Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 156-159. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.01.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
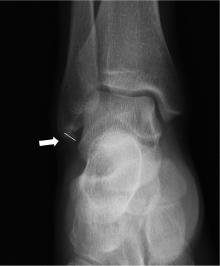
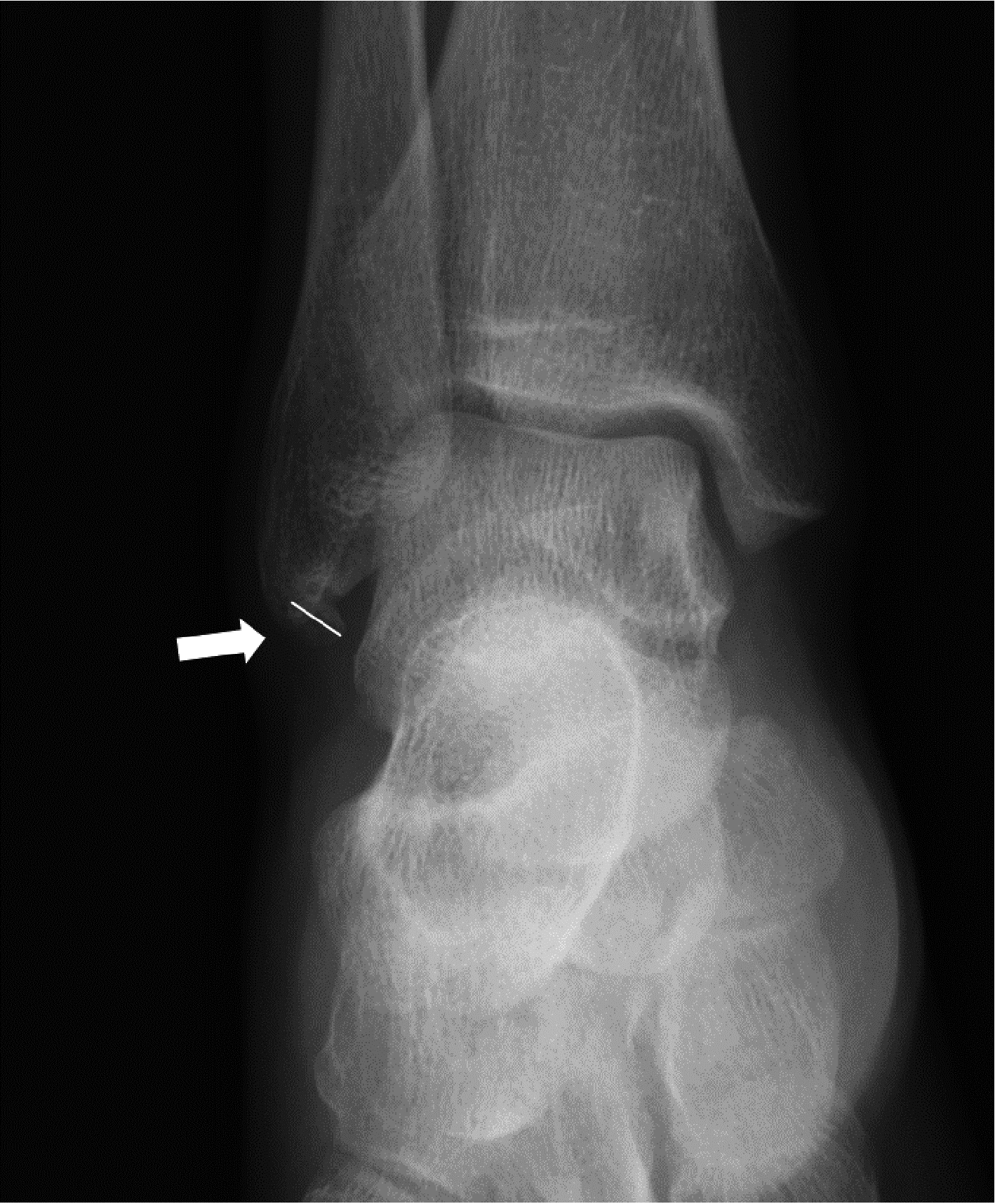
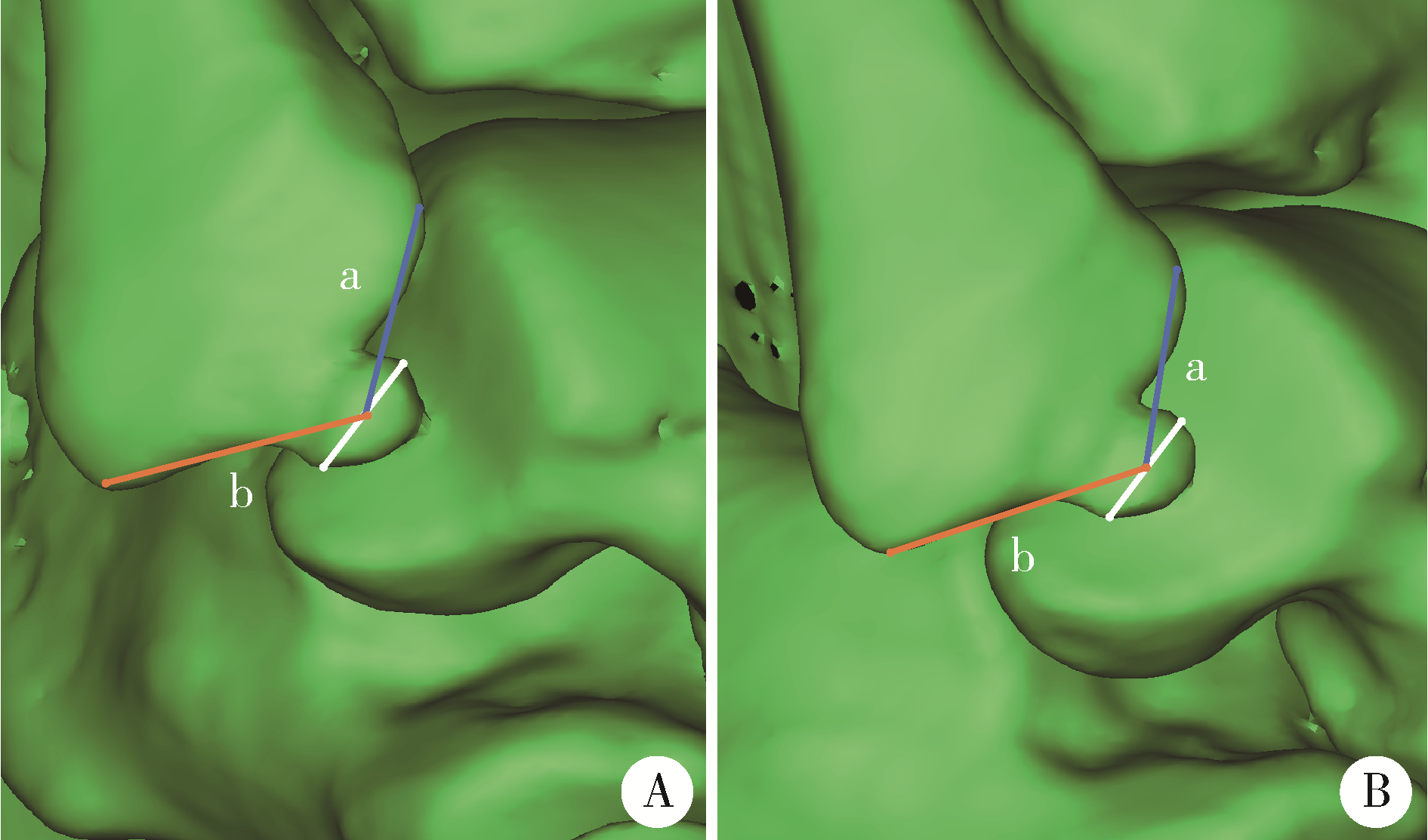
Radiographic diagnosis of distal fibula avulsion fractures: Comparison of ankle X-ray and three-dimensional reconstruction of CT
Shi-kai XIONG,Wei-li SHI,An-hong WANG,Xing XIE,Qin-wei GUO*( )
)
- Department of Sports Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital; Institute of Sports Medicine, Peking University; Beijing Key Laboratory of Joint Injuries in Sports Medicine; Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R683.42
| 1 |
Waterman BR , Owens BD , Davey S , et al. The epidemiology of ankle sprains in the United States[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2010, 92 (13): 2279- 2284.
doi: 10.2106/JBJS.I.01537 |
| 2 |
Milgrom C , Shlamkovitch N , Finestone A , et al. Risk factors for lateral ankle sprain: A prospective study among military recruits[J]. Foot Ankle, 1991, 12 (1): 26- 30.
doi: 10.1177/107110079101200105 |
| 3 |
Bridgman SA , Clement D , Downing A , et al. Population based epidemiology of ankle sprains attending accident and emergency units in the West Midlands of England, and a survey of UK practice for severe ankle sprains[J]. Emerg Med J, 2003, 20 (6): 508- 510.
doi: 10.1136/emj.20.6.508 |
| 4 |
Cordova ML , Sefton JM , Hubbard TJ . Mechanical joint laxity associated with chronic ankle instability: A systematic review[J]. Sports Health, 2010, 2 (6): 452- 459.
doi: 10.1177/1941738110382392 |
| 5 |
Reiner MM , Sharpe JJ . The role of the accessory malleolar ossicles and malleolar avulsion fractures in lateral ankle ligament reconstruction[J]. Foot Ankle Spec, 2018, 11 (4): 308- 314.
doi: 10.1177/1938640017729498 |
| 6 |
Kim BS , Choi WJ , Kim YS , et al. The effect of an ossicle of the lateral malleolus on ligament reconstruction of chronic lateral ankle instability[J]. Foot Ankle Int, 2010, 31 (3): 191- 196.
doi: 10.3113/FAI.2010.0191 |
| 7 |
Choi WJ , Lee JW , Han SH , et al. Chronic lateral ankle instability: The effect of intra-articular lesions on clinical outcome[J]. Am J Sports Med, 2008, 36 (11): 2167- 2172.
doi: 10.1177/0363546508319050 |
| 8 |
Chun TH , Park YS , Sung KS . The effect of ossicle resection in the lateral ligament repair for treatment of chronic lateral ankle instability[J]. Foot Ankle Int, 2013, 34 (8): 1128- 1133.
doi: 10.1177/1071100713481457 |
| 9 |
Haraguchi N , Kato F , Hayashi H . New radiographic projections for avulsion fractures of the lateral malleolus[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1998, 80 (4): 684- 688.
doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.80B4.0800684 |
| 10 |
Boutis K , Narayanan UG , Dong FF , et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of clinically suspected Salter-Harris I fracture of the distal fibula[J]. Injury, 2010, 41 (8): 852- 856.
doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2010.04.015 |
| 11 |
Nakasa T , Fukuhara K , Adachi N , et al. Evaluation of anterior talofibular ligament lesion using 3-dimensional computed tomography[J]. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 2006, 30 (3): 543- 547.
doi: 10.1097/00004728-200605000-00032 |
| 12 |
Allen GM , Wilson DJ , Bullock SA , et al. Extremity CT and ultrasound in the assessment of ankle injuries: Occult fractures and ligament injuries[J]. Br J Radiol, 2020, 93 (1105): 20180989.
doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180989 |
| 13 |
Boszczyk A , Fudalej M , Kwapisz S , et al. X-ray features to predict ankle fracture mechanism[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2018, 291, 185- 192.
doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.08.042 |
| 14 | Han SH , Choi WJ , Kim S , et al. Ossicles associated with chronic pain around the malleoli of the ankle[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2008, 90 (8): 1049- 1054. |
| 15 |
Vahvanen V , Westerlund M , Nikku R . Lateral ligament injury of the ankle in children. Follow-up results of primary surgical treatment[J]. Acta Orthop Scand, 1984, 55 (1): 21- 25.
doi: 10.3109/17453678408992305 |
| 16 |
Takakura Y , Yamaguchi S , Akagi R , et al. Diagnosis of avulsion fractures of the distal fibula after lateral ankle sprain in children: A diagnostic accuracy study comparing ultrasonography with radiography[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2020, 21 (1): 276.
doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03287-1 |
| 17 |
Davidson RS , Mistovich RJ . Operative indications and treatment for chronic symptomatic os subfibulare in children[J]. JBJS Essent Surg Tech, 2014, 4 (3): e18.
doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.M.00065 |
| 18 | Ahn HW , Lee KB . Comparison of the modified Broström procedure for chronic lateral ankle instability with and without subfibular ossicle[J]. Am J Sports Med, 2016, 44 (12): 3158- 3164. |
| 19 |
Kim BS , Woo S , Kim JY , et al. Radiologic findings for prediction of rehabilitation outcomes in patients with chronic symptomatic os subfibulare[J]. Radiol Med, 2017, 122 (10): 766- 773.
doi: 10.1007/s11547-017-0786-y |
| 20 |
Kubo M , Yasui Y , Sasahara J , et al. Simultaneous ossicle resection and lateral ligament repair give excellent clinical results with an early return to physical activity in pediatric and adolescent patients with chronic lateral ankle instability and os subfibulare[J]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2020, 28 (1): 298- 304.
doi: 10.1007/s00167-019-05718-6 |
| [1] | Wenjing LI,Baozhou ZHANG,Heng LI,Liangpeng LAI,Hui DU,Ning SUN,Xiaofeng GONG,Ying LI,Yan WANG,Yong WU. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis for end-stage ankle and hindfoot arthropathy: Short- and mid-term clinical outcomes [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 299-306. |
| [2] | HOU Zong-chen,AO Ying-fang,HU Yue-lin,JIAO Chen,GUO Qin-wei,HUANG Hong-shi,REN Shuang,ZHANG Si,XIE Xing,CHEN Lin-xin,ZHAO Feng,PI Yan-bin,LI Nan,JIANG Dong. Characteristics and related factors of plantar pressure in the chronic ankle instability individuals [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 279-285. |
| [3] | Dong JIANG,Yue-lin HU,Chen JIAO,Qin-wei GUO,Xing XIE,Lin-xin CHEN,Feng ZHAO,Yan-bin PI. Mid-to-long term outcomes and influence factors of postoperative concurrent chronic ankle instability and posterior ankle impingement [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 505-509. |
| [4] | WANG Rong-li, ZHOU Zhi-hao, XI Yu-cheng, WANG Qi-ning, WANG Ning-hua, HUANG Zhen. Preliminary study of robot-assisted ankle rehabilitation for children with cerebral palsy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 207-212. |
| [5] | JI Hong-quan, ZHOU Fang, TIAN Yun, ZHANG Zhi-shan, GUO Yan, LV Yang, YANG Zhong-wei, HOU Guo-jin. One of the pitfalls in the surgical treatment of maisonneuve fractures: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 354-356. |
| [6] | GONG Xiao-feng, LYU Yan-wei, WANG Jin-hui, WANG Yan, WU Yong, WANG Man-yi. A correlation analysis of the ankle CT and ankle fracture classification [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 281-285. |
| [7] | WANG Zi-yun, WU Xin-bao. Anterior dislocation of the fibula resulting from surgical malreduction: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(2): 361-365. |
| [8] | ZHANG Zi-an, WU Xin-bao, WANG Man-yi. A comparative research on the treatment of ankle fracture with dislocation between emergency surgery and selective surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(5): 791-795. |
|
||