Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 971-974. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.030
Previous Articles Next Articles
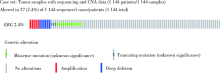
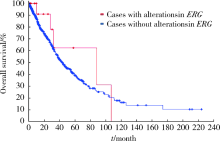
Concordant point mutation of ETS-related gene (ERG) in tumor tissues from a synchronous multiple primary lung cancer: A case report
- 1. Department of Oncology, The Second Hospital of Jiaxing, Jiaxing 314000, Zhejiang, China
2. Key Laboratory, The Second Hospital of Jiaxing, Jiaxing 314000, Zhejiang, China
CLC Number:
- R734.2
| [1] |
Kumar-Sinha C, Tomlins SA, Chinnaiyan AM. Recurrent gene fusions in prostate cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2008,8(7):497-511.
doi: 10.1038/nrc2402 pmid: 18563191 |
| [2] |
Brenner JC, Ateeq B, Li Y, et al. Mechanistic rationale for inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in ETS gene fusion-positive prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2011,19(5):664-678.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.04.010 |
| [3] |
Wang X, Qiao Y, Asangani IA, et al. Development of peptidomimetic inhibitors of the ERG gene gusion product in prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2017,31(4):532-548.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.02.017 pmid: 28344039 |
| [4] |
Martini N, Melamed MR. Multiple primary lung cancers[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 1975,70(4):606-612.
pmid: 170482 |
| [5] |
Kozower BD, Larner JM, Detterbeck FC. Special treatment issues in non-small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines[J]. Chest, 2013,143(5 Suppl):e369S-e399S.
doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2362 pmid: 23649447 |
| [6] |
Slaughter DP, Southwick HW, Smejkal W. Field cancerization in oral stratified squamous epithelium; clinical implications of multicentric origin[J]. Cancer, 1953,6(5):963-968.
doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195309)6:5<963::aid-cncr2820060515>3.0.co;2-q pmid: 13094644 |
| [7] |
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Nature, 2014,511(7511):543-550.
doi: 10.1038/nature13385 |
| [8] |
Jamal-Hanjani M, Wilson GA, McGranahan N, et al. Tracking the evolution of non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017,376(22):2109-2121.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1616288 pmid: 28445112 |
| [9] |
Adamo P, Ladomery MR. The oncogene ERG: A key factor in prostate cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2016,35(4):403-414.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.109 pmid: 25915839 |
| [10] |
Ida K, Kobayashi S, Taki T, et al. EWS-FLI-1 and EWS-ERG chimeric mRNAs in Ewing’s sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumor[J]. Int J Cancer, 1995,63(4):500-504.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910630407 pmid: 7591257 |
| [11] |
Nagai N, Ohguchi H, Nakaki R, et al. Downregulation of ERG and FLI1 expression in endothelial cells triggers endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. PLoS Genet, 2018,14(11):e1007826.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007826 pmid: 30500808 |
| [1] | Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG, Qian ZHANG. Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | Yuxuan TIAN,Mingjian RUAN,Yi LIU,Derun LI,Jingyun WU,Qi SHEN,Yu FAN,Jie JIN. Predictive effect of the dual-parametric MRI modified maximum diameter of the lesions with PI-RADS 4 and 5 on the clinically significant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [3] | Kaifeng YAO,Mingjian RUAN,Derun LI,Yuxuan TIAN,Yuke CHEN,Yu FAN,Yi LIU. Diagnostic efficacy of targeted biopsy combined with regional systematic biopsy in prostate cancer in patients with PI-RADS 4-5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [4] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [5] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [6] | Yi LIU,Chang-wei YUAN,Jing-yun WU,Qi SHEN,Jiang-xi XIAO,Zheng ZHAO,Xiao-ying WANG,Xue-song LI,Zhi-song HE,Li-qun ZHOU. Diagnostic efficacy of prostate cancer using targeted biopsy with 6-core systematic biopsy for patients with PI-RADS 5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [7] | Min QIU,You-long ZONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Bin YANG,Chu-xiao XU,Zheng-hui SUN,Min LU,Lei ZHAO,Jian LU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA. Treatment outcome of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in patients with renal tumors of moderate to high complexity [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [8] | Chang-wei YUAN,De-run LI,Zhi-hua LI,Yi LIU,Gang-zhi SHAN,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of dynamic contrast enhanced status in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer with PI-RADS 4 lesion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [9] | Hui-li LIU,Yan-han LV,Xiao-xiao WANG,Min LI. Factors influencing the chronic post-surgical pain after laparoscopic surgery for elderly patients with urinary tract tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [10] | Zhong CAO,Hong-bing CEN,Jian-hong ZHAO,Jun MEI,Ling-zhi QIN,Wei LIAO,Qi-lin AO. Expression and significance of INSM1 and SOX11 in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and solid pseudopapillary neoplasm [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 575-581. |
| [11] | Jian-xun MA,You-chen XIA,Bi LI,Hong-mei ZHAO,Yu-tao LEI,Xi BU. Choice of immediate breast reconstructive methods after modified radical mastectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 612-618. |
| [12] | Yu-xiao WU,Yi-fan KANG,Qian-ying MAO,Zi-meng LI,Xiao-feng SHAN,Zhi-gang CAI. Application of methylene blue near-infrared fluorescence imaging for oral sentinel lymph node mapping in rats [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 684-688. |
| [13] | Shang XIE,Zhi-gang CAI,Xiao-feng SHAN. Application value of whole exon sequencing and immune related indicators in the precision treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 697-701. |
| [14] | Han LU,Jian-yun ZHANG,Rong YANG,Le XU,Qing-xiang LI,Yu-xing GUO,Chuan-bin GUO. Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [15] | Yun-jing ZHANG,Li-ying QIAO,Meng QI,Ying YAN,Wei-wei KANG,Guo-zhen LIU,Ming-yuan WANG,Yun-feng XI,Sheng-feng WANG. Development and validation of risk prediction model for new-onset cardiovascular diseases among breast cancer patients: Based on regional medical data of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 471-479. |
|
||