Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 657-662. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.04.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
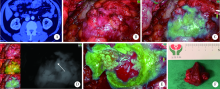
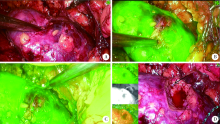
Usefulness of the indocyanine green fluorescence imaging technique in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy
Shu-dong ZHANG1,Peng HONG1,Bin-shuai WANG1,Shao-hui DENG1,Fan ZHANG1,Li-yuan TAO2,Cai-guang CAO3,Zhen-hua HU3,Lu-lin MA1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Clinical Research Center of Epidemiology, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
3. Chinese Academy of Sciences Automation Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Sciences Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Beijing 100190, China
CLC Number:
- R737.11
| [1] |
Lane BR, Gill IS. 7-year oncological outcomes after laparoscopic and open partial nephrectomy[J]. J Urol, 2010,183(2):473-479.
pmid: 20006866 |
| [2] | Teishima J, Takayama Y, Iwagum S, et al. Usefulness of persona-lized three-dimensional printed model on the satisfaction of pre-operative education for patients undergoing robot-assisted partial nephrectomy and their families[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2018,50(6):1061-1066. |
| [3] |
Hekman MCH, Rijpkema M, Langenhuijsen JF, et al. Intraoperative imaging techniques to support complete tumor resection in partial nephrectomy[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2018,4(6):960-968.
pmid: 28753888 |
| [4] | 朱刚, 邢金春, 翁国斌, 等. 全息影像术中导航在泌尿外科腹腔镜和机器人手术中的应用价值[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2020,41(2):131-135. |
| [5] | Kutikov A, Uzzo RG. The R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth[J]. J Urol, 2009,182(3):844-853. |
| [6] | 张树栋. 复杂情况腹腔镜肾部分切除术的方法探讨(附光盘)[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2016,21(5):325-328. |
| [7] | 张树栋, 马潞林, 黄毅, 等. 改良Pfannenstiel 切口取肾的经腹途径腹腔镜肾癌根治术[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2014,46(4):638-641. |
| [8] | Garisto J, Bertolo R, Dagenais J, et al. Robotic versus open partial nephrectomy for highly complex renal masses: comparison of perioperative, functional, and oncological outcomes[J]. Urol Oncol, 2018, 471.e1-471.e9. |
| [9] | 张树栋. 肾门区肿瘤腹腔镜保留肾单位手术的决策(附光盘)[J]. 现代泌尿外科杂志, 2018,23(5):323-327. |
| [10] |
Reinhart MB, Huntington CR, Blair LJ, et al. Indocyanine green: Historical context, current complications,and future considerations[J]. Surg Innov, 2016,23(2):166-175.
pmid: 26359355 |
| [11] |
Simone G, Gabriele Tuderti G, Anceschi U, et al. Ride the green light: Indocyanine green-marked off-clamp robotic partial nephrectomy for totally endophytic renal masses[J]. Eur Urol, 2019,75(6):1008-1014.
pmid: 30262342 |
| [12] | Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, et al. European Association of Urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: The 2019 update[J]. Eur Urol, 2019,75(5):799-810. |
| [13] | Fernando A, Fowler S, O’Brien T. Nephron-sparing surgery across a nation-outcomes from the British Association of Urological Surgeons 2012 National Partial Nephrectomy Audit[J]. BJU Int, 2016,117(6):874-882. |
| [1] | Kewei CHEN,Zhuo LIU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Jianfei YE,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of renal angiomyolipoma with inferior vena cava tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 617-623. |
| [2] | Fan SHU,Yichang HAO,Zhanyi ZHANG,Shaohui DENG,Hongxian ZHANG,Lei LIU,Guoliang WANG,Xiaojun TIAN,Lei ZHAO,Lulin MA,Shudong ZHANG. Functional and oncologic outcomes of partial nephrectomy for cystic renal cell carcinoma: A single-center retrospective study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 667-672. |
| [3] | Min QIU,You-long ZONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Bin YANG,Chu-xiao XU,Zheng-hui SUN,Min LU,Lei ZHAO,Jian LU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA. Treatment outcome of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in patients with renal tumors of moderate to high complexity [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [4] | Zhan-yi ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Cai-guang CAO,Chang-jian LI,Shao-hui DENG,Yue-hao SUN,Tian-liang HUANG,Yun-he GUAN,Nan LI,Min LU,Zhen-hua HU,Shu-dong ZHANG. Near-infrared targeted probe designed for intraoperative imaging of prostatic neurovascular bundles [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 843-850. |
| [5] | Hui-li LIU,Yan-han LV,Xiao-xiao WANG,Min LI. Factors influencing the chronic post-surgical pain after laparoscopic surgery for elderly patients with urinary tract tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [6] | Yu-xiao WU,Yi-fan KANG,Qian-ying MAO,Zi-meng LI,Xiao-feng SHAN,Zhi-gang CAI. Application of methylene blue near-infrared fluorescence imaging for oral sentinel lymph node mapping in rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 684-688. |
| [7] | Wei WANG,Xin LI,Ping LIU,Ying DONG. Clinical value of fluorescence in situ hybridization with MDM2 and DDIT3 probe in diagnosis of liposarcoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 228-233. |
| [8] | Ling-fu ZHANG,Chun-sheng HOU,Zhi XU,Li-xin WANG,Xiao-feng LING,Gang WANG,Long CUI,Dian-rong XIU. Clinical effect of laparoscopic transcystic drainage combined with common bile duct exploration for the patients with difficult biliary stones [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1185-1189. |
| [9] | Li-zhe AN,Liu-lin XIONG,Liang CHEN,Huan-rui WANG,Wei-nan CHEN,Xiao-bo HUANG. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty combined with ultrasonic lithotripsy via nephroscope for treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction with renal calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 746-750. |
| [10] | ZHANG Fan,CHEN Qu,HAO Yi-chang,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and preoperative/postoperative membranous urethral length [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [11] | ZHANG Fan,HUANG Xiao-juan,YANG Bin,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,ZHANG Shu-dong,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between prostate apex depth and early recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 692-696. |
| [12] | QIU Min,WANG Lu,DENG Shao-hui,TA Peng-fei,GUO Wei,LU Jian,LIU Cheng,MA Lu-lin. Primary application of Gerota’s fascia suspension device in retroperitoneal laparoscopic partial nephrectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 789-792. |
| [13] | CHI Yan-ting,ZHANG Yan-ping,ZHANG Qiu-lu,LIU Cui-ling,LI bin-bin. Clinicopathological analysis of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma secondary to Sjögren’s syndrome in salivary gland [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 40-45. |
| [14] | Bing-wei HUANG,Jie WANG,Peng ZHANG,Zhe LI,Si-cheng BI,Qiang WANG,Cai-bo YUE,Kun-lin YANG,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of indocyanine green in complex upper urinary tract repair surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 651-656. |
| [15] | Si-da CHENG,Xin-fei LI,Sheng-wei XIONG,Shu-bo FAN,Jie WANG,Wei-jie ZHU,Zi-ao LI,Guang-pu DING,Ting YU,Wan-qiang LI,Yong-ming SUN,Kun-lin YANG,Lei ZHANG,Han HAO,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Robot-assisted laparoscopic upper urinary tract reconstruction surgery: A review of 108 cases by a single surgeon [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 771-779. |
|
||