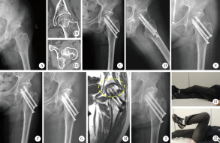
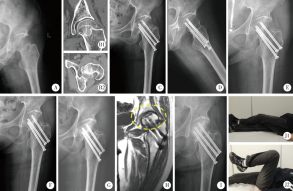
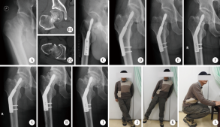
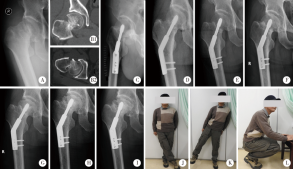
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 290-297. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.02.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of risk factors for necrosis of femoral head after internal fixation surgery in young and mid-aged patients with femoral neck fracture
Bing-chuan LIU,Chuan SUN,Yong XING,Fang ZHOU,Yun TIAN( ),Hong-quan JI,Zhi-shan ZHANG,Yan GUO,Yang LV,Zhong-wei YANG,Guo-jin HOU,Shan GAO
),Hong-quan JI,Zhi-shan ZHANG,Yan GUO,Yang LV,Zhong-wei YANG,Guo-jin HOU,Shan GAO
- Department of Orthopedics, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing 100191, China
CLC Number:
- R683.4
| [1] | Sprague S, Slobogean GP, Scott T , et al. Young femoral neck fractures: are we measuring outcomes that matter?[J] Injury, 2015,46(3):507-514. |
| [2] | Rodriguez-Merchan EC, Gomez-Cardero P, Jimenez-Yuste V . Late avascular necrosis of the femoral head (anfh) after the percutaneous fixation of a non-displaced fracture of the femoral neck in a haemophilic patient with inhibitors: a non-reported association[J]. Haemophilia, 2012,18(1):e4-e5. |
| [3] | Murphy DK, Randell T, Brennan KL , et al. Treatment and displacement affect the reoperation rate for femoral neck fracture[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2013,471(18):2691-2702. |
| [4] | Schweitzer D, Melero P, Zylberberg A , et al. Factors associated with avascular necrosis of the femoral head and nonunion in patients younger than 65 years with displaced femoral neck fractures treated with reduction and internal fixation[J]. Eur J Orthopaedic Surg Traumatol, 2013,23(1):61-65. |
| [5] | Damany DS, Parker MJ, Chojnowski A . Complications after intracapsular hip fractures in young adults: a meta-analysis of 18 published studies involving 564 fractures[J]. Injury, 2005,36(1):131-141. |
| [6] | Stacey SC, Renninger CH, Hak D , et al. Tips and tricks for ORIF of displaced femoral neck fractures in the young adult patient[J]. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol, 2016,26(4):355-363. |
| [7] | Zielinski SM, Meeuwis MA, Heetveld MH , et al. Adherence to a femoral neck fracture treatment guideline[J]. Int Orthop, 2013,37(7):1327-1334. |
| [8] | Pauyo T, Drager J, Albers A , et al. Management of femoral neck fractures in the young patient: a critical analysis review[J]. World J Orthop, 2014,5(3):204-217. |
| [9] | Bhandari M, Swiontkowski M . Management of acute hip fracture[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017,377(21):2053-2062. |
| [10] | 曹发奇, 周武, 刘国辉 , 等. 股骨颈骨折复位内固定术后股骨头坏死的相关因素分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2017,37(17):1088-1092. |
| [11] | Wang T, Sun JY, Zha GC , et al. Analysis of risk factors for femoral head necrosis after internal fixation in femoral neck fractures[J]. Orthopedics, 2014,37(12):1117-1123. |
| [12] | Zhao DW, Hu YC . Chinese experts' consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults[J]. Orthop Surg, 2012,4(3):125-130. |
| [13] | Slobogean GP, Sprague SA, Scott T , et al. Management of young femoral neck fracutures; is there a consensus[J]. Injury, 2015,43(3):435-440. |
| [14] | Al-Ani AN, Neander G, Samuelsson B , et al. Risk factors for osteoporosis are common in young and middle-aged patients with femoral neck fractures regardless of trauma mechanism[J]. Acta Orthop, 2013,84(1):54-59. |
| [15] | Slobogean GP, Sprague SA, Scott T , et al. Complications fol-lowing young femoral neck fractures[J]. Injury, 2015,46(3):484-491. |
| [16] | Duckworth AD ,Bennet SJ,derinto JA, et al.Fixation of intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck in young patients[J]. J Bone Joint Surg, 2011,93(6):811-816. |
| [17] | Lee RH, Lyles KW, Colon-Emeric C . A review of the effect of anticonvulsant medications on bone mineral density and fracture risk[J]. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother, 2010,8(1):34-46. |
| [18] | Guimarães JAM, Rocha LR, Noronha Rocha TH , et al. Vertical femoral neck fractures in young adults: a closed fixation strategy using a transverse cancellous lag screw[J]. Injury, 2017,48(Suppl 4):S10-S16. |
| [19] | Razik F, Alexopoulos A, EI-Osta B , et al. Time to internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in patients under sixty years: does this matter in the development of osteonecrosis of femoral head?[J]. Int Orthop, 2012,36(10):2127-2132. |
| [20] | Papakostidis C, Panagiotopoulos A, Piccioli A , et al. Timing of internal fixation of femoral neck fractures. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the final outcome[J]. Injury, 2015,46(3):459-466. |
| [21] | Lamb JN, Panteli, Pneumaticos SG , et al. Epidemiolog of pertrochanteric fractures: our institutional experience[J]. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg, 2014,40(3):225-232. |
| [22] | Basso T, Klaksvik J, Syversen U , et al. Biomechanical femoral neck fracture experiments: a narrative review[J]. Injury, 2012,43(10):1633-1639. |
| [23] | van Embden D, Roukema GR, Rhemrev SJ , et al. The Pauwels classification for intracapsular hip fractures: is it reliable?[J]. Injury, 2011,42(11):1238-1240. |
| [24] | Wang SH, Yang JJ, Shen HC , et al. Using a modified Pauwels method to predict the outcome of femoral neck fracture in relatively young patients[J]. Injury, 2015,46(10):1969-1974. |
| [25] | Florschutz AV, Langford JR, Haidukewych GJ , et al. Femoral neck fractures: current management[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2015,29(3):121-129. |
| [26] | Parker MJ, Blundell C . Choice of implant for internal fixation of femoral neck fractures. Meta-analysis of 25 randomised trials including 4,925 patients[J]. Acta Orthop Scand, 1998,69(2):138-143. |
| [27] | Bhandari M, Tornetta P, Hanson B , et al. Optimal internal fixation for femoral neck fractures: multiple screws or sliding hip screws?[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2009,23(6):403-407. |
| [28] | Gardner S, Weaver MJ, Jerabek S , et al. Predictors of early fai-lure in young patients with displaced femoral neck fractures[J]. J Orthop, 2014,12(2):75-80. |
| [29] | Johnson JP, Borenstein TR, Waryasz GR , et al. Vertically oriented femoral neck fractures: a biomechanical comparison of 3 fixation contructs[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2017,31(7):363-368. |
| [30] | Noda M, Saegusa Y, Takahashi M , et al. Biomechanical study using the finite element method of internal fixation in Pauwels type III vertical femoral neck fractures[J]. Arch Trauma Res, 2015,4(3):e23167. |
| [31] | Samsami S, Saberi S, Bagheri N , et al. Interfragmentary motion assessment for three different fixation techniques of femoral neck fractures in young adults[J]. Biomed Mater Eng, 2016,27(4):389-404. |
| [32] | Min BW, Kim SJ . Avascular necrosis of the femoral head after osteosynjournal of femoral neck fracture[J]. Orthopedics, 2011,34(5):349. |
| [33] | Hoshino CM, Christian MW ,O'Toole RV, et al.Fixation of displaced femoral neck fractures in young adults: fixed-angle devices or Pauwel screws?[J]. Injury, 2016,47(8):1676-1694. |
| [34] | FIlipov O, Stoffel K, Gueorguiev B , et al. Femoral neck fracture osteosynjournal by the biplane double-supported screw fixation method (BDSF) reduces the risk of fixation failure: clinical outcomes in 207 patients[J]. Arch Orchop Trauma Surg, 2017,137(6):779-788. |
| [35] | Khani GMK, Hafeez K, Bux M , et al. Use of fibular bone graft and cancellous screw fixation in the management of neglected femur neck fractures in young patients[J]. Int J Health Sci (Qassim), 2017,11(5):7-10. |
| [36] | Li G, Jin D, Shao X , et al. Effect of cannulated screws with deep circumflex iliac artery-bone grafting in the treatment of femoral neck fracture in young adults[J]. Injury, 2018,49(8):1587-1593. |
| [37] | Kalsbeek JH, van Walsum ADP, Vroemen JPAM , et al. Displaced femoral neck fractures in patients 60 years of age or younger: results of internal fixation with the dynamic locking blade plate[J]. Bone Joint J, 2018,100(4):443-449. |
| [1] | Zhicun LI, Tianyu WU, Lei LIANG, Yu FAN, Yisen MENG, Qian ZHANG. Risk factors analysis and nomogram model construction of postoperative pathological upgrade of prostate cancer patients with single core positive biopsy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(5): 896-901. |
| [2] | Ye YAN,Xiaolong LI,Haizhui XIA,Xuehua ZHU,Yuting ZHANG,Fan ZHANG,Ke LIU,Cheng LIU,Lulin MA. Analysis of risk factors for long-term overactive bladder after radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 589-593. |
| [3] | Yan CHEN,Kuangmeng LI,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG,Jianxing CHENG,Zhongjie ZHENG,Wenhao TANG,Lianming ZHAO,Haitao ZHANG,Hui JIANG,Haocheng LIN. Retrospective study on the impact of penile corpus cavernosum injection test on penile vascular function [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 680-686. |
| [4] | Bo PANG,Tongjun GUO,Xi CHEN,Huaqi GUO,Jiazhang SHI,Juan CHEN,Xinmei WANG,Yaoyan LI,Anqi SHAN,Hengyi YU,Jing HUANG,Naijun TANG,Yan WANG,Xinbiao GUO,Guoxing LI,Shaowei WU. Personal nitrogen oxides exposure levels and related influencing factors in adults over 35 years old in Tianjin and Shanghai [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 700-707. |
| [5] | Jing HE,Zhongze FANG,Ying YANG,Jing LIU,Wenyao MA,Yong HUO,Wei GAO,Yangfeng WU,Gaoqiang XIE. Relationship between lipid metabolism molecules in plasma and carotid atheroscle-rotic plaques, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and dietary factors [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 722-728. |
| [6] | Shan CAI,Yihang ZHANG,Ziyue CHEN,Yunfe LIU,Jiajia DANG,Di SHI,Jiaxin LI,Tianyu HUANG,Jun MA,Yi SONG. Status and pathways of factors influencing physical activity time among elementary and junior high school students in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 403-410. |
| [7] | Zuhong ZHANG,Tianjiao CHEN,Jun MA. Associations between puberty timing and cardiovascular metabolic risk factors among primary and secondary students [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 418-423. |
| [8] | Yuting LIN,Huali WANG,Yu TIAN,Litong GONG,Chun CHANG. Factors influencing cognitive function among the older adults in Beijing [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 456-461. |
| [9] | Jinrong ZHU,Yana ZHAO,Wei HUANG,Weiwei ZHAO,Yue WANG,Song WANG,Chunyan SU. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 infection in patients undergoing hemodialysis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 267-272. |
| [10] | Zhanhong LAI,Jiachen LI,Zelin YUN,Yonggang ZHANG,Hao ZHANG,Xiaoyan XING,Miao SHAO,Yuebo JIN,Naidi WANG,Yimin LI,Yuhui LI,Zhanguo LI. A unicenter real-world study of the correlation factors for complete clinical response in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 284-292. |
| [11] | Xiaoqian SI,Xiujuan ZHAO,Fengxue ZHU,Tianbing WANG. Risk factors for acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with traumatic hemorrhagic shock [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(2): 307-312. |
| [12] | Yangyang LI,Lin HOU,Zijun MA,Shanyamei HUANG,Jie LIU,Chaomei ZENG,Jiong QIN. Association of pregnancy factors with cow's milk protein allergy in infants [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 144-149. |
| [13] | Xiaoqiang LIU,Yin ZHOU. Risk factors of perioperative hypertension in dental implant surgeries with bone augmentation [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(1): 93-98. |
| [14] | Liang LUO,Yun LI,Hong-yan WANG,Xiao-hong XIANG,Jing ZHAO,Feng SUN,Xiao-ying ZHANG,Ru-lin JIA,Chun LI. Anti-endothelial cell antibodies in predicting early miscarriage [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1039-1044. |
| [15] | Yu-fei LI,Ya-ni YAN,Jia-yang JIN,Chun LI,Qiu-yan PEI. Clinical characteristics of fetal cardiac disease in patients with anti-SSA antibody positive [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1053-1057. |
|
||