Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 139-143. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.01.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
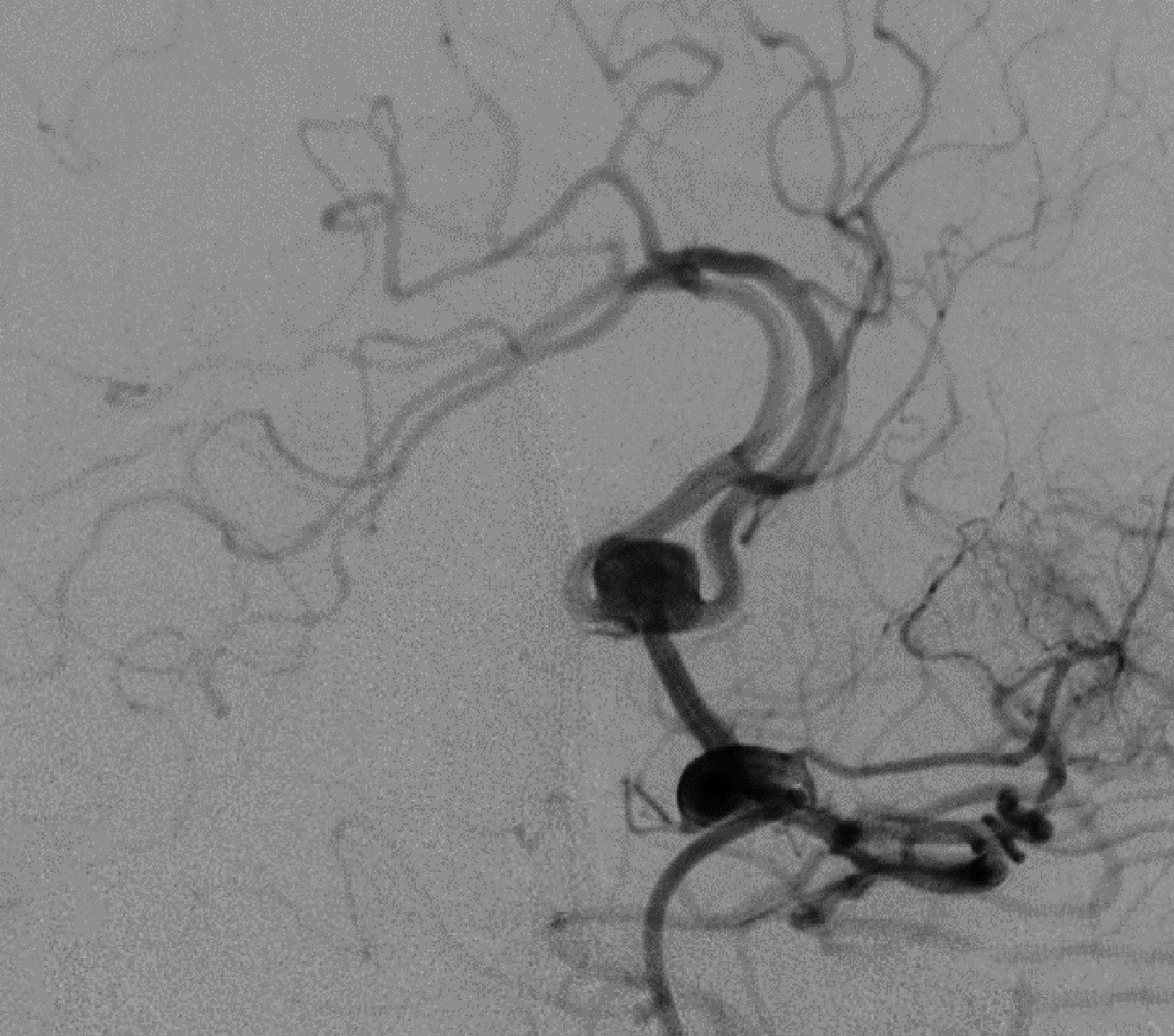
Clinical application of Neuroform Atlas stent-assisted coiling in the treatment of unruptured wide-neck intracranial aneurysms
Jin-tao HAN1,Yu-xiang ZHANG1,Zi-chang JIA1,*( ),Chu-han JIANG2,Lian LIU2,Jing-yuan LUAN1,Fei LIANG1,Yan-qing ZHAO1
),Chu-han JIANG2,Lian LIU2,Jing-yuan LUAN1,Fei LIANG1,Yan-qing ZHAO1
- 1. Department of Interventional Radiology and Vascular Surgery, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
2. Department of Neurosurgery, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100070, China
CLC Number:
- R654.3
| 1 |
Li MH , Chen SW , Li YD , et al. Prevalence of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in Chinese adults aged 35 to 75 years: Across-sectional study[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2013, 159 (8): 514- 521.
doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-8-201310150-00004 |
| 2 |
Wiebers DO , Whisnant JP , Huston J , et al. International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Investigators. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment[J]. Lancet, 2003, 362 (9378): 103- 110.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13860-3 |
| 3 |
Mokin M , Primiani CT , Ren Z , et al. Stent-assisted coiling of cerebral aneurysms: Multi-center analysis of radiographic and clinical outcomes in 659 patients[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2020, 12 (3): 289- 297.
doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-015182 |
| 4 |
曾文贤, 李振均, 张剑波, 等. 支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞治疗急性期颅内破裂宽颈动脉瘤的临床分析[J]. 中华神经医学杂志, 2019, 18 (3): 243- 249.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-8925.2019.03.005 |
| 5 | Sato H , Haraguchi K . Comparison of stent-assisted coiling for unruptured internal carotid artery aneurysms between LVIS or LVIS Jr. and enterprise VRD: A retrospective and single-center analysis[J]. Turk Neurosurg, 2021, 31 (3): 379- 384. |
| 6 |
Ghinda D , Dos-Santos MP , Sabri A , et al. Clinical and angiogra-phic outcomes of stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms[J]. Interv Neuroradiol, 2015, 21 (2): 146- 154.
doi: 10.1177/1591019915582152 |
| 7 |
Hanel RA , Yoon N , Sauvageau E , et al. Neuroform Atlas stent for treatment of middle cerebral artery aneurysms: 1-year outcomes from Neuroform Atlas stent pivotal trial[J]. Neurosurgery, 2021, 89 (1): 102- 108.
doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyab090 |
| 8 |
Jankowitz BT , Jadhav AP , Gross B , et al. Pivotal trial of the Neuroform Atlas stent for treatment of posterior circulation aneurysms: One-year outcomes[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2022, 14 (2): 143- 148.
doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-017115 |
| 9 | 邵秋季, 李立, 李天晓, 等. Neuroform Atlas支架辅助弹簧圈治疗颅内宽颈动脉瘤的初步应用[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2022, 38 (1): 59- 64. |
| 10 |
Cognard C , Pierot L , Anxionnat R , et al. Results of embolization used as the first treatment choice in a consecutive non-selected population of ruptured aneurysms: Clinical results of the Clarity GDC study[J]. Neurosurgery, 2011, 69 (4): 837- 841.
doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182257b30 |
| 11 | Roh H , Kim J , Bae H , et al. Comparison of stent-assisted and no-stent coil embolization for safety and effectiveness in the treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms[J]. J Neurosurg, 2019, 30, 1- 7. |
| 12 | 中华医学会神经外科学分会神经介入学组. 颅内动脉瘤血管内介入治疗中国专家共识(2013)[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2013, 10 (11): 606- 616. |
| 13 | Khattak YJ , Sibaie AA , Anwar M , et al. Stents and stent mimickers in endovascular management of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms[J]. Cureus, 2018, 10 (10): e3420. |
| 14 | 李淦诚, 张炘, 范海燕, 等. 支架辅助弹簧圈栓塞治疗颅内动脉瘤围手术期并发症的危险因素分析[J]. 中华神经医学杂志, 2019, 18 (2): 136- 143. |
| 15 |
Jankowitz BT , Hanel R , Jadhav AP , et al. Neuroform Atlas stent system for the treatment of intracranial aneurysm: Primary results of the Atlas humanitarian device exemption cohort[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2019, 11 (8): 801- 806.
doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2018-014455 |
| 16 |
Lynch J , Sciacca S , Siddiqui J , et al. Safety and efficacy of the Neuroform Atlas stent for treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Neuroradiol, 2021, 31 (4): 1167- 1180.
doi: 10.1007/s00062-020-00979-y |
| 17 | Kim J , Han HJ , Lee W , et al. Safety and efficacy of stent-assisted coiling of unruptured intracranial aneurysms using low-profile stents in small parent arteries[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2021, 42 (9): 1621- 1626. |
| 18 | Lefevre PH , Schramm P , Kemmling A , et al. Multi-centric European post-market follow-up study of the Neuroform Atlas stent system: Primary results[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2022, 14 (7): 694- 698. |
| [1] | Jin-man ZHUANG,Tian-run LI,Xuan LI,Jing-yuan LUAN,Chang-ming WANG,Qi-chen FENG,Jin-tao HAN. Application of Rotarex catheter system in femoropopliteal artery stenosis accompanied with thrombosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 328-332. |
| [2] | LI Wei-hao,LI Wei,ZHANG Xue-min,LI Qing-le,JIAO Yang,ZHANG Tao,JIANG Jing-jun,ZHANG Xiao-ming. Comparison of the outcomes between open and hybrid approaches in the treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms repair [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 177-181. |
| [3] | ZHUANG Jin-man, LI Xuan, LI Tian-run, FU Jun, LUAN Jing-yuan, WANG Chang-ming. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty versus stent implantation for treatment of femoral and popliteal artery lesion resulted from arteriosclerosis obliterans [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(1): 160-165. |
| [4] | QING Hong-kun, ZHANG Xue-min, JIANG Jing-jun, ZHANG Xiao-ming, HE Chang-shun, SUN Zhan-guo. Endovascular repair of an iliac artery aneurysm after endovascular aneurysm repair with handmade iliac branch device: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 888-890. |
|
||