Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2018, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1009-1013. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2018.06.012
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
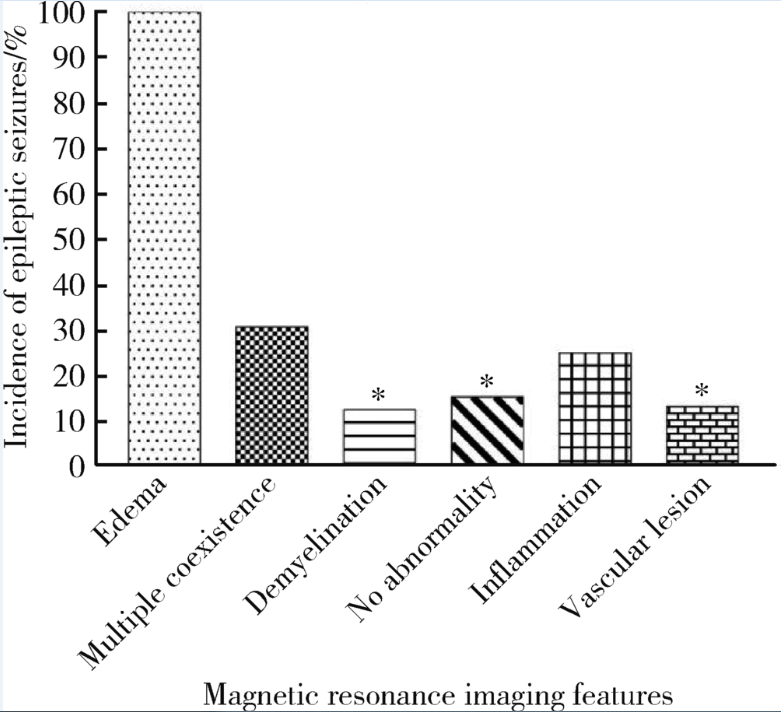
Multidisciplinary classification of magnetic resonance imaging features of neuropsychiatric lupus
Jun-ying CHANG1,Mei ZHENG2,Ying LIU3,Rui LIU4,Jing-feng ZHANG4,Xiao-li DENG4,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology,Handan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Handan 056001, Hebei, China
2. Department of Neurology
3. Department of Radiology
4. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R593.24
| [1] |
Ainiala H, Loukkola J, Peltola J , et al. The prevalence of neuropsychiatric syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Neurology, 2001,57(3):496-500.
doi: 10.1212/WNL.58.12.1867 pmid: 12084902 |
| [2] |
Brey RL, Holliday SL, Saklad AR , et al. Neuropsychiatric syndromes in lupus: prevalence using standardized definitions[J]. Neurology, 2002,58(8):1214-1220.
doi: 10.1212/WNL.58.8.1214 |
| [3] |
Jonsen A, Bengtsson AA, Nived O , et al. Outcome of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus within a defined Swedish population: increased morbidity but low mortality[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2002,41(11):1308-1312.
doi: 10.1097/00003072-199902000-00007 pmid: 12422005 |
| [4] | Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML, Cuadrado MJ , et al. Neuropsychiatric manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence and association with antiphospholipid antibodies[J]. J Rheumatol, 2003,30(5):985-992. |
| [5] |
Afeltra A, Garzia P, Mitterhofer AP , et al. Neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes: relationship with antiphospholipid antibodies[J]. Neurology, 2003,61(1):108-110.
doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000058904.94330.A7 pmid: 12847168 |
| [6] |
Hanly JG, Mccurdy G, Fougere L , et al. Neuropsychiatric events in systemic lupus erythematosus: attribution and clinical significance[J]. J Rheumatol, 2004,31(111):2156-2162.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2004.07.009 pmid: 15517627 |
| [7] |
Mikdashi J, Handwerger B . Predictors of neuropsychiatric damage in systemic lupus erythematosus: data from the Maryland lupus cohort[J]. Rheumatology, 2004,43(12):1555-1560.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh384 pmid: 15342927 |
| [8] |
Zhou HQ, Zhang FC, Tian XP , et al. Clinical features and outcome of neuropsychiatric lupus in Chinese: analysis of 240 hospitalized patients[J]. Lupus, 2008,17(2):93-99.
doi: 10.1177/0961203307085671 pmid: 18250131 |
| [9] |
Bultink IE, Turkstra F, Dijkmans BA , et al. High prevalence of unemployment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: association with organ damage and health-related quality of life[J]. J Rheumatol, 2008,35(6):1053-1057.
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e3181778cb5 pmid: 18381792 |
| [10] |
Hanly JG, Su L, Farewell V , et al. Prospective study of neuropsychiatric events in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. J Rheumatol, 2009,36(71):1449-1459.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.081133 pmid: 19447937 |
| [11] |
Briani C, Lucchetta M, Ghirardello A , et al. Neurolupus is associated with anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies: an inception cohort study[J]. J Autoimmun, 2009,32(2):79-84.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2008.12.002 pmid: 19171463 |
| [12] |
Gonzalez LA, Pons-Estel GJ, Zhang J , et al. Time to neuropsychiatric damage occurrence in LUMINA: a multi-ethnic lupus cohort[J]. Lupus, 2009,18(9):822-830.
doi: 10.1177/0961203309104392 |
| [13] |
The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1999,42(4):599-608.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1529-0131 |
| [14] |
Benseler SM, Silverman ED . Neuropsychiatric involvement in pe-diatric systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2007,16(8):564-571.
doi: 10.1177/0961203307078971 pmid: 17711889 |
| [15] |
Ainiala H, Dastidar P, Loukkola J , et al. Cerebral MRI abnormalities and their association with neuropsychiatric manifestations in SLE: a population-based study[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2005,34(5):376-382.
doi: 10.1080/03009740510026643 pmid: 16234185 |
| [16] |
Peterson PL, Axford JS, Isenberg D . Imaging in CNS lupus[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol, 2005,19(5):727-739.
doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2005.04.001 |
| [17] |
Hanly JG, Walsh NM, Sangalang V . Brain pathology in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. J Rheumatol, 1992,19(5):732-741.
pmid: 1613703 |
| [18] |
Kiss E, Shoenfeld Y . Are anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies relevant in systemic lupus erythematosus?[J]. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, 2007,32(1):37-46.
doi: 10.1007/BF02686080 pmid: 17426359 |
| [19] |
王元, 顾越英, 鲍春德 . 神经精神狼疮的诊断和治疗[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2004,8(4):230-233.
doi: 10.3760/j:issn:1007-7480.2004.04.010 |
| [20] |
Govoni M, Castellino G, Padovan M , et al. Recent advances and perspective in neuroimaging in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Lupus, 2004,13(3):149-158.
doi: 10.1191/0961203304lu1000rr |
| [21] | 杨燕, 刘秀梅, 孙美珍 . 神经精神性狼疮的临床表现和MRI特点分析[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志, 2011,18(4):287-289. |
| [22] |
Sarbu N, Alobeidi F, Toledano P , et al. Brain abnormalities in newly diagnosed neuropsychiatric lupus: systematic MRI approach and correlation with clinical and laboratory data in a large multicenter cohort[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2015,14(2):153-159.
doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.001 pmid: 25461835 |
| [23] |
Luyendijk J, Steens SC, Ouwendijk WJ , et al. Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: lessons learned from magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2011,63(3):722-732.
doi: 10.1002/art.30157 pmid: 21360502 |
| [1] | Yuxuan TIAN,Mingjian RUAN,Yi LIU,Derun LI,Jingyun WU,Qi SHEN,Yu FAN,Jie JIN. Predictive effect of the dual-parametric MRI modified maximum diameter of the lesions with PI-RADS 4 and 5 on the clinically significant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [2] | Yi LIU,Chang-wei YUAN,Jing-yun WU,Qi SHEN,Jiang-xi XIAO,Zheng ZHAO,Xiao-ying WANG,Xue-song LI,Zhi-song HE,Li-qun ZHOU. Diagnostic efficacy of prostate cancer using targeted biopsy with 6-core systematic biopsy for patients with PI-RADS 5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [3] | Chang-wei YUAN,De-run LI,Zhi-hua LI,Yi LIU,Gang-zhi SHAN,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of dynamic contrast enhanced status in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer with PI-RADS 4 lesion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [4] | Ying LIU,Ran HUO,Hui-min XU,Zheng WANG,Tao WANG,Hui-shu YUAN. Correlations between plaque characteristics and cerebral blood flow in patients with moderate to severe carotid stenosis using magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 646-651. |
| [5] | Qiang FU,Guan-ying GAO,Yan XU,Zhuo-hua LIN,You-jing SUN,Li-gang CUI. Comparative study of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of asymptomatic anterosuperior acetabular labrum tears [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 665-669. |
| [6] | Shan YE,Ping-ping JIN,Nan ZHANG,Hai-bo WU,Lin SHI,Qiang ZHAO,Kun YANG,Hui-shu YUAN,Dong-sheng FAN. Cortical thickness and cognitive impairment in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1158-1162. |
| [7] | Ying CAI,Qiao-qin WAN,Xian-jie CAI,Ya-juan GAO,Hong-bin HAN. Epidural photobiomodulation accelerates the drainage of brain interstitial fluid and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 1000-1005. |
| [8] | WANG Shu-lei,GAO Yang-xu,ZHANG Hong-wu,YANG Hai-bo,LI Hui,LI Yu,SHEN Li-xue,YAO Hong-xin. Clinical analysis of 30 cases of basal ganglia germinoma in children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 222-226. |
| [9] | ZHANG Fan,CHEN Qu,HAO Yi-chang,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and preoperative/postoperative membranous urethral length [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [10] | Yi-fan WU,Xiao-yuan ZHANG,Shuang REN,Ying-xiang YU,Cui-qing CHANG. Measurement and evaluation of the quadriceps muscle mass in young men based on magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 843-849. |
| [11] | Hui SHENG,Lei LIANG,Tong-liang ZHOU,Yan-xing JIA,Tong WANG,Lan YUAN,Hong-bin HAN. Improved synthesis process of optical-magnetic bimodal probe of Gd-[4,7-Bis-carboxymethyl-10-(2-fluoresceinthioureaethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraaza-cyclododec-1-yl]-acetic acid complexes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(5): 959-963. |
| [12] | Shi-ming ZHAO,Tie-jun YANG,Chun-miao XU,Xiao-feng GUO,Yong-kang MA,Xue-jun CHEN,Xiang LI,Chao-hong HE. Bladder cancer local staging about muscle invasion: 3.0T MRI performance following transurethral resection [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 701-704. |
| [13] | Yu SONG,Hong-bin HAN,Jun YANG,Ai-bo WANG,Qing-yuan HE,Yuan-yuan LI,Guo-mei ZHAO,Ya-juan GAO,Rui WANG,Yi-xing HAN,Ai-lian LIU,Qing-wei SONG. Effect of convection enhanced delivery on the microstructure of brain extracellular space in aged rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 362-367. |
| [14] | Li XU,Ming-jie HU,Yu-yu LI,Hong-dang QU,Wei-dong QIAN,Xiao-lin LIU. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system caused by myxopapillary ependymoma of conus medullaris and cauda equine: a case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 769-774. |
| [15] | Jing-yun WU,Yue MI,Shui LIU,Lin YAO,Qi TANG,Zhi-song HE,Xiao-ying WANG. Evaluating inferior vena cava wall invasion in renal cell carcinoma tumor thrombus with MRI [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 673-677. |
|
||