Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 633-643. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
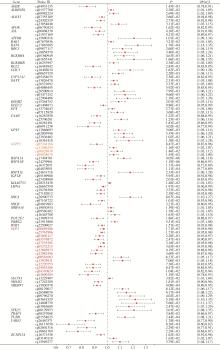
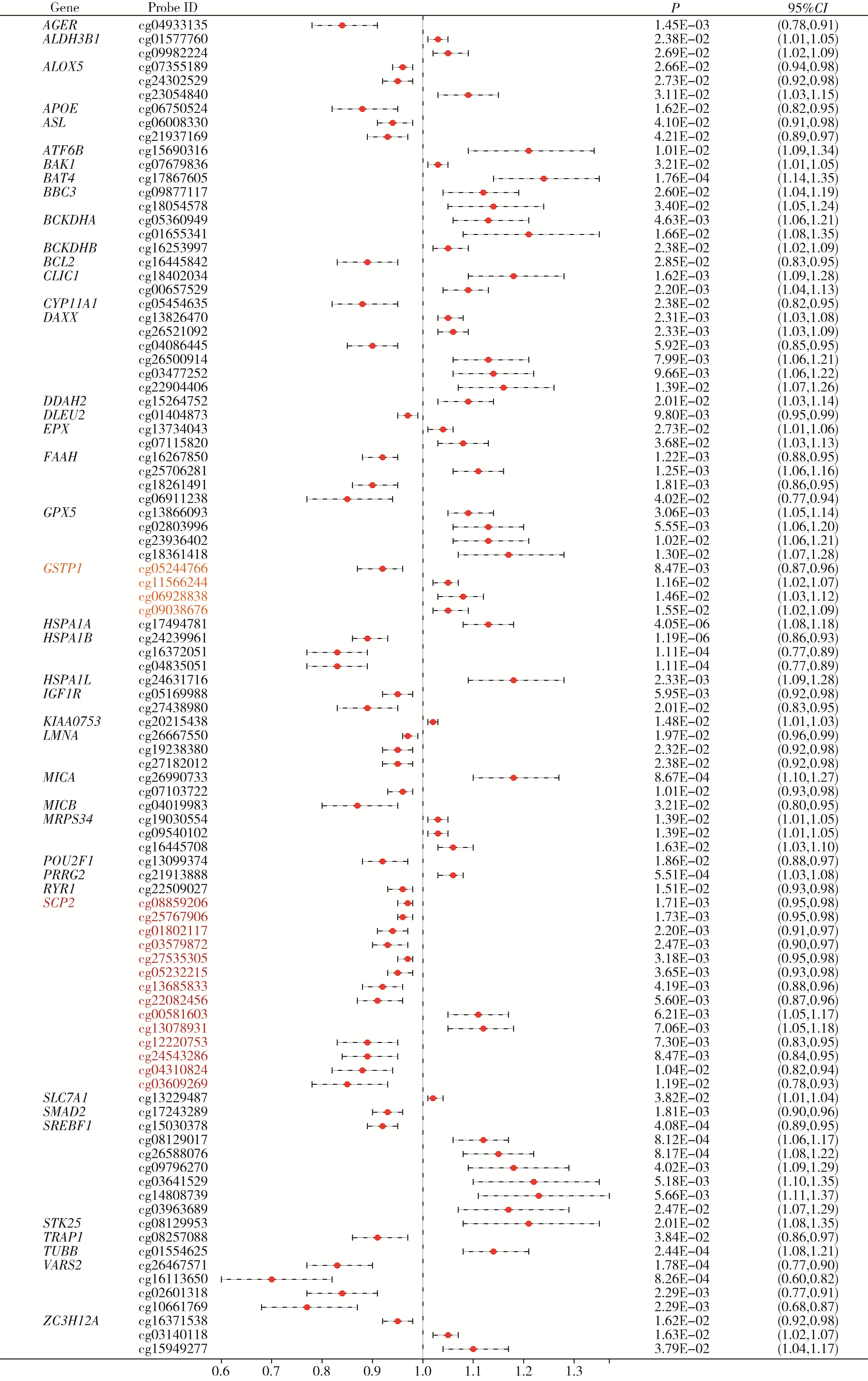
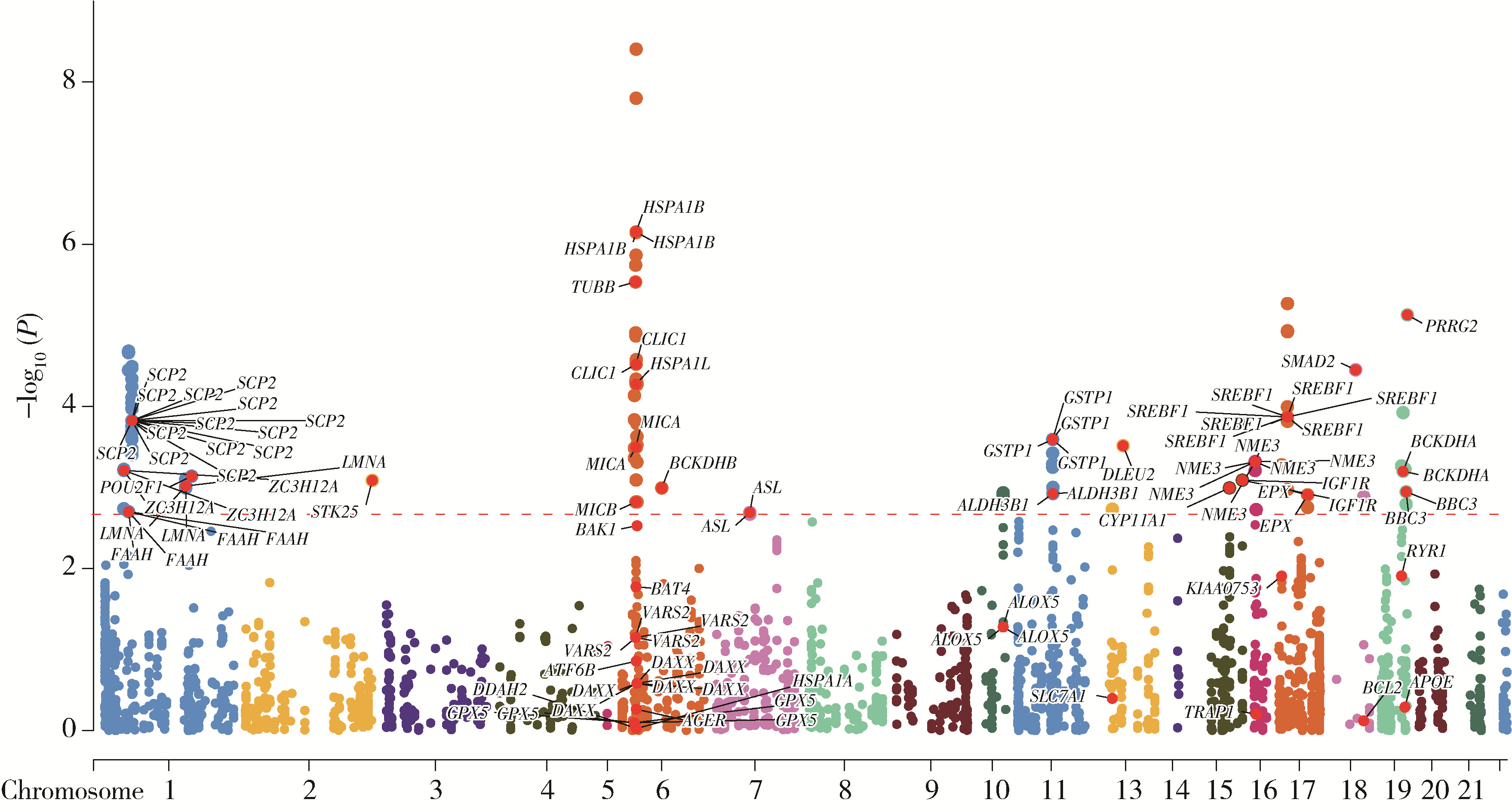
Multi-omics analysis of the relationship between oxidative stress-related gene and prostate cancer
Jiaxin NING1,2, Haoran WANG1,2, Shuhang LUO1,2, Jibo JING1,2, Jianye WANG1,2, Huimin HOU1,*( ), Ming LIU1,2,*(
), Ming LIU1,2,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Urology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Beijing 100005, China
2. Peking Union Medical College & Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China
CLC Number:
- R737.25
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
|
| 17 |
|
| 18 |
|
| 19 |
|
| 20 |
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
|
| 24 |
|
| 25 |
|
| 26 |
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
|
| 40 |
|
| 41 |
|
| 42 |
|
| 43 |
|
| 44 |
|
| 45 |
|
| 46 |
|
| 47 |
|
| 48 |
|
| 49 |
|
| [1] | Zeyuan WANG, Shuanbao YU, Haoke ZHENG, Jin TAO, Yafeng FAN, Xuepei ZHANG. A preoperative prediction model for pelvic lymph node metastasis in prostate cancer: Integrating clinical characteristics and multiparametric MRI [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2025, 57(4): 684-691. |
| [2] | Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG, Qian ZHANG. Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [3] | Yuxuan TIAN,Mingjian RUAN,Yi LIU,Derun LI,Jingyun WU,Qi SHEN,Yu FAN,Jie JIN. Predictive effect of the dual-parametric MRI modified maximum diameter of the lesions with PI-RADS 4 and 5 on the clinically significant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 567-574. |
| [4] | Kaifeng YAO,Mingjian RUAN,Derun LI,Yuxuan TIAN,Yuke CHEN,Yu FAN,Yi LIU. Diagnostic efficacy of targeted biopsy combined with regional systematic biopsy in prostate cancer in patients with PI-RADS 4-5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 575-581. |
| [5] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [6] | Yi LIU,Chang-wei YUAN,Jing-yun WU,Qi SHEN,Jiang-xi XIAO,Zheng ZHAO,Xiao-ying WANG,Xue-song LI,Zhi-song HE,Li-qun ZHOU. Diagnostic efficacy of prostate cancer using targeted biopsy with 6-core systematic biopsy for patients with PI-RADS 5 [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 812-817. |
| [7] | Chang-wei YUAN,De-run LI,Zhi-hua LI,Yi LIU,Gang-zhi SHAN,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of dynamic contrast enhanced status in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer with PI-RADS 4 lesion [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 838-842. |
| [8] | BAI Feng,HE Yi-fan,NIU Ya-nan,YANG Ruo-juan,CAO Jing. Effects of ultrafine particulates on cardiac function in rat isolated heart [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 240-245. |
| [9] | Yi LIU,Zhi-jian LIU,Qi SHEN,Jing-yun WU,Yu FAN,De-run LI,Wei YU,Zhi-song HE. A clinical analysis of 14 cases of prostatic stromal tumor of uncertain malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 621-624. |
| [10] | Yi-chang HAO,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Min QIU,Lang ZHOU,Ke LIU,Jian LU,Chun-lei XIAO,Yi HUANG,Cheng LIU,Lu-lin MA. Surgical strategy selection and experience summary of prostate cancer with positive single needle biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 625-631. |
| [11] | Yan XUAN,Yu CAI,Xiao-xuan WANG,Qiao SHI,Li-xin QIU,Qing-xian LUAN. Effect of Porphyromonas gingivalis infection on atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein-E knockout mice [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 743-749. |
| [12] | Ye YAN,Hai-zhui XIA,Xu-sheng LI,Wei HE,Xue-hua ZHU,Zhi-ying ZHANG,Chun-lei XIAO,Yu-qing LIU,Hua HUANG,Liang-hua HE,Jian LU. Application of U-shaped convolutional neural network in auto segmentation and reconstruction of 3D prostate model in laparoscopic prostatectomy navigation [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 596-601. |
| [13] | WANG Hao, CHEN Liang, YE Xiao-yun. Triptolide induces oxidative stress and apoptosis and activates PIK3/Akt signaling pathway in TM4 sertoli cells [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 607-612. |
| [14] | ZHANG Fan, XIAO Chun-lei, ZHANG Shu-dong, HUANG Yi, MA Lu-lin. Relationship between recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and prostatic volume and intravesical prostatic protursion length [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 621-625. |
| [15] | BI Yong-xiang, XIAO Min-hui, ZHANG Ning-nan, LI Xiao-yun, MAO Xiao-peng, ZHANG Ke, ZHANG Zhuo-rui, ZHAO Liang-yun. Construction and improvement of animal models with different positional osseous metastasis of prostate cancer in vivo [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 590-596. |
|
||