Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 131-135. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.01.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
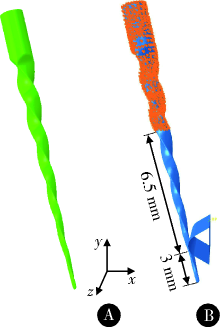
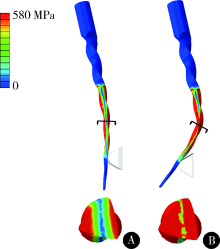
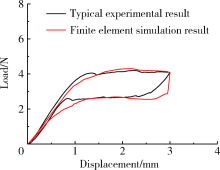
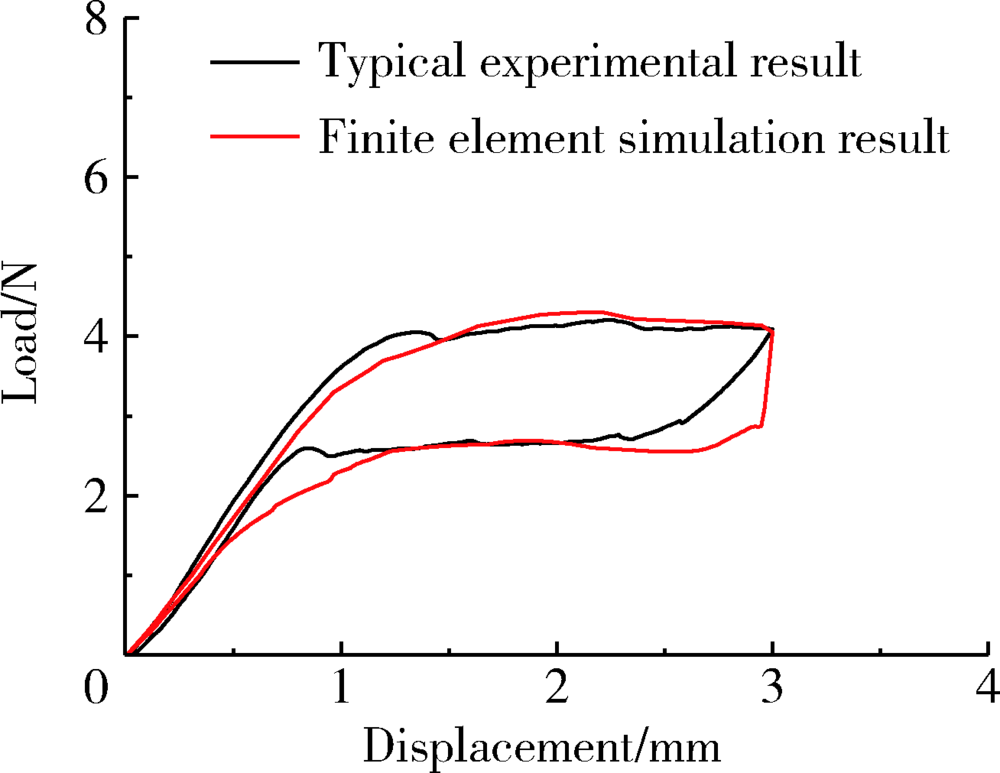
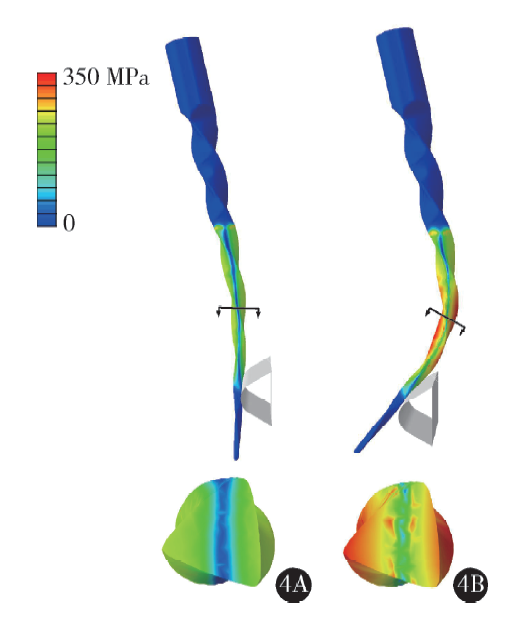
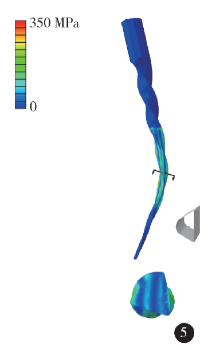
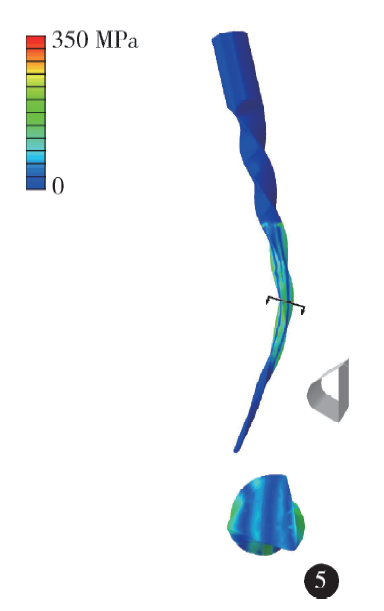
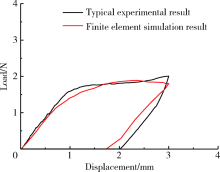
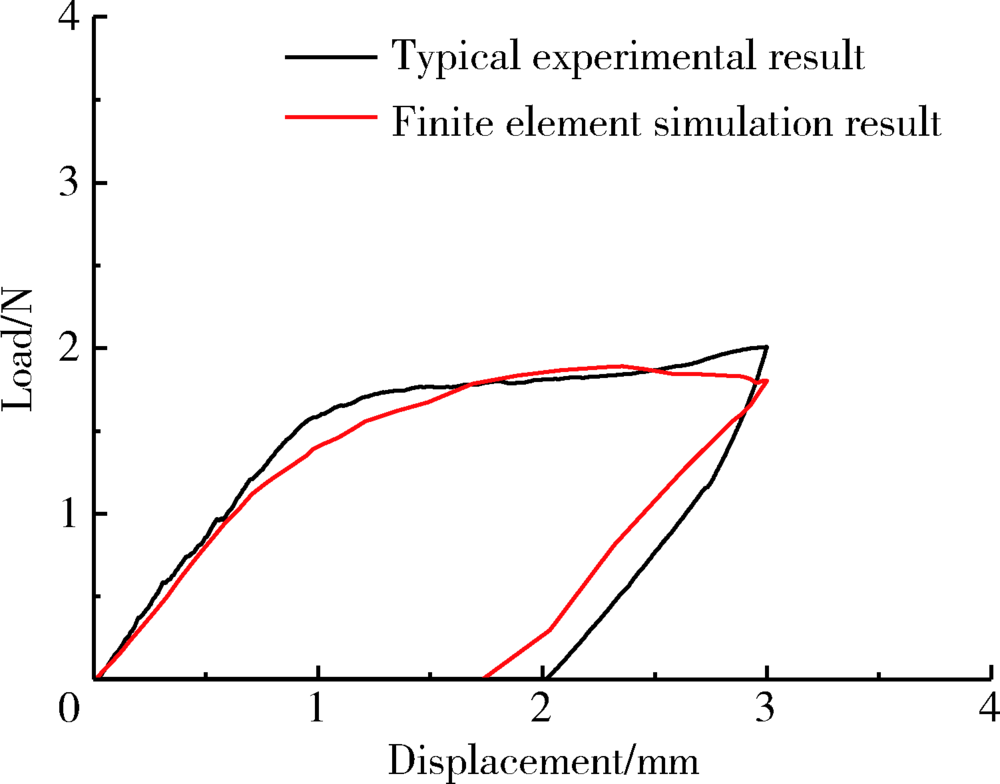
Construction and mechanical analysis of finite element model for bending property of controlled memory wire nickel-titanium rotary file
Hong-yu FU1,Fang-fang WANG2,Xiao-mei HOU3,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Stomatology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Department of Stomatology, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100053, China
3. Second Clinical Division, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology & Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing 100101, China
CLC Number:
- R783.1
| [1] |
Santos AL, BahiaMG, De ELC ,et al. Comparison of the mecha-nical behavior between controlled memory and superelastic nickel-titanium files via finite element analysis[J]. J Endod, 2013,39(11):1444-1447.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.07.030 pmid: 24139271 |
| [2] |
Montalvao D, Alcada FS, Braz FM , et al. Structural characterization and mechanical FE analysis of conventional and M-Wire Ni-Ti alloys used in endodontic rotary instruments[J]. Sci World J, 2014,2014:1-8.
doi: 10.1155/2014/976459 pmid: 3918393 |
| [3] |
Montalvao D, Alcada FS . Numeric comparison of the static mechanical behavior between ProFile GT and ProFile GT series X rotary nickel-titanium files[J]. J Endod, 2011,37(8):1158-1161.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2011.05.018 pmid: 21763913 |
| [4] |
Auricchio F, Taylor RL . Shape-memory alloys: modelling and numerical simulations of the finite-strain superelastic behavior[J]. Comput Methods Mech Engrg, 1997,143(1):175-194.
doi: 10.1016/S0045-7825(96)01147-4 |
| [5] | 徐秉业 . 应用弹塑性力学 [M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1995. |
| [6] |
Santos L, López JB, Casas EB , et al. Mechanical behavior of three nickel-titanium rotary files: A comparison of numerical simulation with bending and torsion tests[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2014,37(1):258-263.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2014.01.025 pmid: 24582247 |
| [7] |
Hou X, Yahata Y, Hayashi Y . Phase transformation behaviour and bending property of twisted nickel-titanium endodontic instruments[J]. Int Endod J, 2011,44(3):253-258.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01818.x pmid: 21219356 |
| [8] |
Pongione G, Milana V . Flexibility and resistance to cyclic fatigue of endodontic instruments made with different nickel-titanium alloys: a comparative test[J]. Ann Stomatol, 2012,3(3-4):119-122.
pmid: 23386933 |
| [9] |
Zinelis S, Eliades T, Eliades G . A metallurgical characterization of ten endodontic Ni-Ti instruments: assessing the clinical relevance of shape memory and superelastic properties of Ni-Ti endodontic instruments[J]. Int Endod J, 2010,43(2):125-134.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2009.01651.x pmid: 20078701 |
| [10] |
Yahata Y, Yoneyama T, Hayashi Y , et al. Effect of heat treatment on transformation temperatures and bending properties of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments[J]. Int Endod J, 2010,42(7):621-626.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2009.01563.x pmid: 19467049 |
| [11] |
Alapati SB, Brantley WA, Lijima M , et al. Metallurgical characterization of a new nickel-titanium wire for rotary endodontic instruments[J]. J Endod, 2009,35(11):1589-1593.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2009.08.004 pmid: 19840654 |
| [12] |
Shen Y, Coil JM, Zhou H , et al. HyFlex nickel-titanium rotary instruments after clinical use: metallurgical properties[J]. Int Endod J, 2013,46(8):720-729.
doi: 10.1111/iej.12049 pmid: 23330612 |
| [13] |
Ninan E, Berzins DW . Torsion and bending properties of shape memory and superelastic nickel-titanium rotary instruments[J]. J Endod, 2013,39(1):101-104.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2012.08.010 pmid: 23228266 |
| [14] |
Shen Y, Qian W, Abtin H , et al. Fatigue testing of controlled memory wire nickel-titanium rotary instruments[J]. J Endod, 2011,37(7):997-1001.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2011.03.023 pmid: 21689559 |
| [1] | Meng-en OU,Yun DING,Wei-feng TANG,Yong-sheng ZHOU. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cement flow in abutment margin-crown platform switching [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 548-552. |
| [2] | Wei ZHOU,Jin-gang AN,Qi-guo RONG,Yi ZHANG. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of traumatic mechanism of mandibular symphyseal fracture combined with bilateral intracapsular condylar fractures [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 983-989. |
| [3] | Shuang REN,Hui-juan SHI,Jia-hao ZHANG,Zhen-long LIU,Jia-yi SHAO,Jing-xian ZHU,Xiao-qing HU,Hong-shi HUANG,Ying-fang AO. Finite element analysis of the graft stresses after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(5): 865-870. |
| [4] | JIANG You-sheng,FENG Lin,GAO Xue-jun. Influence of base materials on stress distribution in endodontically treated maxillary premolars restored with endocrowns [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 764-769. |
| [5] | Chun-ping LIN,Song-he LU,Jun-xin ZHU,Hong-cheng HU,Zhao-guo YUE,Zhi-hui TANG. Influence of thread shapes of custom-made root-analogue implants on stress distribution of peri-implant bone: A three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1130-1137. |
| [6] | Jia-hao ZHANG,Shuang REN,Jia-yi SHAO,Xing-yue NIU,Xiao-qing HU,Ying-fang AO. Anatomical and finite element analysis of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction within biomechanical insertion [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(3): 586-590. |
| [7] | . Stress change of periodontal ligament of the anterior teeth at the stage of space closure in lingual appliances: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(1): 141-147. |
| [8] | ZHAO Xu, ZHANG Lei, SUN Jian, YANG Zhen-yu, XIE Qiu-fei. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of influence of occlusal surface height on stress distribution around posterior implant-supported single crown [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2016, 48(1): 94-100. |
| [9] | ZHEN Min, HU Wen-jie, RONG Qi-guo. Finite element analysis of the maxillary central incisor with crown lengthening surgery and post-core restoration in management of crown-root fracture [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(6): 1015-1021. |
| [10] | ZHOU Tuan-Feng, ZHANG Xiang-Hao, WANG Xin-Zhi. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of one-piece computer aided design and computer aided manufacture involved zirconia post and core [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(1): 78-84. |
| [11] | YANG Xue, RONG Qi-Guo, YANG Ya-Dong. Influence of attachment type on stress distribution of implant-supported removable partial dentures [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2015, 47(1): 72-77. |
|
||