Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1185-1189. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
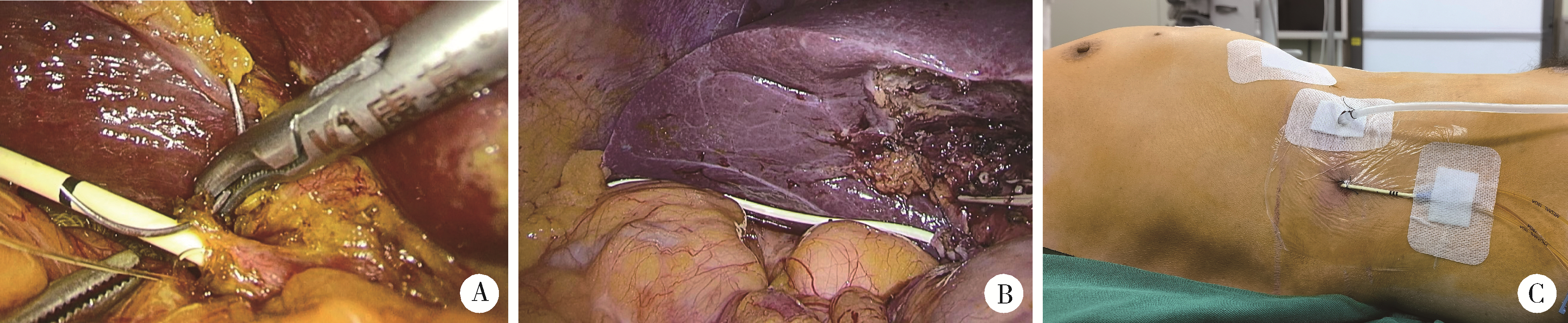
Clinical effect of laparoscopic transcystic drainage combined with common bile duct exploration for the patients with difficult biliary stones
Ling-fu ZHANG,Chun-sheng HOU*( ),Zhi XU,Li-xin WANG,Xiao-feng LING,Gang WANG,Long CUI,Dian-rong XIU
),Zhi XU,Li-xin WANG,Xiao-feng LING,Gang WANG,Long CUI,Dian-rong XIU
- Department of General Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R657.4
| 1 |
Vu AN , Eskander J , Chan STF , et al. Impact of single-stage laparoscopic trans-cystic exploration on hospital procedures, admissions and length-of-stay in common bile duct stone clearance[J]. ANZ J Surg, 2021, 91 (12): 2695- 2700.
doi: 10.1111/ans.17255 |
| 2 |
Ma Z , Zhou J , Yao L , et al. Safety and efficacy of laparoscopic common bile duct exploration for the patients with difficult biliary stones: 8 years of experiences at a single institution and literature review[J]. Surg Endosc, 2022, 36 (1): 718- 727.
doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08340-1 |
| 3 |
Jin Z , Wei Y , Tang X , et al. Single-operator peroral cholangioscope in treating difficult biliary stones: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Dig Endosc, 2019, 31 (3): 256- 269.
doi: 10.1111/den.13307 |
| 4 |
Panaro F , Glaise A , Miggino M , et al. Rubber transcystic drai-nage reduces the post-removal biliary complications in liver transplantation: A matched case-control study[J]. Langenbecks Arch Surg, 2013, 398 (1): 169- 176.
doi: 10.1007/s00423-012-0970-4 |
| 5 | Guan H , Jiang G , Mao X . Primary duct closure combined with transcystic drainage versus T-tube drainage after laparoscopic choledochotomy[J]. ANZ J Surg, 2019, 89 (7/8): 885- 888. |
| 6 |
Dindo D , Demartines N , Clavien PA . Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey[J]. Ann Surg, 2004, 240 (2): 205- 213.
doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae |
| 7 |
Al-Ardah M , Barnett RE , Morris S , et al. Lessons learnt from the first 200 unselected consecutive cases of laparoscopic exploration of common bile duct stones at a district general hospital[J]. Surg Endosc, 2021, 35 (11): 6268- 6277.
doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-08127-w |
| 8 |
Ali N , Nadeem M , Nauyan F , et al. Laparoscopic management of common bile duct stones: Stratifying risks, a district hospital experience[J]. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A, 2022, 32 (2): 165- 170.
doi: 10.1089/lap.2021.0022 |
| 9 |
Maghsoudi H , Garadaghi A , Jafary GA . Biliary peritonitis requiring reoperation after removal of T-tubes from the common bile duct[J]. Am J Surg, 2005, 190 (3): 430- 433.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.04.015 |
| 10 |
Parra-Membrives P , Martinez-Baena D , Marquez-Munoz M , et al. Does laparoscopic approach impair T-tube-related sinus-tract formation?[J]. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech, 2013, 23 (1): 55- 60.
doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e3182747b19 |
| 11 | 管辉球, 景岚, 徐锁青. 胆总管一期缝合经胆囊管胆管引流与鼻胆管引流的对比研究[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2018, 56 (2): 130- 134. |
| 12 |
de Araujo TB , Jotz GP , Zaki CH , et al. Intraoperative cholangiography with filling defects: Comparative complication analysis of postoperative transcystic duct (TCD) catheter maintenance[J]. Surg Endosc, 2021, 35 (12): 6438- 6448.
doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-08133-y |
| [1] | Min QIU,You-long ZONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Bin YANG,Chu-xiao XU,Zheng-hui SUN,Min LU,Lei ZHAO,Jian LU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA. Treatment outcome of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in patients with renal tumors of moderate to high complexity [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [2] | Hui-li LIU,Yan-han LV,Xiao-xiao WANG,Min LI. Factors influencing the chronic post-surgical pain after laparoscopic surgery for elderly patients with urinary tract tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [3] | Wei ZHENG,Yong-hui HUANG,Hong CHANG,Wei YAO,Ke LI,Xiu-e YAN,Yao-peng ZHANG,Ying-chun WANG,Wen-zheng LIU. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in patients after bilioenteric anstomosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1178-1184. |
| [4] | Li-zhe AN,Liu-lin XIONG,Liang CHEN,Huan-rui WANG,Wei-nan CHEN,Xiao-bo HUANG. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty combined with ultrasonic lithotripsy via nephroscope for treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction with renal calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 746-750. |
| [5] | ZHANG Fan,CHEN Qu,HAO Yi-chang,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and preoperative/postoperative membranous urethral length [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [6] | ZHANG Fan,HUANG Xiao-juan,YANG Bin,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,ZHANG Shu-dong,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between prostate apex depth and early recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 692-696. |
| [7] | Bing-wei HUANG,Jie WANG,Peng ZHANG,Zhe LI,Si-cheng BI,Qiang WANG,Cai-bo YUE,Kun-lin YANG,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of indocyanine green in complex upper urinary tract repair surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 651-656. |
| [8] | Shu-dong ZHANG,Peng HONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Shao-hui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Li-yuan TAO,Cai-guang CAO,Zhen-hua HU,Lu-lin MA. Usefulness of the indocyanine green fluorescence imaging technique in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 657-662. |
| [9] | Si-da CHENG,Xin-fei LI,Sheng-wei XIONG,Shu-bo FAN,Jie WANG,Wei-jie ZHU,Zi-ao LI,Guang-pu DING,Ting YU,Wan-qiang LI,Yong-ming SUN,Kun-lin YANG,Lei ZHANG,Han HAO,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Robot-assisted laparoscopic upper urinary tract reconstruction surgery: A review of 108 cases by a single surgeon [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 771-779. |
| [10] | Hai-wen HUANG,Bing YAN,Mei-xia SHANG,Li-bo LIU,Han HAO,Zhi-jun XI. Propensity-matched comparison of laparoscopic and open radical cystectomy for female patients with bladder cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 698-705. |
| [11] | Hai-yue ZHAO,Xiong-jun YE,Wei-nan CHEN,Li-zhe AN,Jun LIU,Liu-lin XIONG,Xiao-bo HUANG. Treatment of crossing vessels in laparoscopic pyeloplasty [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 660-664. |
| [12] | Si-da CHENG,Wan-qiang LI,Li MU,Guang-pu DING,Bo ZHANG,Cheng SHEN,Ze-wei YING,Kun-lin YANG,Han HAO,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of totally extraperitoneal renal autotransplantation with Boari flap-pelvis anastomosis in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinomas treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 758-763. |
| [13] | Ling-fu ZHANG,Chun-sheng HOU,Yong-hui HUANG,Zhi XU,Li-xin WANG,Xiao-feng LING,Gang WANG,Long CUI,Dian-rong XIU. Comparison of the minimally invasive treatments of laparoscopic and endosopic for common bile duct stones after gastrojejunostomy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 345-348. |
| [14] | Xiao-jun TIAN,Min QIU,Zhuo LIU,Ruo-tao XIAO,Yi HUANG,Guo-liang WANG,Xiao-fei HOU,Shu-dong ZHANG,Shen-rong ZHUANG,Lu-lin MA. Single-center study of laparoscopic radical nephrectomy with Mayo 0-2 level inferior vena cava thrombectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(6): 1053-1056. |
| [15] | XU Ben, ZHANG Zhe-nan, LUO Cheng, SONG Hai-feng, ZHANG Qian. Comparison of safety and effectiveness between retroperitoneal laparoscopic tumor aspiration and laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in the treatment of renal angiomyolipoma [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 700-704. |
|
||