Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 907-912. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
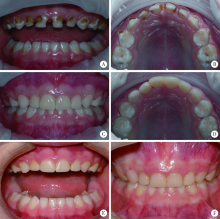
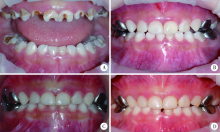
Clinical performance of rensin-bonded composite strip crowns in primary incisors
Xiao-xian CHEN1,Jie ZHONG1,Wen-juan YAN1,Hong-mei ZHANG1,Xia JIANG1,Qian HUANG1,Shi-hua XUE1,Xing-gang LIU2,∆( )
)
- 1. Department of Pediatric Dentistry, First Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Prosthodontics, Beijing Stomatological Hospital & School of Stomatology, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China
CLC Number:
- R783.3
| [1] | 王兴. 第四次全国口腔健康流行病学调查报告 [M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018: 8. |
| [2] | Jeong M, Kim A, Shim Y, et al. Restoration of strip crown with a resin-bonded composite cement in early childhood caries[J]. Case Rep Dent, 2013(2):660-672. |
| [3] | Waggoner WF. Restorative dentistry for the primary dentition[M] // Pinkham JR. Pediatric dentistry: Infancy through adolescence. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W. B. Saunders, 1994: 298-325. |
| [4] |
Waggoner WF. Restoring primary anterior teeth: updated for 2014[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2015,37(2):163-170.
pmid: 25905657 |
| [5] |
Almeida AG, Roseman MM, Sheff M, et al. Future caries susceptibility in children with early childhood caries following treatment under general anesthesia[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2000,22(4):302-306.
pmid: 10969437 |
| [6] |
Cuvillon P, Nouvellon E, Marret E, et al. American Society of Anesthesiologists’ physical status system: a multicentre Francophone study to analyses reasons for classification disagreement[J]. Eur J Anaesthesiol, 2011,28(10):742-747.
doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e328348fc9d pmid: 21912242 |
| [7] | 中华口腔医学会. 口腔医学行业标准规范及指南 [M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2015. |
| [8] |
Ryge G. Clinical criteria[J]. Int Dent J, 1980,30(4):347-358.
pmid: 6935165 |
| [9] |
Kupietzky A, Waggoner WF, Galea J. The clinical and radiographic success of bonded resin composite strip crowns for primary incisors[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2003,25(6):577-581.
pmid: 14733473 |
| [10] |
Al-Eheideb AA, Herman NG. Outcomes of dental procedures performed on children under general anesthesia[J]. J Clin Pediatr Dent, 2003,27(2):181-183.
doi: 10.17796/jcpd.27.2.k3307186n7086r11 pmid: 12597693 |
| [11] | 李永吉, 滕立群, 张英华, 等. 透明成形冠在大面积龋损乳前牙修复中的应用[J]. 广东牙病防治, 2011,19(6):299-301. |
| [12] |
Kupietzky A, Waggoner WE, Galea J. Long-term photographic and radiographic assessment of bonded resin composite strip crowns for primary incisors: results after 3 years[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2005,27(3):221-225.
pmid: 16173227 |
| [13] |
Ram D, Fuks AB. Clinical performance of resin-bonded composite strip crowns in primary incisors: a retrospective study[J]. Int J Paediatr Dent, 2006,16(1):49-54.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-263X.2006.00680.x pmid: 16364093 |
| [14] |
Duhan H, Pandit IK, Srivastava N, et al. Clinical comparison of various esthetic restorative options for coronal build-up of primary anterior teeth[J]. Dent Res J, 2015,12(6):574-580.
doi: 10.4103/1735-3327.170578 |
| [15] |
Eidelman E, Faibis S, Peretz B. A comparison of restorations for children treated under general anesthesia or conscious sedation[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2000,22(1):33-37.
pmid: 10730284 |
| [16] |
Dietschi D, Campanile G, Holz J, et al. Comparison of the color stability of ten new-generation composites: an in vitro study[J]. Dent Mater, 1994,10(6):353-362.
doi: 10.1016/0109-5641(94)90059-0 pmid: 7498599 |
| [17] |
Ernst CP, Brandenbusch M, Meyer G, et al. Two-year clinical performance of a nanofiller vs a fine-particle hybrid resin composite[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2006,10(2):119-125.
doi: 10.1007/s00784-006-0041-8 pmid: 16555069 |
| [18] |
El Shahawy OI, O’Connell AC. Successful restoration of severely mutilated primary incisors using a novel method to retain zirconia crowns—two year results[J]. J Clin Pediatr Dent, 2016,40(6):425-430.
doi: 10.17796/1053-4628-40.6.425 pmid: 27805887 |
| [1] | Shuangyun ZHAO, Siyu ZOU, Xueying LI, Lijuan SHEN, Hong ZHOU. Evaluation of reliability and validity of Chinese version of a short-form of Health Literacy Dental scale (HeLD-14) in the application among parents of preschool children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 828-832. |
| [2] | Xinxin CHEN, Zhe TANG, Yanchun QIAO, Wensheng RONG. Caries experience and its correlation with caries activity of 4-year-old children in Miyun District of Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 833-838. |
| [3] | Zhihan YUE,Na HAN,Zheng BAO,Jinlang LYU,Tianyi ZHOU,Yuelong JI,Hui WANG,Jue LIU,Haijun WANG. A prospective cohort study of association between early childhood body mass index trajectories and the risk of overweight [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 390-396. |
| [4] | Xiuwen FEI,Si LIU,Bo WANG,Aimei DONG. Clinical characteristics and treatment in adults and children with histiocytic necroti-zing lymphadenitis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 533-540. |
| [5] | Xiao-jin YAN,Yun-fei LIU,Ning MA,Jia-jia DANG,Jing-shu ZHANG,Pan-liang ZHONG,Pei-jin HU,Yi SONG,Jun MA. Assessment of prevalence of malnutrition among Chinese primary and secondary school students and analysis of policy effect during the period of the Program for the Development of Chinese Children 2011-2020 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 593-599. |
| [6] | Xiao-yi MI,Shan-shan HOU,Zi-yuan FU,Mo ZHOU,Xin-xuan LI,Zhao-xue MENG,Hua-fang JIANG,Hong Zhou. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of adverse childhood experiences international questionnaire in parents of preschool children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 408-414. |
| [7] | Meng-jie CUI,Qi MA,Man-man CHEN,Tao MA,Xin-xin WANG,Jie-yu LIU,Yi ZHANG,Li CHEN,Jia-nuo JIANG,Wen YUAN,Tong-jun GUO,Yan-hui DONG,Jun MA,Yi XING. Association between different growth patterns and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents aged 7 to 17 years [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 415-420. |
| [8] | Jia-jia DANG,Shan CAI,Pan-liang ZHONG,Ya-qi WANG,Yun-fei LIU,Di SHI,Zi-yue CHEN,Yi-hang ZHANG,Pei-jin HU,Jing LI,Jun MA,Yi SONG. Association of outdoor artificial light at night exposure with overweight and obesity among children and adolescents aged 9 to 18 years in China [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 421-428. |
| [9] | Hui LI,Yang-xu GAO,Shu-lei WANG,Hong-xin YAO. Surgical complications of totally implantable venous access port in children with malignant tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1167-1171. |
| [10] | Jing LIU,Ai-dong LU,Ying-xi ZUO,Jun WU,Zhi-zhuo HUANG,Yue-ping JIA,Ming-ming DING,Le-ping ZHANG,Jiong QIN. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of seizures in 75 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 948-953. |
| [11] | Ya-xi CUI,Jun-bao DU,Qing-you ZHANG,Ying LIAO,Ping LIU,Yu-li WANG,Jian-guang QI,Hui YAN,Wen-rui XU,Xue-qin LIU,Yan SUN,Chu-fan SUN,Chun-yu ZHANG,Yong-hong CHEN,Hong-fang JIN. A 10-year retrospective analysis of spectrums and treatment options of orthostatic intolerance and sitting intolerance in children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 954-960. |
| [12] | Tao MA,Yan-hui LI,Man-man CHEN,Ying MA,Di GAO,Li CHEN,Qi MA,Yi ZHANG,Jie-yu LIU,Xin-xin WANG,Yan-hui DONG,Jun MA. Associations between early onset of puberty and obesity types in children: Based on both the cross-sectional study and cohort study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(5): 961-970. |
| [13] | Yan-yan DU,Jian WANG,Lan HE,Li-na JI,Xi-wei XU. Kawasaki disease complicated with mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 756-761. |
| [14] | Yun-fei LIU,Jia-jia DANG,Pan-liang ZHONG,Ning MA,Di SHI,Yi SONG. Injury mortality among Chinese aged 5 to 24 years from 1990 to 2019 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 498-504. |
| [15] | Jing QIAN,You-jia WEI,Yi-jing CHENG,Yi ZHANG,Bo PENG,Chun-mei ZHU. Analysis of clinical features and risk factors of necrotizing pneumonia in children [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(3): 541-547. |
|
||