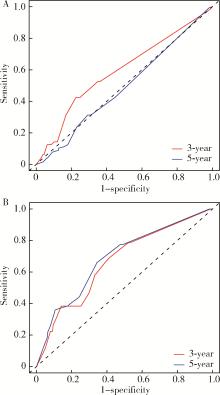
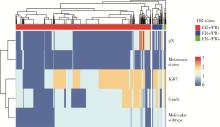
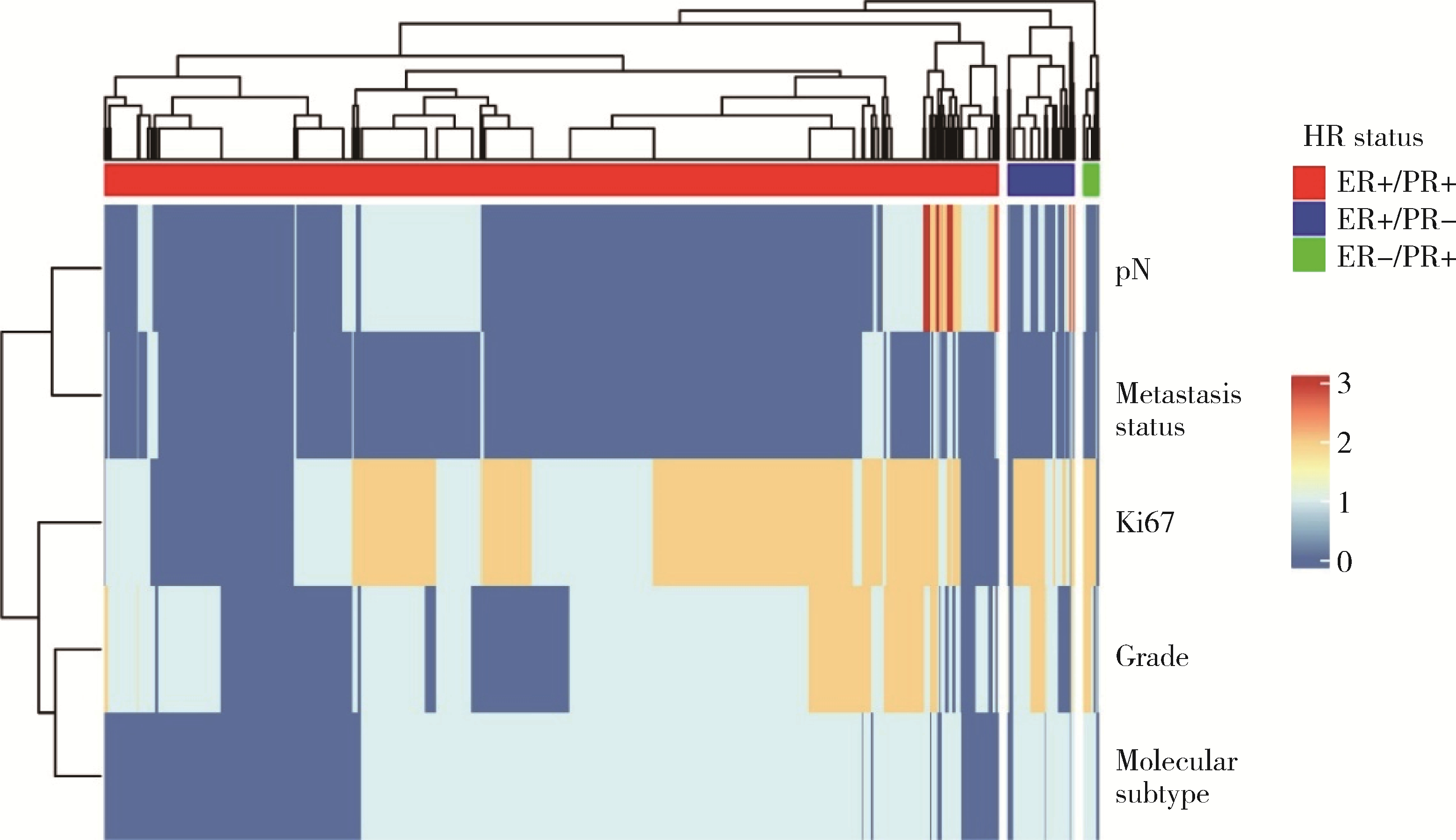
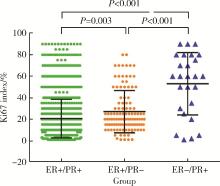
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2022, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 853-862. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.05.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
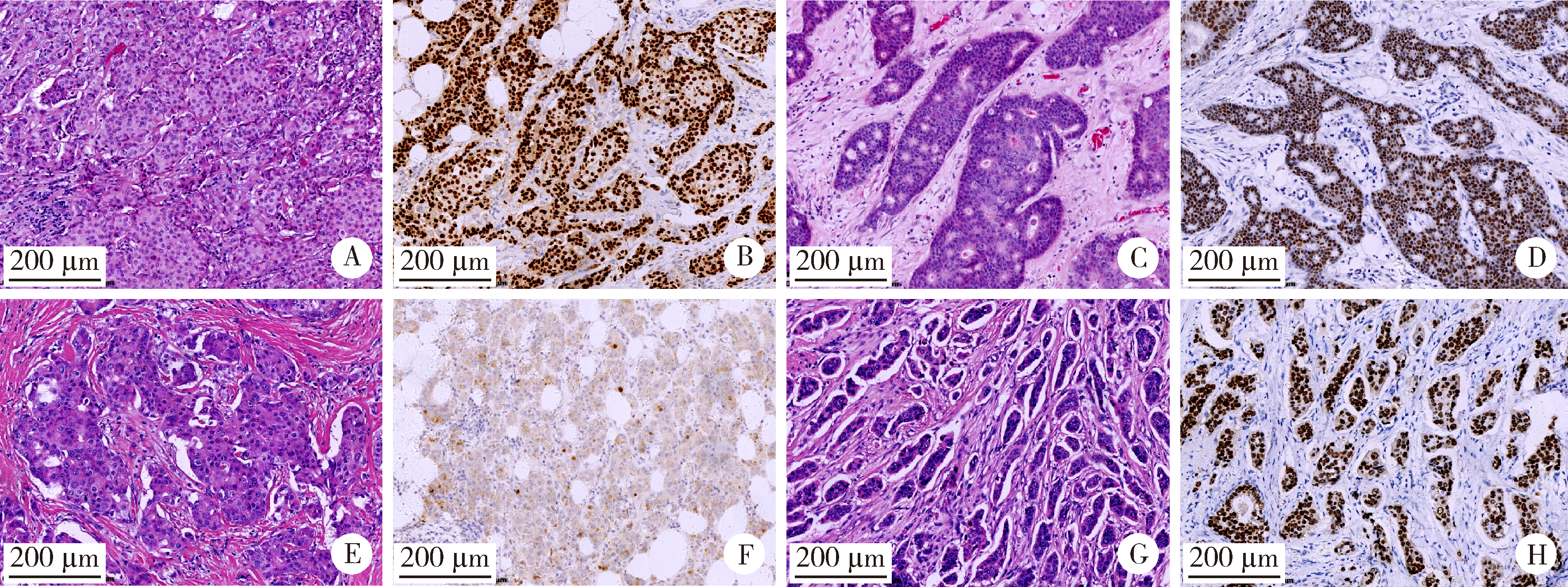
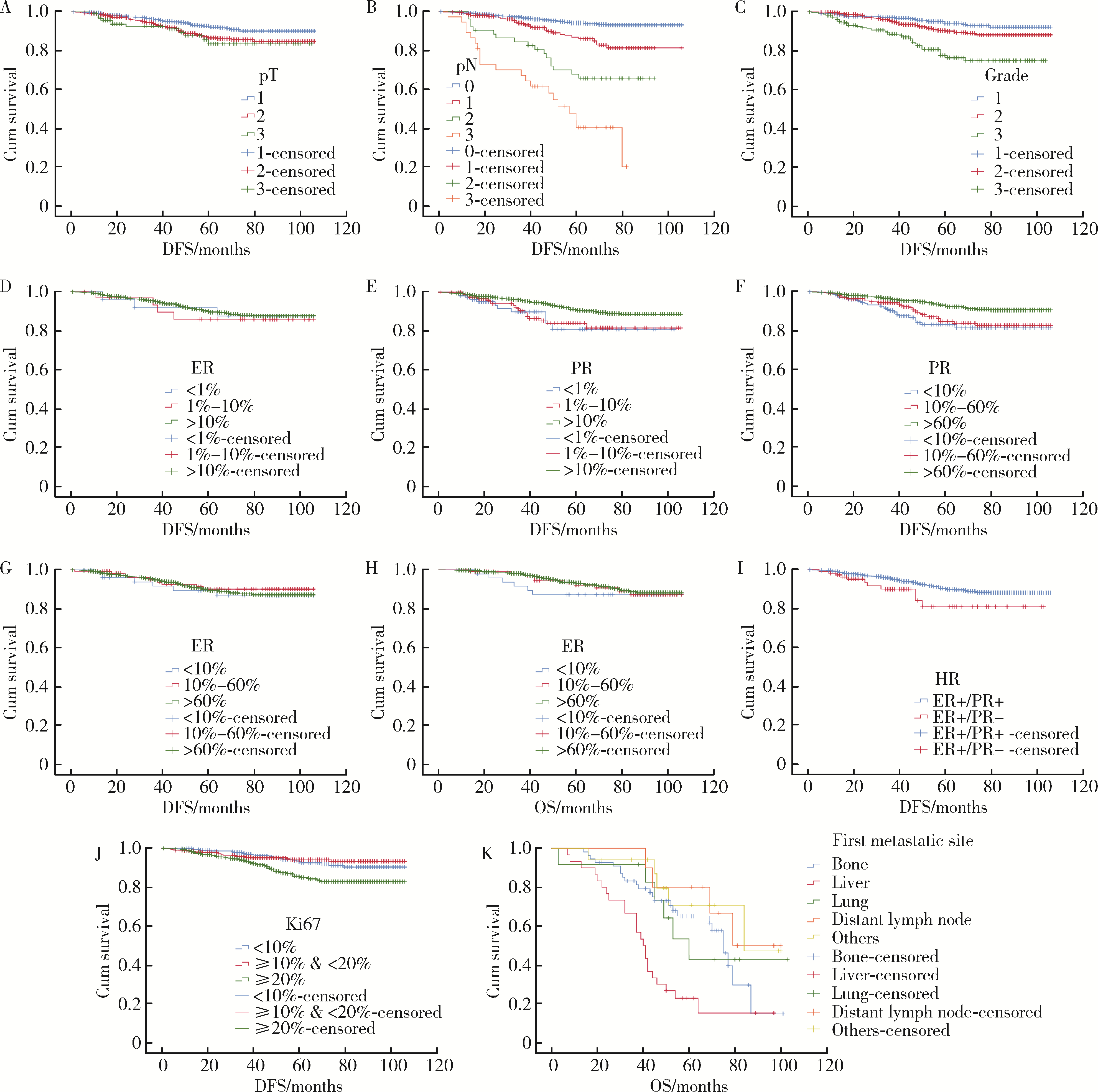
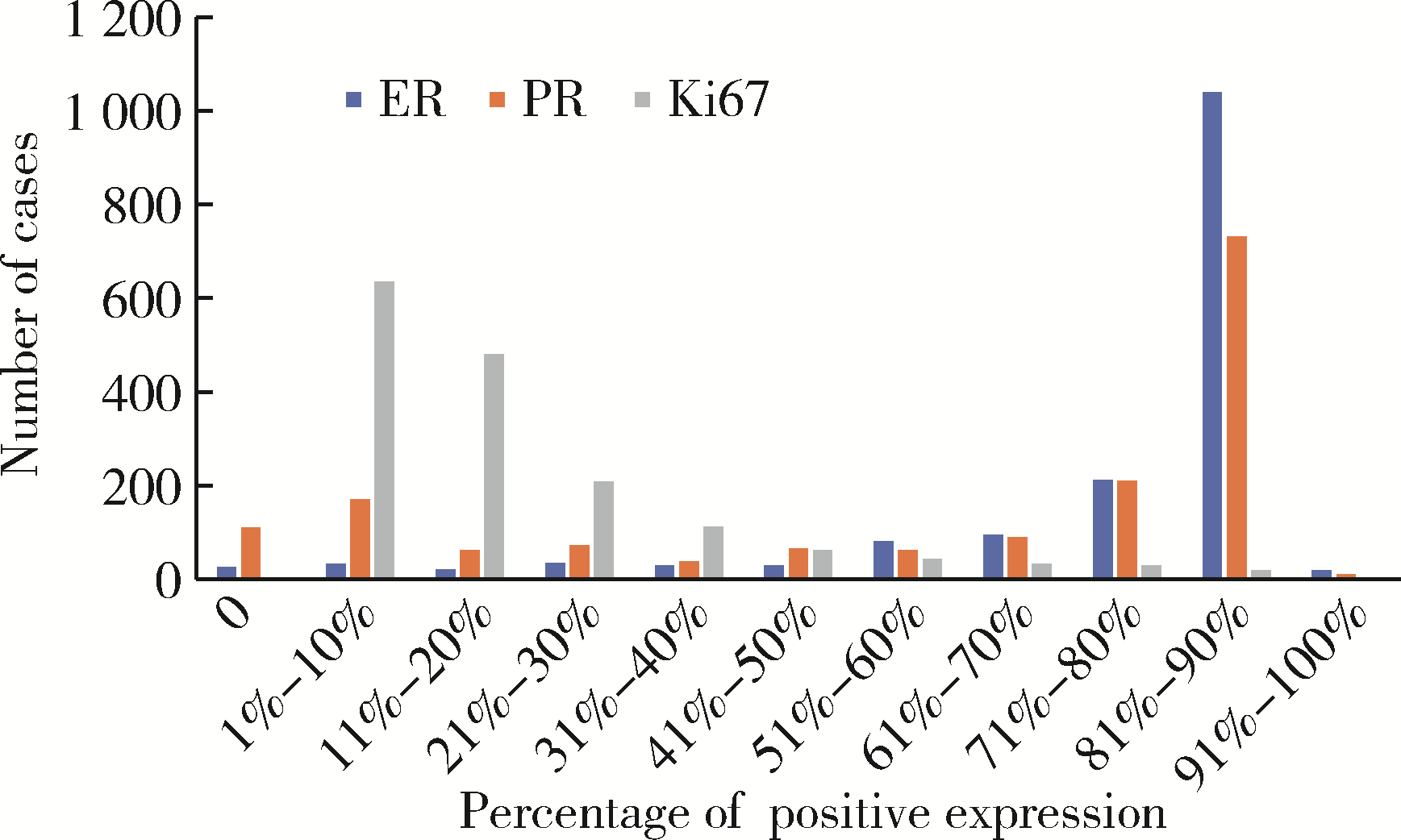
Clinicopathological features and prognosis of hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer
Yue WANG1,Shuang ZHANG1,Hong ZHANG1,Li LIANG1,Ling XU2,Yuan-jia CHENG2,Xue-ning DUAN2,Yin-hua LIU2,Ting LI1,*( )
)
- 1. Department of Pathology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Breast Disease Center, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R737.9
| 1 |
Cao W , Chen HD , Yu YW , et al. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2021, 134 (7): 783- 791.
doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001474 |
| 2 |
Wolff AC , Hammond ME , Schwartz JN , et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2007, 25 (1): 118- 145.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.09.2775 |
| 3 | WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board . WHO classification of tumours[M]. 5th ed Lyon: IARC Press, 2019. |
| 4 | Amin MB , Edge SB , Greene FL , et al. AJCC cancer staging ma-nual[M]. 8th ed New York: Springer, 2017. |
| 5 |
Goldhirsch A , Wood WC , Coates AS , et al. Strategies for subtypes-dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St. Gallen international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2011[J]. Ann Oncol, 22 (8): 1736- 1747.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr304 |
| 6 |
Hammond ME , Hayes DF , Dowsett M , et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline re-commendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28 (16): 2784- 2795.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.6529 |
| 7 |
Wolff AC , Hammond ME , Hicks DG , et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Patho-logists clinical practice guideline update[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2014, 138 (2): 241- 256.
doi: 10.5858/arpa.2013-0953-SA |
| 8 | Cheang MC , Chia SK , Voduc D , et al. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer[J]. J Nat Cancer Inst, 2009, 101 (10): 731- 750. |
| 9 |
Wolff AC , Hammond MEH , Allison KH , et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36 (20): 2105- 2122.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.77.8738 |
| 10 |
李挺. 乳腺癌异质性的分子遗传学基础及临床应用[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2017, 55 (2): 104- 108.
doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5815.2017.02.006 |
| 11 | 李挺. 乳腺癌病理诊断评估与治疗决策[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2008, 28 (7): 74- 76. |
| 12 |
Perou CM , Sorlie T , Eisen MB , et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours[J]. Nature, 2000, 406 (6797): 747- 752.
doi: 10.1038/35021093 |
| 13 | Zhang S , Huang S , Zhang H , et al. Histo-and clinico-pathological analysis of a large series of triple-negative breast cancer in a single center in China: Evidences on necessity of histological subtyping and grading[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2020, 32 (5): 580- 595. |
| 14 |
André F , Ciruelos E , Rubovszky G , et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380 (20): 1929- 1940.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1813904 |
| 15 |
van't Veer LJ , Dai H , van de Vijver MJ , et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer[J]. Nature, 2002, 415 (6871): 530- 536.
doi: 10.1038/415530a |
| 16 |
Sparano JA , Crager MR , Tang G , et al. Development and validation of a tool integrating the 21-gene recurrence score and clinical-pathological features to individualize prognosis and prediction of chemotherapy benefit in early breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39 (6): 557- 564.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03007 |
| 17 |
Pan H , Gray R , Braybrooke J , et al. 20-year risks of breast-cancer recurrence after stopping endocrine therapy at 5 years[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377 (19): 1836- 1846.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1701830 |
| 18 |
Duffy MJ , Harbeck N , Nap M , et al. Clinical use of biomarkers in breast cancer: Updated guidelines from the European Group on Tumor Markers (EGTM)[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2017, 75, 284- 298.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.01.017 |
| 19 |
Zhao H , Gong Y . The prognosis of single hormone receptor-positive breast cancer stratified by HER2 status[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11, 643956.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.643956 |
| 20 |
Dauphine C , Moazzez A , Neal J , et al. Single hormone receptor-positive breast cancers have distinct characteristics and survival[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2020, 27 (12): 4687- 4694.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-020-08898-5 |
| 21 |
Li Z , Tu Y , Wu Q , et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of single versus double hormone receptor-positive breast cancer in 2 large databases[J]. Clin Breast Cancer, 2020, 20 (2): e151- e163.
doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2019.07.002 |
| 22 | Ye J , Wang W , Xin L , et al. The clinicopathological factors associated with disease progression in luminal A breast cancer and characteristics of metastasis: A retrospective study from a single center in China[J]. Anticancer Res, 2017, 37 (8): 4549- 4556. |
| 23 |
Yamamura J , Kamigaki S , Fujita J , et al. New insights into patterns of first metastatic sites influencing survival of patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer: A multicenter study of 271 patients[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21 (1): 476.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08219-3 |
| [1] | Jian-xun MA,You-chen XIA,Bi LI,Hong-mei ZHAO,Yu-tao LEI,Xi BU. Choice of immediate breast reconstructive methods after modified radical mastectomy [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 612-618. |
| [2] | Yun-jing ZHANG,Li-ying QIAO,Meng QI,Ying YAN,Wei-wei KANG,Guo-zhen LIU,Ming-yuan WANG,Yun-feng XI,Sheng-feng WANG. Development and validation of risk prediction model for new-onset cardiovascular diseases among breast cancer patients: Based on regional medical data of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 471-479. |
| [3] | Xiao-juan ZHU,Hong ZHANG,Shuang ZHANG,Dong LI,Xin LI,Ling XU,Ting LI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of breast cancer with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 low expression [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 243-253. |
| [4] | Guo-hong SONG,Hui-ping LI,Li-jun DI,Ying YAN,Han-fang JIANG,Ling XU,Dong-gui WAN,Ying LI,Mo-pei WANG,Yu XIAO,Ru-yan ZHANG,Ran RAN,Huan WANG. Efficacy and safety of oral pyrotinib in HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer: real-world practice [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2020, 52(2): 254-260. |
| [5] | Xu-chu ZHANG,Jian-hua ZHANG,Rong-fu WANG,Yan FAN,Zhan-li FU,Ping YAN,Guang-yu ZHAO,Yan-xia BAI. Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT and tumor markers (CEA, CA19-9, CA24-2) in recurrence and metastasis of postoperative colorectal moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(6): 1071-1077. |
| [6] | Xue-jun LIANG,Li-ying GONG,Fei ZHOU,De-min ZHOU,Jing-jing ZHU. Pharmacological effects of site specific conjugated anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-antibody drug conjugate using unnatural amino acid technology [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2019, 51(5): 797-804. |
| [7] | HUANG Zi-xiong, DU Yi-qing, ZHANG Xiao-peng, LIU Shi-jun, XU Tao. Clinical and pathological analysis of renal cell carcinoma bone metastasis [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(5): 811-815. |
| [8] | HUANG Zi-xiong, ZHANG Xiao-peng, DONG Sen, LIU Shi-jun, YANG Rong-li, ZHOU Yu-shi, MA Wei-guo. Renal mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma combined with multiple bone metastasis: a case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(4): 732-735. |
| [9] | ZHU Yan,SHI Yong-jin,ZHAO Yu-liang, ZHU Ping. Topoisomerase inhibitor upregulates MICA/B expression in breast cancer cells through ATM/ATR and NF-κB pathway [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 318-325. |
| [10] | KANG Lei, HUO Yan, WANG Rong-fu, ZHANG Chun-li, YAN Ping, XU Xiao-jie. In vivo imaging of breast tumors by a 99mTc radiolabeled probe targeting microRNA-155 in mice models [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2018, 50(2): 326-330. |
| [11] | ZHAO Yi-guo, YANG Xiao-dong, ZHANG Yan-kai, NING Ning, XING Zhao-dong, YE Ying-jiang. #br# Adenocarcinoma in a Meckel’s diverticulum with multiple liver metastases and gastrointestinal hemorrhage: a case report [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(6): 1095-1097. |
| [12] | WANG Wei, ZHENG Lei, LIU Shu-ming, HUANG Ming-wei, SHI Yan, LV Xiao-ming, ZHANG Jie, ZHANG Jian-guo. Distant metastases of malignant salivary gland carcinoma after treated by 125Ⅰinternal brachy therapy alone [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(3): 547-550. |
| [13] | GUO Fu-xin, JIANG Yu-liang, JI Zhe, PENG Ran, SUN Hai-tao, WANG Jun-jie. 3D printed template-assisted and computed tomography image-guided 125-iodine seed implantation for supraclavicular metastatic tumor: a dosimetric study [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(3): 506-511. |
| [14] | LI Xiu-nan, LIU Ai-hui, TANG Xin, REN Yu. Urothelial carcinoma-associated 1 enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells through competitively inhibiting miR-18a [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 295-302. |
| [15] | FANG Wei-gang, TIAN Xin-xia. Identification of a new pro-invasion factor in tumor microenvironment: progress in function and mechanism of extracellular ATP [J]. Journal of Peking University(Health Sciences), 2017, 49(2): 188-195. |
|
||