Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 234-239. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.02.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
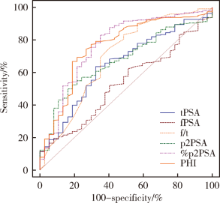
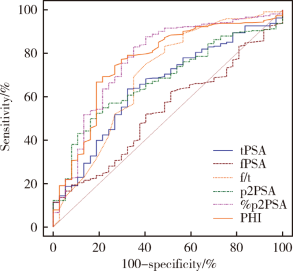
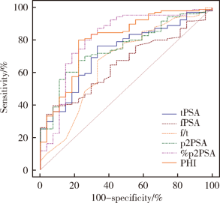
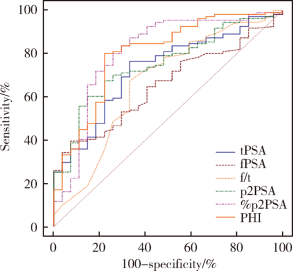
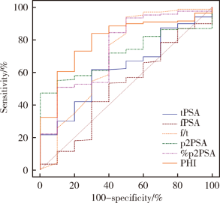
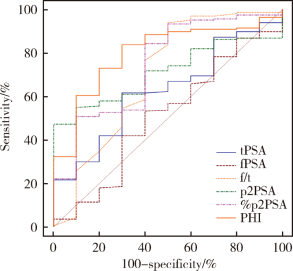
Clinical value of serum isoform [-2] proprostate-specific antigen and its derivatives in predicting aggressive prostate cancer
Kui-xia SUN,Cun-ling YAN( ),Zhi-yan LI,Ping LIU,Wei ZHANG,Qun HE
),Zhi-yan LI,Ping LIU,Wei ZHANG,Qun HE
- Department of Clinical Laboratory, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R737.2
| [1] | Stephan C, Vincendeau S, Houlgatte A , et al. Multicenter evaluation of [-2]proprostate-specific antigen and the prostate health index for detecting prostate cancer[J]. Clin Chem, 2013,59(1):306-314. |
| [2] | 黄宜, 王文涓, 许静 , 等. p2PSA及其相关指标 PHI 在前列腺癌诊断中的应用价值[J]. 检验医学, 2019,34(7):600-604. |
| [3] | Quinn D, Gross M . Show us a sign: the search for "game changing" prostate cancer biomarkers[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2011,12(3):204-206. |
| [4] | Vukovic I, Djordjevic D, Bojanic N , et al. Predictive value of [-2]propsa(p2psa) and its derivatives for the prostate cancer detection in the 2.0 to 10.0 ng/mL PSA range[J]. Int Braz J Urol, 2017,43(1):48-56. |
| [5] | 朱耀, 唐钵, 戴波 , 等. 前列腺健康指数在中国男性前列腺癌诊断中的应用研究[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2017,55(10):734-737. |
| [6] | 闫存玲, 李志艳, 何群 , 等. 血清前列腺特异性抗原同源异构体-2在前列腺癌中的应用价值[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2015,38(12):813-817. |
| [7] | Catalona WJ, Partin AW, Sanda MG , et al. A multicenter study of [-2]pro-prostate specific antigen combined with prostate speci-fic antigen and free prostate specific antigen for prostate cancer detection in the 2.0 to 10.0 ng/ml prostate specific antigen range[J]. J Urol, 2011,185(5):1650-1655. |
| [8] | Jansen FH, van Schaik RHN, Kurstjens J , et al. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) isoform p2PSA in combination with total PSA and free PSA improves diagnostic accuracy in prostate cancer detection[J]. Eur Urol, 2010,57(6):921-927 |
| [9] | Fossati N, Buffi NM, Haese A , et al. Preoperative prostate speci-fic antigen isoform p2PSA and its derivatives, %p2PSA and prostate health index, predict pathologic outcomes in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer: results from a multicentric European prospective study[J]. Eur Urol, 2015,68(1):132-138 |
| [10] | Eminaga O, Bögemann M, Breil B , et al. Preoperative prostate-specific antigen isoform p2PSA ≤ 22.5 pg/ml predicts advanced prostate cancer in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy[J]. Urol Oncol, 2014,32(8):1117-1126. |
| [11] | Guazzoni G, Lazzeri M, Nava L , et al. Preoperative prostate-specific antigen isoform p2PSA and its derivatives, %p2PSA and prostate health index, predict pathologic outcomes in patients undergoing radicalprostatectomy for prostate cancer[J]. Eur Urol, 2012,61(3):455-466. |
| [12] | Schwen ZR, Tosoian JJ, Sokoll LJ , et al. Prostate Health Index (PHI) Predicts High-stage Pathology in African American Men[J]. Urology, 2016,90:136-140. |
| [13] | Dolejsova O, Kucera R, Fuchsova R , et al. The ability of Prostate Health Index (PHI) to predict gleason score in patients with prostate cancer and discriminate patients between gleason score 6 and gleason score higher than 6: a study on 320 patients after radical prostatectomy[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2018,17:1-6. |
| [14] | Chiu PK, Lai FM, Teoh JY , et al. Prostate health index and %p2PSA predict aggressive prostate cancer pathology in Chinese[J]. Ann Surg Onclo, 2016,23(8):2707-2714. |
| [15] | 王友林, 朱磊一, 姜波 , 等. 超声引导下经直肠前列腺穿刺与前列腺癌根治术后病理组织Gleason评分差异性的研究[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2015,30(7):628-630. |
| [1] | Ye YAN,Xiaolong LI,Haizhui XIA,Xuehua ZHU,Yuting ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ke LIU,Cheng LIU,Lulin MA. Analysis of risk factors for long-term overactive bladder after radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [2] | Sheng-jie LIU,Hui-min HOU,Zheng-tong LV,Xin DING,Lu WANG,Lei ZHANG,Ming LIU. Bipolar androgen therapy followed by immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer: A report of 4 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2022, 54(4): 766-769. |
| [3] | BAI Gao-chen,SONG Yi,JIN Jie,YU Wei,HE Zhi-song. Clinical efficacy of docetaxel combined with carboplatin in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2021, 53(4): 686-691. |
| [4] | Wen-qing LI,Si-mei REN,Xing-bo LONG,Yu-qing TIAN. Palmitoylome profiling indicates that androgens promote the palmitoylation of metabolism-related proteins in prostate cancer-derived LNCaP cells [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 227-233. |
| [5] | Kuan-gen ZHANG,Yu-he ZHOU,Ya-kun SHAO,Fang MEI,Jiang-feng YOU,Bei-ying LIU,Fei PEI. Novel tumor metastasis suppressorgene LASS2/TMSG1 S248A mutant promotes invasion of prostate cancer cells through increasing ATP6V0C expression [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(2): 210-220. |
| [6] | TANG Xu, ZHAO Wei-hong, SONG Qin-qin, YIN Hua-qi, DU Yi-qing, SHENG Zheng-zuo, WANG Qiang, ZHANG Xiao-wei, LI Qing, LIU Shi-jun, XU Tao. Influence of SOX10 on the proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 602-606. |
| [7] | ZOU Peng-cheng, YANG Yi-feng, XU Xiao-yan LIU Bei-ying, MEI Fang, YOU Jiang-feng, LIU Qi-chen, PEI Fei . Silencing of vacuolar ATPase c subunit ATP6V0C inhibits invasion of prostate cancer cells [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(6): 937-947. |
| [8] | JI Guang-jie, HUANG Cong, SONG Gang, LI Xue-song, SONG Yi, ZHOU Li-qun. Predictive factor analysis of time to progression of castration-resistant prostate cancer after androgen deprivation therapy [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(4): 657-662. |
|
||