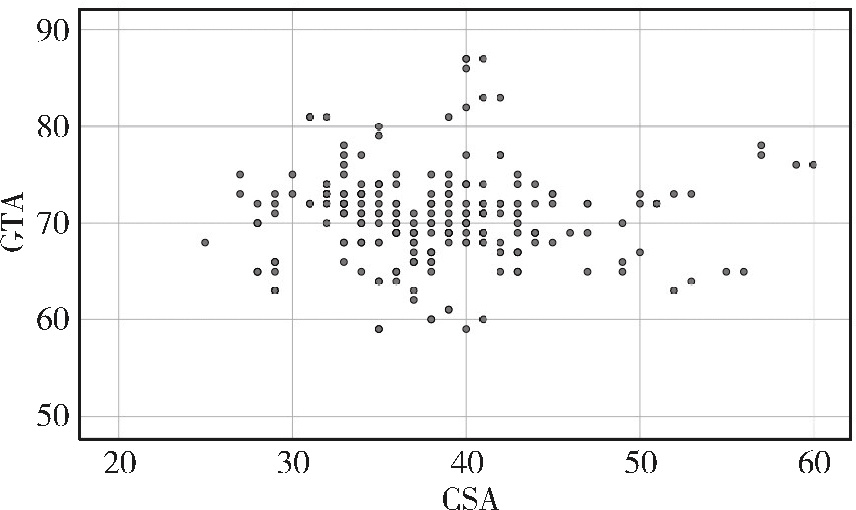
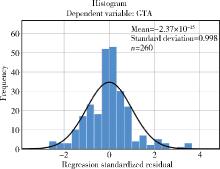
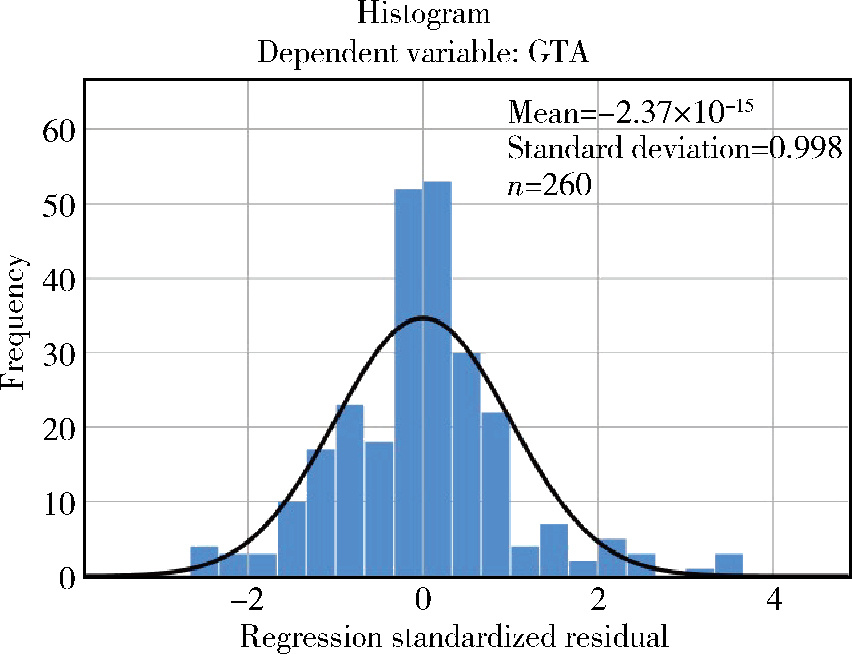
Association of increased greater tubercle angle and critical shoulder angle with rotator cuff tears
Hua JIANG1, Yu YAN2, Panpan LI1, Kang CHEN1, Hongbing MA1, Yong ZENG1, Xin TANG2, Guoqing CUI3,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Orthopedics, Chengdu Second People ' s Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu 610017, China
2. Department of Orthopedics, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China
3. Department of Sports Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R684
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
王琦, 王会祥, 吴晓明. 峰盂角的定义及临床研究进展[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2020, 40 (1): 55- 59.
|
| 8 |
陈俊, 楼珏翔, 申屠国建, 等. 肩关节峰盂角对肩袖撕裂修补术后再撕裂的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2022, 41 (6): 423- 429.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2022.06.002 |
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
|
| [1] | Silan AN,Qunyi ZHENG,Kai WANG,Shan GAO. Characteristics and influencing factors of early pain in patients after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 167-173. |
| [2] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [3] | Hao WU,Li-ping PAN,Heng LIU,Hong-bin WANG,Tai-guo NING,Yong-ping CAO. Effect of posterior tibial slope on the short-term outcome in mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 877-882. |
| [4] | Jia-peng ZHENG,Qi XIAO,Hui-yun DENG,Qing-quan WU,Wen-liang ZHAI,Da-sheng LIN. Arthroscopic classification and management for the popliteal hiatus of the lateral meniscus tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 891-895. |
| [5] | Zhen-xing SHAO,Qing-fa SONG,Yu-qing ZHAO,Guo-qing CUI. An arthroscopic “inlay” Bristow procedure with suture button fixation: Surgical technique and radiology evaluation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 896-901. |
| [6] | Jing-xian ZHU,Sheng-nan LU,Yan-fang JIANG,Ling JIANG,Jian-quan WANG. Influencing factors of preoperative pulmonary function in elderly patients undergoing rotator cuff surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 902-906. |
| [7] | Zhong-di LIU,Ting-min XU,Yu DANG,Dian-ying ZHANG,Zhong-guo FU. A mid-term clinical follow-up study on repair of the meniscus tears by a modified arthroscopic outside-in puncture suture technique [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 870-874. |
| [8] | Dong JIANG,Yue-lin HU,Chen JIAO,Qin-wei GUO,Xing XIE,Lin-xin CHEN,Feng ZHAO,Yan-bin PI. Mid-to-long term outcomes and influence factors of postoperative concurrent chronic ankle instability and posterior ankle impingement [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 505-509. |
| [9] | Cui-ping ZHANG,Pei-pei LIU,Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Li-gang CUI,Yan XU,Jian-quan WANG. Application of ultrasound-guided hip joint drug injection in the postoperative rehabilitation of arthroscopie repair of acetabular labral tears [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 265-267. |
| [10] | LV Ming, ZHANG Jin-qing, WANG Xing-shan, HUANG Ye, LI Wei, ZHANG Chun-yu. Surgical technique and early clinical outcomes of direct anterior approach to total hip arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 206-213. |
| [11] | LI Yang, LI Zi-jian, ZHANG Ke, TIAN Hua, LIU Yan-qing, CAI Hong, LI Feng, ZHAO Min-wei. Analysis on the causes of unscheduled suspensions of knee and hip arthroplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 231-235. |
| [12] | ZHANG Tie-chao, ZHANG Zhi-shan, ZHOU Fang, TIAN Yun, JI Hong-quan, GUO Yan, LV Yang, YANG Zhong-wei, HOU Guo-jin. Diagnosis and treatment for the basicervical fractures of the trochanteric region [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 246-251. |
| [13] | YU Zheng-rong, LI Chun-de, ZHU Sai-nan, SUN Hao-lin, ZHAO Yao, QI Long-tao. Efficacy of transforaminal endoscopic nerve root decompression in the treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 252-255. |
| [14] | LI Wei, JIANG Chun-yan, WANG Zhan-wei, XIAO De-ming. Intraarticular injection of bevacizumab in treatment of osteoarthritis: a laboratory research on a rabbit model [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 203-209. |
| [15] | ZHA Ye-jun, JIANG Xie-yuan, GONG Mao-qi. Treatment of the old terrible triad of the elbow without operative history [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 224-229. |
|
||