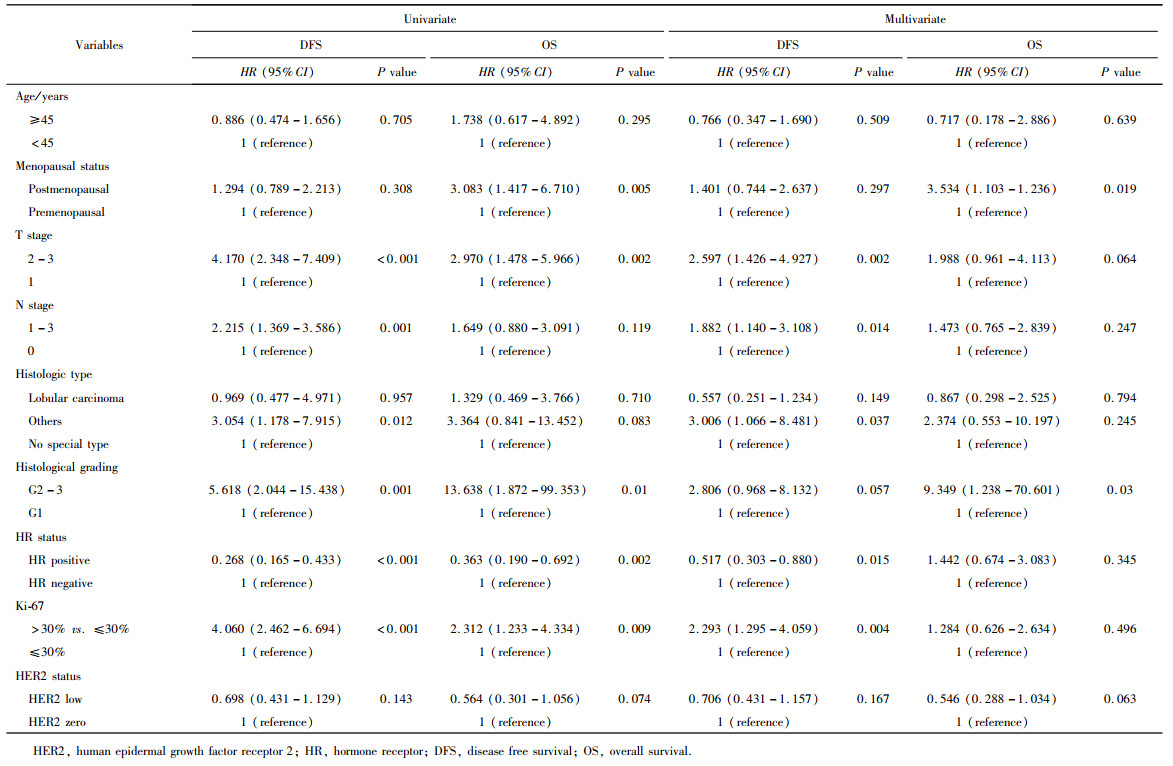
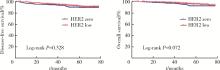
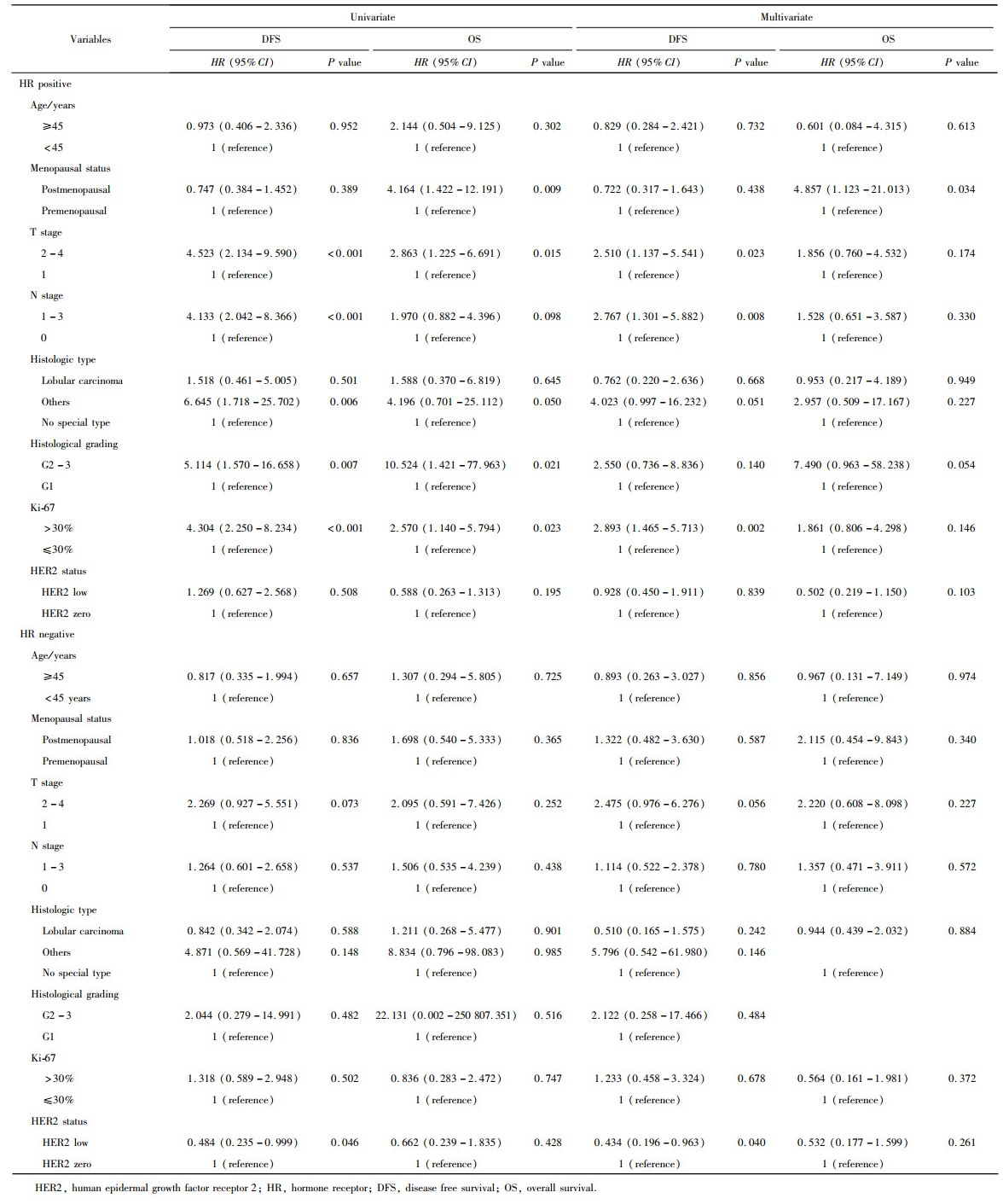
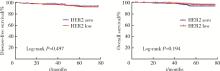
Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 243-253. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2023.02.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
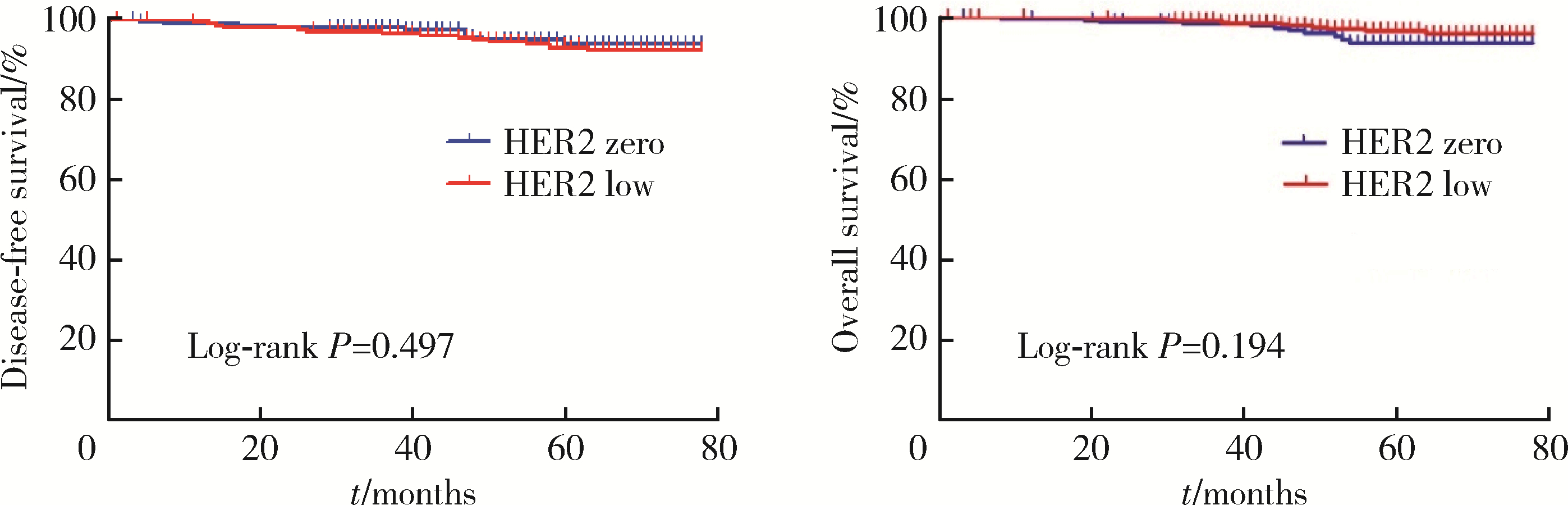
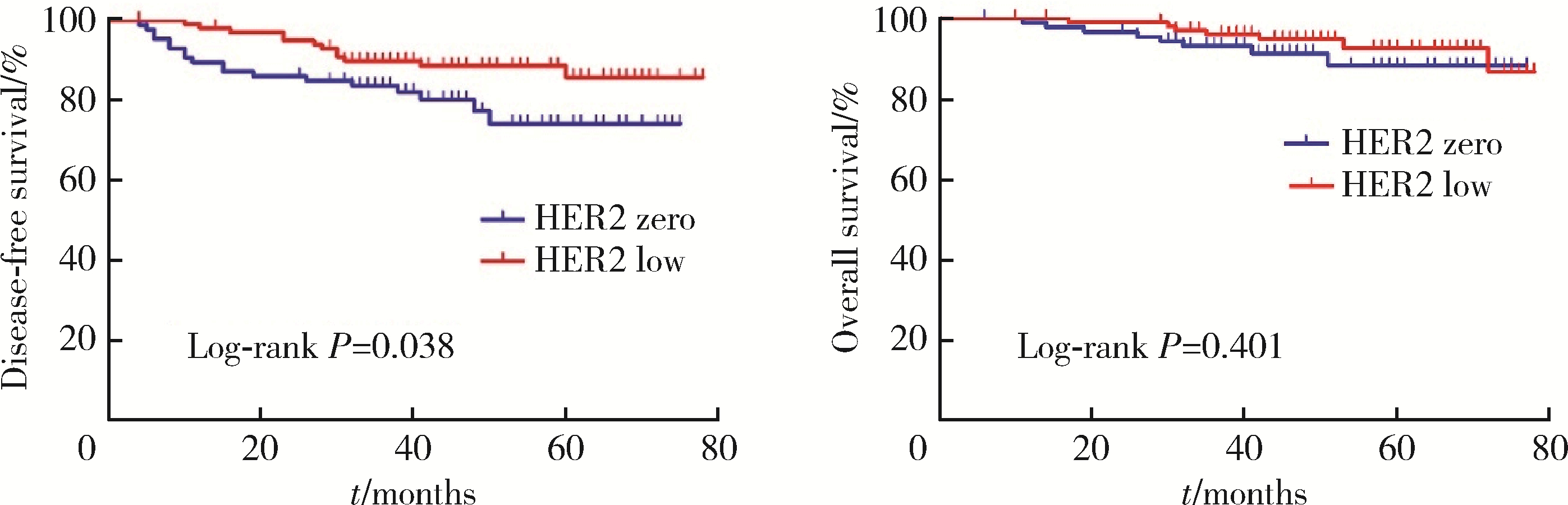
Clinicopathological features and prognosis of breast cancer with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 low expression
Xiao-juan ZHU1,Hong ZHANG1,*( ),Shuang ZHANG1,Dong LI1,Xin LI1,Ling XU2,Ting LI1
),Shuang ZHANG1,Dong LI1,Xin LI1,Ling XU2,Ting LI1
- 1. Department of Pathology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
2. Breast Disease Center, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
CLC Number:
- R737.9
| 1 | Yarden Y . Biology of HER2 and its importance in breast cancer[J]. Oncology, 2001, 61 (Suppl 2): 1- 13. |
| 2 |
Choong GM , Cullen GD , O'Sullivan CC , et al. Evolving stan-dards of care and new challenges in the management of HER2-positive breast cancer[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70 (5): 355- 374.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21634 |
| 3 |
Swain SM , Baselga J , Kim SB , et al. Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 372 (8): 724- 734.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1413513 |
| 4 |
Wolff AC , Hammond ME , Hicks DG , et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Patho-logists clinical practice guideline update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2013, 31 (31): 3997- 4013.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.50.9984 |
| 5 |
Gilcrease MZ , Woodward WA , Nicolas MM , et al. Even low-level HER2 expression may be associated with worse outcome in node-positive breast cancer[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2009, 33 (5): 759- 767.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31819437f9 |
| 6 |
Modi S , Park H , Murthy RK , et al. Antitumor activity and safety of trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with HER2-low-expressing advanced breast cancer: Results from a phase Ⅰb study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38 (17): 1887- 1896.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02318 |
| 7 |
Tarantino P , Hamilton E , Tolaney SM , et al. HER2-low breast cancer: Pathological and clinical landscape[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38 (17): 1951- 1962.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02488 |
| 8 |
Hammond ME , Hayes DF , Dowsett M , et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28 (16): 2784- 2795.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.6529 |
| 9 |
Schalper KA , Kumar S , Hui P , et al. A retrospective population-based comparison of HER2 immunohistochemistry and fluorescence in situ hybridization in breast carcinomas: Impact of 2007 American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists criteria[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2014, 138 (2): 213- 219.
doi: 10.5858/arpa.2012-0617-OA |
| 10 |
Xin L , Wu Q , Zhan C , et al. Multicenter study of the clinico-pathological features and recurrence risk prediction model of early-stage breast cancer with low-positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 expression in China (Chinese Society of Breast Surgery 021)[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2022, 135 (6): 697- 706.
doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002056 |
| 11 |
Schettini F , Chic N , Brasó-Maristany F , et al. Clinical, patholo-gical, and PAM50 gene expression features of HER2-low breast cancer[J]. NPJ Breast Cancer, 2021, 7 (1): 1.
doi: 10.1038/s41523-020-00208-2 |
| 12 |
Denkert C , Seither F , Schneeweiss A , et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of HER2-low-positive breast cancer: Pooled analysis of individual patient data from four prospective, neoadjuvant clinical trials[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22 (8): 1151- 1161.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00301-6 |
| 13 |
Rossi V , Sarotto I , Maggiorotto F , et al. Moderate immunohistochemical expression of HER-2 (2+) without HER-2 gene amplification is a negative prognostic factor in early breast cancer[J]. Oncologist, 2012, 17 (11): 1418- 1425.
doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0194 |
| 14 |
Won HS , Ahn J , Kim Y , et al. Clinical significance of HER2-low expression in early breast cancer: A nationwide study from the Korean Breast Cancer Society[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2022, 24 (1): 22.
doi: 10.1186/s13058-022-01519-x |
| 15 |
Horisawa N , Adachi Y , Takatsuka D , et al. The frequency of low HER2 expression in breast cancer and a comparison of prognosis between patients with HER2-low and HER2-negative breast cancer by HR status[J]. Breast Cancer, 2022, 29 (2): 234- 241.
doi: 10.1007/s12282-021-01303-3 |
| 16 |
Dehghani M , Keshavarz P , Talei A , et al. The Effects of Low HER2/neu expression on the clinicopathological characteristics of triple-negative breast cancer patients[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2020, 21 (10): 3027- 3032.
doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.10.3027 |
| 17 |
Jacot W , Maran-Gonzalez A , Massol O , et al. Prognostic value of HER2-low expression in non-metastatic triple-negative breast cancer and correlation with other biomarkers[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13 (23): 6059.
doi: 10.3390/cancers13236059 |
| [1] | Junyong OU,Kunming NI,Lulin MA,Guoliang WANG,Ye YAN,Bin YANG,Gengwu LI,Haodong SONG,Min LU,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Prognostic factors of patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer with intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 582-588. |
| [2] | Shuai LIU,Lei LIU,Zhuo LIU,Fan ZHANG,Lulin MA,Xiaojun TIAN,Xiaofei HOU,Guoliang WANG,Lei ZHAO,Shudong ZHANG. Clinical treatment and prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 624-630. |
| [3] | Le YU,Shaohui DENG,Fan ZHANG,Ye YAN,Jianfei YE,Shudong ZHANG. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 661-666. |
| [4] | Zezhen ZHOU,Shaohui DENG,Ye YAN,Fan ZHANG,Yichang HAO,Liyuan GE,Hongxian ZHANG,Guoliang WANG,Shudong ZHANG. Predicting the 3-year tumor-specific survival in patients with T3a non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 673-679. |
| [5] | Yangyi FANG,Qiang LI,Zhigao HUANG,Min LU,Kai HONG,Shudong ZHANG. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the tunica vaginalis: A case report [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(4): 741-744. |
| [6] | Yuanyuan ZENG,Yun XIE,Daonan CHEN,Ruilan WANG. Related factors of euthyroid sick syndrome in patients with sepsis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2024, 56(3): 526-532. |
| [7] | Jian-bin LI,Meng-na LYU,Qiang CHI,Yi-lin PENG,Peng-cheng LIU,Rui WU. Early prediction of severe COVID-19 in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(6): 1007-1012. |
| [8] | Huan-rui LIU,Xiang PENG,Sen-lin LI,Xin GOU. Risk modeling based on HER-2 related genes for bladder cancer survival prognosis assessment [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 793-801. |
| [9] | Zi-xuan XUE,Shi-ying TANG,Min QIU,Cheng LIU,Xiao-jun TIAN,Min LU,Jing-han DONG,Lu-lin MA,Shu-dong ZHANG. Clinicopathologic features and prognosis of young renal tumors with tumor thrombus [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(5): 802-811. |
| [10] | Han LU,Jian-yun ZHANG,Rong YANG,Le XU,Qing-xiang LI,Yu-xing GUO,Chuan-bin GUO. Clinical factors affecting the prognosis of lower gingival squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(4): 702-707. |
| [11] | Yun-fei SHI,Hao-jie WANG,Wei-ping LIU,Lan MI,Meng-ping LONG,Yan-fei LIU,Yu-mei LAI,Li-xin ZHOU,Xin-ting DIAO,Xiang-hong LI. Analysis of clinicopathological and molecular abnormalities of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(3): 521-529. |
| [12] | Yu-mei LAI,Zhong-wu LI,Huan LI,Yan WU,Yun-fei SHI,Li-xin ZHOU,Yu-tong LOU,Chuan-liang CUI. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of anorectal melanoma: A report of 68 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 262-269. |
| [13] | Qi SHEN,Yi-xiao LIU,Qun HE. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma of kidney: Clinicopathology and prognosis [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(2): 276-282. |
| [14] | Qian SU,Xin PENG,Chuan-xiang ZHOU,Guang-yan YU. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in oral and maxillofacial regions: An analysis of 369 cases [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 13-21. |
| [15] | Quan ZHANG,Hai-feng SONG,Bing-lei MA,Zhe-nan ZHANG,Chao-hui ZHOU,Ao-lin LI,Jun LIU,Lei LIANG,Shi-yu ZHU,Qian ZHANG. Pre-operative prognostic nutritional index as a predictive factor for prognosis in non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with surgery [J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences), 2023, 55(1): 149-155. |
|
||