Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 660-664. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
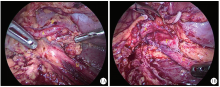
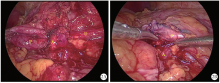
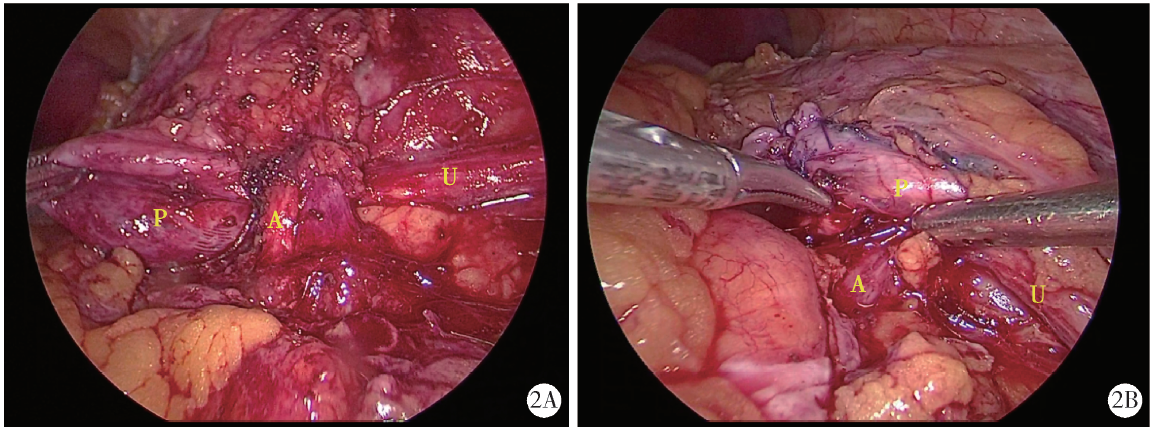
Treatment of crossing vessels in laparoscopic pyeloplasty
Hai-yue ZHAO,Xiong-jun YE( ),Wei-nan CHEN,Li-zhe AN,Jun LIU,Liu-lin XIONG,Xiao-bo HUANG
),Wei-nan CHEN,Li-zhe AN,Jun LIU,Liu-lin XIONG,Xiao-bo HUANG
- Department of Urology and Lithotripsy Center, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R699.2
| [1] | Ellerkamp V, Kurth RR, Schmid E , et al. Differences between intrinsic and extrinsic ureteropelvic junction obstruction related to crossing vessels: histology and functional analyses[J]. World J Urol, 2016,34(4):577-583. |
| [2] | Zhang X, Li HZ, Wang SG , et al. Retroperitoneal laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty: experience with 50 eases[J]. Urology, 2005,66(3):514-517. |
| [3] | 张旭, 许凯, 张军 , 等. 后腹腔镜下Hellström术治疗异位血管导致的肾盂输尿管连接处狭窄[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2007,28(7):450-452. |
| [4] | 郭刚, 洪宝发, 符伟军 , 等. 肾迷走血管致肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻20例报告[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2003,18(12):721-723. |
| [5] | 王杭, 王国民 . CT尿路成像和IVU检查诊断泌尿系统疾病的比较研究[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2010,31(6):402-404. |
| [6] | Hellström J, Giertz G, Lindblom K . Pathogenesis and treatment of hydronephrosis[J]. J Belge Drol, 1951,20(1):1-6. |
| [7] | 中华医学会小儿外科学分会内镜外科学组. 腹腔镜肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻手术操作指南(2017版)[J]. 微创泌尿外科杂志, 2017,6(3):129-135. |
| [8] | 邱敏, 吴红章, 马潞林 , 等. 肾异位血管压迫引起肾盂输尿管连接部梗阻的临床诊治分析[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2014,52(9):702-705. |
| [9] | 宋宏程, 白继武, 黄澄如 , 等. 迷走血管压迫致梗阻性肾积水34例临床分析[J]. 临床小儿外科杂志, 2009,8(6):3-5. |
| [10] | Boylu U, Oommen M, Lee BR , et al. Ureteropelvic junction obstruction secondary to crossing vessels-to transpose or not? The robotic experience[J]. J Urol, 2009,181(4):1751-1755. |
| [1] | Min QIU,You-long ZONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Bin YANG,Chu-xiao XU,Zheng-hui SUN,Min LU,Lei ZHAO,Jian LU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Lu-lin MA. Treatment outcome of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in patients with renal tumors of moderate to high complexity [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 833-837. |
| [2] | Hui-li LIU,Yan-han LV,Xiao-xiao WANG,Min LI. Factors influencing the chronic post-surgical pain after laparoscopic surgery for elderly patients with urinary tract tumors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 851-856. |
| [3] | Ling-fu ZHANG,Chun-sheng HOU,Zhi XU,Li-xin WANG,Xiao-feng LING,Gang WANG,Long CUI,Dian-rong XIU. Clinical effect of laparoscopic transcystic drainage combined with common bile duct exploration for the patients with difficult biliary stones [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(6): 1185-1189. |
| [4] | Li-zhe AN,Liu-lin XIONG,Liang CHEN,Huan-rui WANG,Wei-nan CHEN,Xiao-bo HUANG. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty combined with ultrasonic lithotripsy via nephroscope for treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction with renal calculi [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 746-750. |
| [5] | ZHANG Fan,CHEN Qu,HAO Yi-chang,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy and preoperative/postoperative membranous urethral length [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(2): 299-303. |
| [6] | ZHANG Fan,HUANG Xiao-juan,YANG Bin,YAN Ye,LIU Cheng,ZHANG Shu-dong,HUANG Yi,MA Lu-lin. Relationship between prostate apex depth and early recovery of urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 692-696. |
| [7] | Bing-wei HUANG,Jie WANG,Peng ZHANG,Zhe LI,Si-cheng BI,Qiang WANG,Cai-bo YUE,Kun-lin YANG,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of indocyanine green in complex upper urinary tract repair surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 651-656. |
| [8] | Shu-dong ZHANG,Peng HONG,Bin-shuai WANG,Shao-hui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Li-yuan TAO,Cai-guang CAO,Zhen-hua HU,Lu-lin MA. Usefulness of the indocyanine green fluorescence imaging technique in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 657-662. |
| [9] | Meng-meng ZHENG,Guang-pu DING,Wei-jie ZHU,Kun-lin YANG,Shu-bo FAN,Bao GUAN,Xin-fei LI,Yu-kun CAI,Jin-sheng ZHANG,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of preoperative three-dimensional image reconstruction in the treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 705-710. |
| [10] | Si-da CHENG,Xin-fei LI,Sheng-wei XIONG,Shu-bo FAN,Jie WANG,Wei-jie ZHU,Zi-ao LI,Guang-pu DING,Ting YU,Wan-qiang LI,Yong-ming SUN,Kun-lin YANG,Lei ZHANG,Han HAO,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Robot-assisted laparoscopic upper urinary tract reconstruction surgery: A review of 108 cases by a single surgeon [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 771-779. |
| [11] | Sheng-wei XIONG,Jie WANG,Wei-jie ZHU,Si-da CHENG,Lei ZHANG,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Advance in re-do pyeloplasty for the management of recurrent ureteropelvic junction obstruction after surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(4): 794-798. |
| [12] | Hai-wen HUANG,Bing YAN,Mei-xia SHANG,Li-bo LIU,Han HAO,Zhi-jun XI. Propensity-matched comparison of laparoscopic and open radical cystectomy for female patients with bladder cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 698-705. |
| [13] | Si-da CHENG,Wan-qiang LI,Li MU,Guang-pu DING,Bo ZHANG,Cheng SHEN,Ze-wei YING,Kun-lin YANG,Han HAO,Xue-song LI,Li-qun ZHOU. Application of totally extraperitoneal renal autotransplantation with Boari flap-pelvis anastomosis in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinomas treatment [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 758-763. |
| [14] | Ling-fu ZHANG,Chun-sheng HOU,Yong-hui HUANG,Zhi XU,Li-xin WANG,Xiao-feng LING,Gang WANG,Long CUI,Dian-rong XIU. Comparison of the minimally invasive treatments of laparoscopic and endosopic for common bile duct stones after gastrojejunostomy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 345-348. |
| [15] | Xiao-jun TIAN,Min QIU,Zhuo LIU,Ruo-tao XIAO,Yi HUANG,Guo-liang WANG,Xiao-fei HOU,Shu-dong ZHANG,Shen-rong ZHUANG,Lu-lin MA. Single-center study of laparoscopic radical nephrectomy with Mayo 0-2 level inferior vena cava thrombectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(6): 1053-1056. |
|
||