Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences) ›› 2019, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 870-874. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.05.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
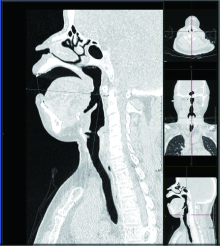
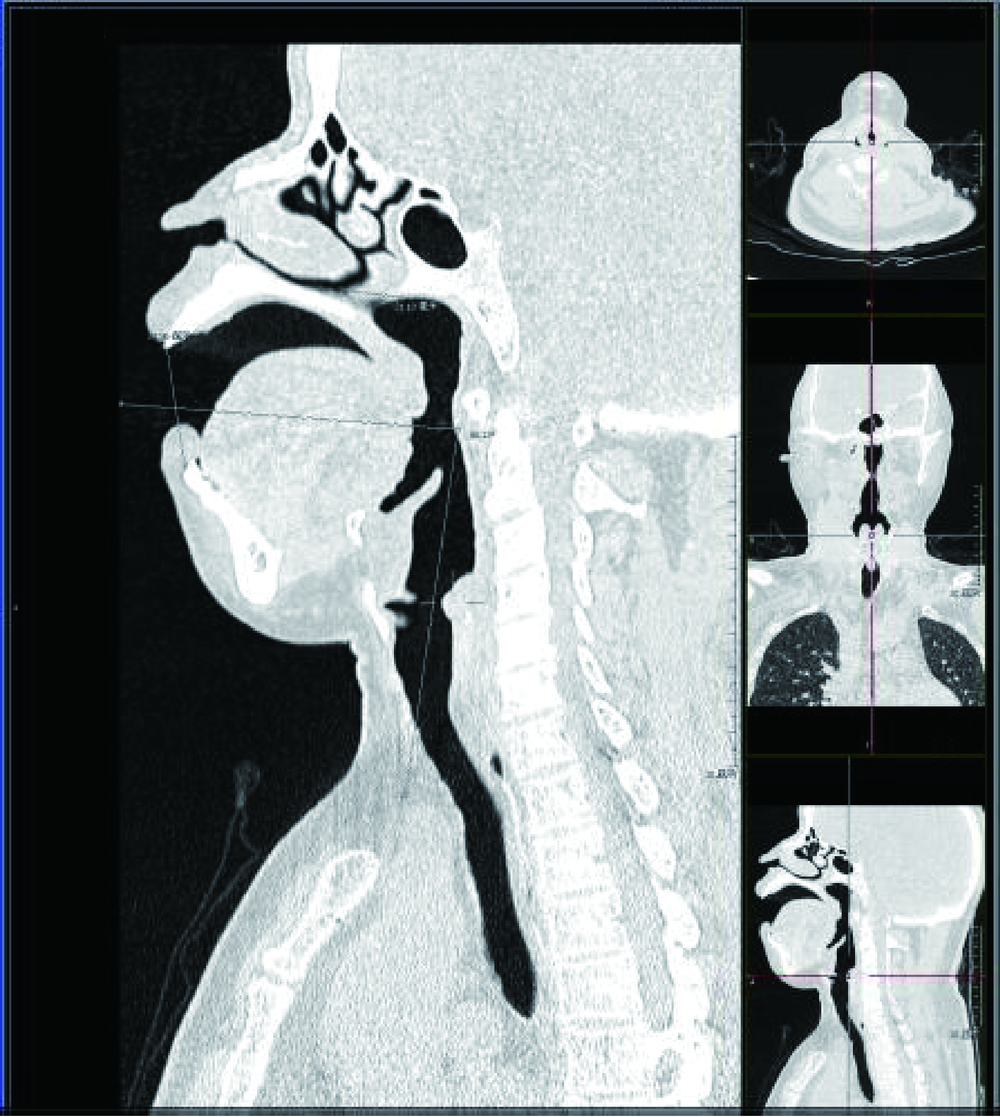
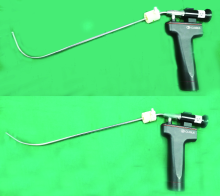
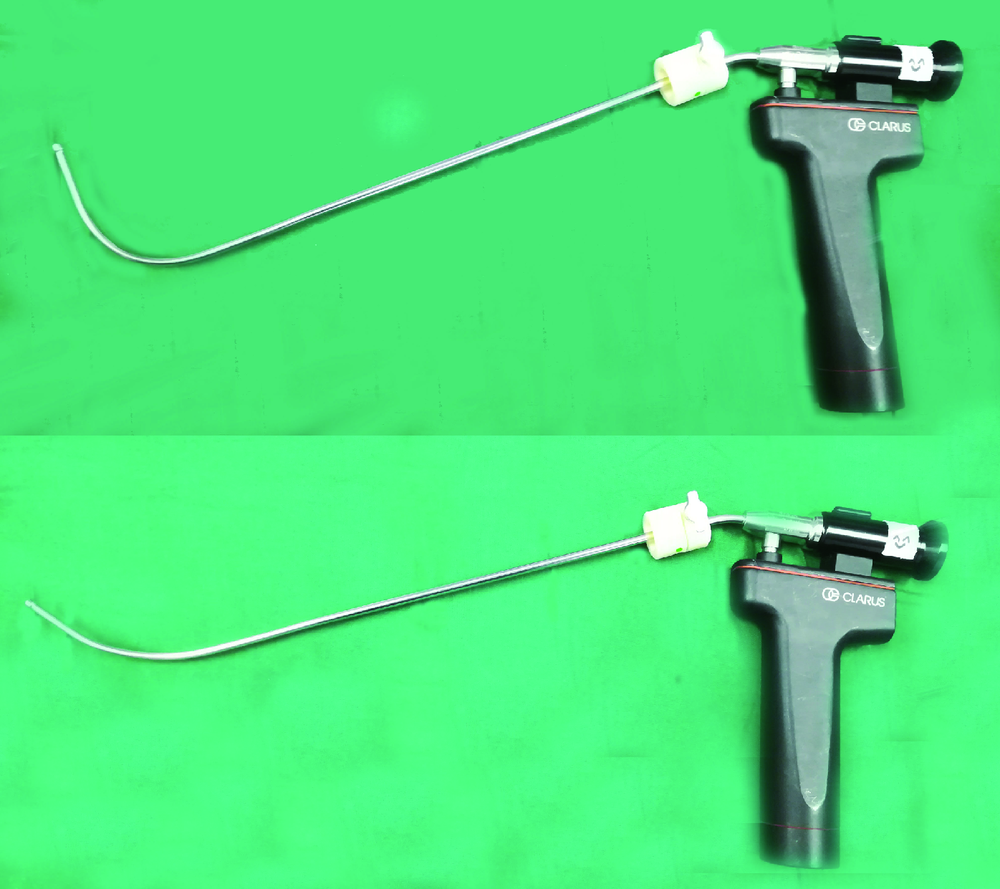
Study on the use of CT three-dimensional reconstruction technique for guiding tracheal intubation with rigid fiber bronchoscope in difficult airway
Hong HONG1,Yu-ting QIAN1,Lei FU2,Wu WANG2,Cheng-hui LI1,Yi-qing YIN1,△( )
)
- 1. Department of Anesthesiology,China-Japan Friendship Hopital,Beijing 100029, China
2. Department of Medical Image,China-Japan Friendship Hopital,Beijing 100029, China
CLC Number:
- R614
| [1] | Kheterpal S, Healy D, Aziz MF , et al. Incidence, predictors, and outcome of difficult mask ventilation combined with difficult laryngoscopy: a report from the multicenter perioperative outcomes group[J]. Anesthesiology, 2013,119(6):1360-1369. |
| [2] | Martini RP, Larson DM . Clinical evaluation and airway management for adults with cervical spine instability[J]. Anesthesiology Clin, 2015,33(2):315-327. |
| [3] | Yao YT, Jia NG, Li CH , et al. Comparison of endotracheal intubation with the Shikani Optical Stylet using the left molar approach and direct laryngoscopy[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2008,121(14):1324-1327. |
| [4] | Suppan L, Tramèr MR, Niquille M , et al. Alternative intubation techniques vs. Macintosh laryngoscopy in patients with cervical spine immobilization: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2016,116(1):27-36. |
| [5] | Turkstra TP, Pelz DM, Shaikh AA , et al. Cervical spine motion: a fluoroscopic comparison of Shikani Optical Stylet vs macintosh laryngoscope[J]. Can J Anaesth, 2007,54(6):441-447. |
| [6] | Rabab SS, Mahrous MD, Ahmed A , et al. The shikani optical stylet as an alternative to awake fiberoptic intubation in patients at risk of secondary cervical spine injury: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Neurosurg Anesthesiol, 2018,30(4):354-358. |
| [7] | 李月光, 张玉龙, 夏阂涛 . 光棒在困难气管插管中的应用[J]. 江苏医药, 2010,36(2):226-227. |
| [8] | 陈洁, 汪小海, 马正良 , 等. 非困难气道光棒气管插管折弯角度的研究[J]. 中华临床医师杂志, 2012,6(19):6110-6111. |
| [9] | 王冬青, 周永连, 张雷波 , 等. 光棒气管插管折弯方法的研究[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2006,22(1):32-33. |
| [10] | Boedeker BH, Barak-Bernhagen MA, Miller DJ , et al. Improving rigid fiberoptic intubation: a comparison of the Bonfils Intubating Fiberscope? with a novel modification[J]. BMC Emerg Med, 2010,10:11. |
| [11] | Marson BA, Anderson E, Wilkes AR , et al. Bougie-related airway trauma: dangers of the hold-up sign[J]. Anaesthesia, 2014,69(3):219-223. |
| [12] | Nagamine Y, Kurahashi K . The use of three-dimensional computed tomography images for anticipated difficult intubation airway evaluation of a patient with treacher Collins syndrome[J]. Anesth Analg, 2007,105(3):626-628. |
| [13] | Lee HC, Kim MK, Kim YH , et al. Radiographic predictors of difficult laryngoscopy in acromegaly patients[J]. Neurosurg Anesthesiol, 2019,31(1):50-56. |
| [1] | Jun WANG, Lan YAO, Ning ZHANG, Libin SUO, Hongpei LI, Yue WEI, Peng CHA, Zheng LIANG, Kunpeng LIU. Effects of unilateral thoracic paravertebal block on hemodynamic and the level of conscionsness during double lumen endotracheal intubation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 890-895. |
| [2] | Yue WEI,Lan YAO,Xi LU,Jun WANG,Li LIN,Kun-peng LIU. Evaluation of gastric emptying after drinking carbohydrates before cesarean section by gastric ultrasonography [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1082-1087. |
| [3] | Yue WEI,Xi LU,Jing ZHANG,Kun-peng LIU,Yong-jun WANG,Lan YAO. Effect of preoperative carbohydrates intake on the gastric volume and the risk of reflux aspiration in patients positioning in trendelenburg undergoing gynecological laparoscopic procedures [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 893-898. |
| [4] | Cheng-mei SHI,Yang ZHOU,Ning YANG,Zheng-qian LI,Yi-fan TAO,Ying DENG,Xiang-yang GUO. Quality of psychomotility recovery after propofol sedation for painless gastroscopy and colonoscopy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 324-327. |
| [5] | Jie-chu WANG,You-xiu YAO,Xiang-yang GUO. Intraoperative management of potentially fatal arrhythmias after anesthesia induced by severe hypokalemia: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 186-189. |
| [6] | Zhi-yu KANG,Lei-lei WANG,Yong-zheng HAN,Xiang-yang GUO. Anesthesia management of athletes' operation in Beijing Olympic Winter Games [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 770-773. |
| [7] | BAI Peng,HUAI Wei,XIA Tian,YANG Zhong-wei,GUO Xiang-yang,ZHOU Fang. Time comparison of artificial airway establishment in operating room and on slope using endotracheal intubation and laryngeal mask [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(1): 166-169. |
| [8] | MU Dong-liang,XUE Cheng,AN Bin,WANG Dong-xin. Epidural block associated with improved long-term survival after surgery for colorectal cancer: A retrospective cohort study with propensity score matching [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(6): 1152-1158. |
| [9] | GENG Zhi-yu,GAO Wei-hua,WANG Dong-xin. Clinical outcomes of vocal fold immobility after tracheal intubation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(2): 337-340. |
| [10] | ZHANG Qing-fen,ZHAO Hong,FENG Yi. Different anesthesia management in preterm infants undergoing surgeries for retinopathy of prematurity: A retrospective study [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 195-199. |
| [11] | MENG Zhao-ting,MU Dong-liang. Impact of oliguria during lung surgery on postoperative acute kidney injury [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(1): 188-194. |
| [12] | Yong-zheng HAN,Feng-yun JING,Mao XU,Xiang-yang GUO. Anesthesia management of cervical chordoma resection: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(5): 981-983. |
| [13] | Kun-peng LIU,Bao-ning WANG,Yan-yan SHEN,Wei-xia LI,Zhao LI,Lan YAO. Effects of thoracic epidural administration of lidocaine on hemodynamic and arousal responses of double lumen tracheal intubation during induction of anesthesia [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(4): 742-747. |
| [14] | Ying DENG,Yan LI,Yao YAO,Dan-dan FENG,Mao XU. C5-6 nerve root block technique for postoperative analgesia of shoulder arthroscope: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(1): 177-181. |
| [15] | CHENG Xiao-e, PENG Hui-zhen, HU Xue-xue, FENG Xiao-jing, MA Long-xian, JIANG Chang-yu, LIU Tao. Minocycline inhibits formalin-induced inflammatory pain and the underlying mechanism [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 797-804. |
|
||